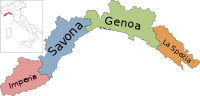
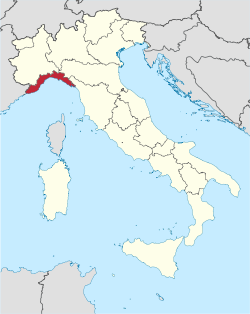
Liguria
Liguria | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Region of Italy | |||
| |||
 | |||
| Country | Italy | ||
| Capital | Genoa | ||
| Government | |||
| • President | Giovanni Toti (Forza Italia) | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 5,422 km2 (2,093 sq mi) | ||
| Population (2012-10-30) | |||
| • Total | 1,565,349 | ||
| • Density | 290/km2 (750/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) | ||
| GDP/ Nominal | €44.1[1] billion (2008) | ||
| GDP per capita | €27,100[2] (2008) | ||
| NUTS Region | ITC | ||
| Website | www.regione.liguria.it | ||
Liguria (Italian pronunciation: [liˈɡuːrja], Ligurian: Ligûria [liˈɡyːɾja], French: Ligurie) is a coastal region of north-western Italy; its capital is Genoa. The region almost coincides with the Italian Riviera and is popular with tourists for its beaches, towns, and cuisine.
Contents
1 Etymology
2 Geography
3 History
3.1 Prehistory and Roman times
3.2 Middle Ages
3.3 Early modern
3.4 Late modern and contemporary
4 Demographics
5 Economy
6 Government and politics
7 Administrative divisions
8 Cuisine
9 References
10 External links
Etymology
The name Liguria predates Latin and is of obscure origin, however the Latin adjectives Ligusticum (as in Mare Ligusticum) and Liguscus[3] reveal the original -sc- in the root ligusc-, which shortened to -s- and turned into -r- in the Latin name Liguria according to rhotacism. The formant -sc- (-sk-) is present in the names Etruscan, Basque, Gascony and is believed by some researchers to relate to maritime people or sailors.[4][5]
Geography

A view of Cinque Terre.
Liguria is bordered by France (Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur) to the west, Piedmont to the north, and Emilia-Romagna and Tuscany to the east. It lies on the Ligurian Sea. The narrow strip of land is bordered by the sea, the Alps and the Apennines mountains. Some mountains rise above 2,000 m (6,600 ft); the watershed line runs at an average altitude of about 1,000 m (3,300 ft). The highest point of the region is the summit of Monte Saccarello (2,201 m, 7,221 ft).
The winding arched extension goes from Ventimiglia to La Spezia. Of this, 3,524.08 km2 (1,360.65 sq mi) are mountainous (65% of the total) and 891.95 km2 (344.38 sq mi) are hills (35% of the total). Liguria's natural reserves cover 12% of the entire region, or 600 km2 (230 sq mi) of land. They are made up of one national reserve, six large parks, two smaller parks and three nature reserves.
The continental shelf is very narrow, and so steep it descends almost immediately to considerable depths along its 350-kilometre (220 mi) coastline. Except for the Portovenere and Portofino promontories, the coast is generally not very jagged, and is often high. At the mouths of the biggest watercourses are small beaches, but there are no deep bays and natural harbours except at Genoa and La Spezia.
The hills lying immediately beyond the coast together with the sea account for a mild climate year-round. Average winter temperatures are 7 to 10 °C (45 to 50 °F) and summer temperatures are 23 to 24 °C (73 to 75 °F), which make for a pleasant stay even in the dead of winter. Rainfall can be abundant at times, as mountains very close to the coast create an orographic effect. Genoa and La Spezia can see up to 2,000 mm (80 in) of rain in a year; other areas instead show the normal Mediterranean rainfall of 500 to 800 mm (20 to 30 in) annually.
History
Prehistory and Roman times

Map of ancient Liguria, between the river Var and Magra.

Map of Roman Liguria, between the River Var and Magra.
Evidence of Neanderthals living in the area was discovered in the region of Loano, whereas in Ventimiglia, in the caves of "Balzi Rossi", numerous remains of the Cro-Magnon man were found.
According to classical sources, the Ligurians (Ligures) once lived in a far broader territory than present-day Liguria. For example, the Greek colony of Massalia, modern Marseille, was recorded to lie in Ligurian territory.

The Roman amphitheatre of Luni (1st century AD).
During the first Punic War, the ancient Ligurians were divided, some of them siding with Carthage and a minority with Rome, whose allies included the future Genoese. Under Augustus, Liguria was designated a region of Italy (Regio IX Liguria) stretching from the coast to the banks of the Po River. The great Roman roads (Aurelia and Julia Augusta on the coast, Postumia and Aemilia Scauri towards the inland) helped strengthen territorial unity and increase communication and trade. Important towns developed on the coast, of which evidence is left in the ruins of Albenga, Ventimiglia and Luni.
Middle Ages

Simonetta Vespucci, a native Ligurian who was a famous beauty during the Renaissance, may have been the model for Botticelli's The Birth of Venus
Between the 4th and the 10th centuries Liguria was dominated by the Byzantines, the Lombards of King Rothari (about 641) and the Franks (about 774). It was also invaded by Saracen and Norman raiders. In the 10th century, once the danger of pirates decreased, the Ligurian territory was divided into three marches: Obertenga (east), Arduinica (west) and Aleramica (centre). In the 11th and 12th centuries the marches were split into fees, and then with the strengthening of the bishops’ power, the feudal structure began to partially weaken. The main Ligurian towns, especially on the coast, became city-states, over which Genoa soon extended its rule. Inland, however, fiefs belonging to noble families survived for a very long time.[vague]

Territories of the Republic of Genoa (shown in purple).
Between the 11th century (when the Genoese ships played a major role in the first crusade, carrying knights and troops to the Middle-East for a fee) and the 15th century, the Republic of Genoa experienced an extraordinary political and commercial success (mainly spice trades with the Orient). It was one of the most powerful maritime republics in the Mediterranean from the 12th to the 14th century: after the decisive victory in the battle of Meloria (1284), it acquired control over the Tyrrhenian Sea and was present in the nerve centres of power during the last phase of the Byzantine empire, having colonies up to Black Sea and Crimean.
After the introduction of the title of doge for life (1339) and the election of Simone Boccanegra, Genoa resumed its struggles against the Marquis of Finale and the Counts of Laigueglia and it conquered again the territories of Finale, Oneglia and Porto Maurizio. In spite of its military and commercial successes, Genoa fell prey to the internal factions which put pressure on its political structure. Due to the vulnerable situation, the rule of the republic went to the hands of the Visconti family of Milan. After their expulsion by the popular forces under Boccanegra’s lead, the republic remained in Genoese hands until 1396, when the internal instability led the doge Antoniotto Adorno to surrender the title of Seignior of Genoa to the king of France. The French were driven away in 1409 and Liguria went back under Milanese control in 1421, thus remaining until 1435.
Early modern

Posthumous portrait of Christopher Columbus by Sebastiano del Piombo.
The alternation of French and Milanese dominions over Liguria went on until the first half of the 16th century. The French influence ceased in 1528, when Andrea Doria allied with the powerful king of Spain and imposed an aristocratic government, which gave the republic a relative stability for about 250 years.

Reparation faite à Louis XIV par le Doge de Gênes.15 mai 1685 by Claude Guy Halle.
Genoese explorer Christopher Columbus's speculative proposal to reach the East Indies by sailing westward received the support of the Spanish crown, which saw in it an opportunity to gain the upper hand over rival powers in the contest for the lucrative spice trade with Asia. During his first voyage in 1492, instead of reaching Japan as he had intended, Columbus landed in the Bahamas archipelago, at a locale he named San Salvador. Over the course of three more voyages, Columbus visited the Greater and Lesser Antilles, as well as the Caribbean coast of Venezuela and Central America, claiming them for the Spanish Empire.
The value of trade routes through Genoa to the Near East declined during the Age of Discovery, when Portuguese explorers discovered routes to Asia around the Cape of Good Hope. The international crises of the seventeenth century, which ended for Genoa with the 1684 bombardment by Louis XIV’s fleet, restored French influence over the republic. Consequently, the Ligurian territory was crossed by the Piedmontese and Austrian armies when these two states came into conflict with France. Austria occupied Genoa in 1746, but the Habsburg troops were driven away by a popular insurrection. Napoleon’s first Italian campaign marked the end of the oligarchic Genoese state, which was transformed into the Ligurian Republic, modelled on the French Republic. After the union of Oneglia and Loano (1801), Liguria was annexed to the French Empire (1805) and divided by Napoleon into three departments: Montenotte, with capital Savona, Genoa and the department of the Apennines, with capital Chiavari.

Giuseppe Mazzini was a patriot, philosopher and politician of the 19th century.
Late modern and contemporary
After a short period of independence in 1814, the Congress of Vienna (1815) decided that Liguria should be annexed to the Kingdom of Sardinia. The Genoese uprising against the House of Savoy in 1821, which was put down with great bloodshed, aroused the population’s national sentiments. Some of the most prestigious figures of Risorgimento were born in Liguria (Giuseppe Mazzini, Mameli, Nino Bixio). Italian patriot and general Giuseppe Garibaldi, who was born in the neighbouring Nice (then part of the Sardinian state), started his Expedition of the Thousand on the evening of 5 May 1860 from a rock in Quarto, a quarter of Genoa.
In late 19th and early 20th century, the region’s economic growth was remarkable: steel mills and ship yards flourished along the coast from Imperia to La Spezia, while the port of Genoa became the main commercial hub of industrializing Northern Italy. During the tragic period of the Second World War, Liguria experienced heavy bombings, hunger and two years of occupation by the German troops, against whom a liberation struggle was led—among the most effective in Italy. When Allied troops eventually entered Genoa, they were welcomed by Italian partisans who, in a successful insurrection, had freed the city and accepted the surrender of the local German command. For this feat the city has been awarded the gold medal for military valour.
Demographics
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1861 | 829,000 | — |
| 1871 | 884,000 | +6.6% |
| 1881 | 936,000 | +5.9% |
| 1901 | 1,086,000 | +16.0% |
| 1911 | 1,207,000 | +11.1% |
| 1921 | 1,338,000 | +10.9% |
| 1931 | 1,423,000 | +6.4% |
| 1936 | 1,467,000 | +3.1% |
| 1951 | 1,567,000 | +6.8% |
| 1961 | 1,735,000 | +10.7% |
| 1971 | 1,854,000 | +6.9% |
| 1981 | 1,808,000 | −2.5% |
| 1991 | 1,676,000 | −7.3% |
| 2001 | 1,572,000 | −6.2% |
| 2011 | 1,617,000 | +2.9% |
| 2017 | 1,565,307 | −3.2% |
| Source: ISTAT 2001 | ||
The population density of Liguria is much higher than the national average (300 inhabitants per km2, or 770 per sq mi), being only less than Campania's, Lombardy's and Lazio's. In the province of Genoa, it reaches almost 500 inhabitants per km2, whereas in the provinces of Imperia and Savona it is less than 200 inhabitants per km2. The Spanish traveller Pedro Tafur, noting it from sea in 1436, remarked "To one who does not know it, the whole coast from Savona to Genoa looks like one continuous city, so well inhabited is it, and so thickly studded with houses,"[6] and today over 80% of the regional population still lives permanently near to the coast, where all the four major cities above 50,000 are located: Genoa (pop. 610,000), La Spezia (pop. 95,000), Savona (pop. 62,000) and Sanremo (pop. 56,000).
The population of Liguria has been declining from 1971 to 2001, most markedly in the cities of Genoa, Savona and La Spezia. The age pyramid now looks more like a 'mushroom' resting on a fragile base.[7] The negative trend has been partially interrupted only in the last decade when, after a successful economic recovery, the region has attracted consistent fluxes of immigrants. As of 2008[update], the Italian national institute of statistics, ISTAT, estimated that 90,881 foreign-born immigrants live in Liguria, equal to 5.8% of the total regional population.[8]
Economy

The port of Genoa is the busiest in Italy.
Ligurian agriculture has increased its specialisation pattern in high-quality products (flowers, wine, olive oil) and has thus managed to maintain the gross value-added per worker at a level much higher than the national average (the difference was about 42% in 1999).[9] The value of flower production represents over 75% of the agriculture sector turnover, followed by animal farming (11.2%) and vegetable growing (6.4%).
Steel, once a major industry during the booming 1950s and 1960s, phased out after the late 1980s crisis, as Italy moved away from the heavy industry to pursue more technologically advanced and less polluting production. So the Ligurian industry has turned towards a widely diversified range of high-quality and high-tech products (food, shipbuilding, electrical engineering and electronics, petrochemicals, aerospace etc.). Nonetheless, the regions still maintains a flourishing shipbuilding sector (yacht construction and maintenance, cruise liner building, military shipyards).[9]
In the services sector, the gross value-added per worker in Liguria is 4% above the national average. This is due to the increasing diffusion of modern technologies, particularly in commerce and tourism.
A good motorways network (376 km (234 mi) in 2000) makes communications with the border regions relatively easy. The main motorway is located along the coastline, connecting the main ports of Nice (in France), Savona, Genoa and La Spezia. The number of passenger cars per 1000 inhabitants (524 in 2001) is below the national average (584).
In average, about 17 million tones of cargo are shipped from the main ports of the region and about 57 million tonnes enter the region.[9] The Port of Genoa, with a trade volume of 58.6 million tonnes [10] it is the first port of Italy,[11] the second in terms of twenty-foot equivalent units after the port of transshipment of Gioia Tauro, with a trade volume of 1.86 million TEUs.[10] The main destinations for the cargo-passenger traffic are Sicily, Sardinia, Corsica, Barcelona and Canary Islands.
The unemployment rate stood at 9.5% in 2017 and was slightly lower than the national average.[12]
| Year | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
unemployment rate (in %) | 4.8% | 4.8% | 5.4% | 5.8% | 6.6% | 6.4% | 8.1% | 9.8% | 10.8% | 9.2% | 9.7% | 9.5% |
Government and politics

View of Portovenere
The politics of Liguria takes place in a framework of a presidential representative democracy, whereby the President of Regional Government is the head of government, and of a pluriform multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the Regional Government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the Regional Council.
The Regional Government is presided by the Governor, who is elected for a five-year term, and is composed by the President and the Ministers, who are currently 11, including a Vice President.[13]
The Regional Council of is composed of 40 members and it's elected for a five-year term, but, if the President suffers a vote of no confidence, resigns or dies, under the simul stabunt vel simul cadent clause (introduced in 1999), also the Council will be dissolved and there will be a fresh election.
In the last regional election, which took place on 31 May 2015, Giovanni Toti (Forza Italia) defeated Raffaella Paita (Democratic Party), after 10 years of regional left-wing government by Claudio Burlando (Democratic Party).
At both national and local level Liguria is considered a swing region, where no one of the two political blocks is dominant, with the two eastern provinces leaning left, and the two western provinces right.
Liguria is one of 20 regions (administrative divisions) of Italy.
Administrative divisions
Liguria is divided into four provinces:
.mw-parser-output .stack-container{box-sizing:border-box}.mw-parser-output .stack-clear-left{float:left;clear:left}.mw-parser-output .stack-clear-right{float:right;clear:right}.mw-parser-output .stack-left{float:left}.mw-parser-output .stack-right{float:right}.mw-parser-output .stack-object{margin:1px;overflow:hidden}
| Province | Area (km²) | Population | Density (inh./km²) |
|---|---|---|---|
Province of Genoa | 1,838 | 884,945 | 481.5 |
Province of Imperia | 1,156 | 220,217 | 190.5 |
Province of La Spezia | 881 | 222,602 | 252.7 |
Province of Savona | 1,545 | 265,194 | 185.2 |

Cuisine

Pasta with pesto, a traditional Ligurian recipe
Liguria is the original source of pesto, one of the most popular sauces in Italian cuisine, made with fresh basil, pine kernels, olive oil, garlic and Parmesan cheese.[14]
Seafood is a major staple of Mediterranean cuisine, the Ligurian variety being no exception, as the sea has been part of the region's culture since its beginning. Ciuppin soup is made from fish leftovers and stale bread, flavoured with white wine, onion, and garlic.[15]
Vegetables, especially beans, are important in Ligurian cooking. Mesciua soup is made from beans, olive oil and farro (old kinds of wheat including emmer).[15]
Ligurian pasta includes trenette and trofie, and the fresh pasta pockets called pansòuti.[15]
References
See also: Bibliography of Liguria
^ "Eurostat – Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table". Epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu. 12 August 2011. Retrieved 16 September 2011..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ EUROPA – Press Releases – Regional GDP per inhabitant in 2008 GDP per inhabitant ranged from 28% of the EU27 average in Severozapaden in Bulgaria to 343% in Inner London Archived 12 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine.
^ http://www.dicolatin.be/EN/LAK/0/LIGUSCUS/index.htm
^ Room, "Placenames of the World," 2006
^ Marie Henri d'Arbois de Jubainville, Premiers Habitants de l'Europe (2nd edition 1889-1894)
^ Pedro Tafur, Andanças e viajes por diversas partes del mundo
^ "Eurostat". Circa.europa.eu. Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
^ "Statistiche demografiche ISTAT". Demo.istat.it. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
^ abc "Eurostat". Circa.europa.eu. Archived from the original on 16 September 2008. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
^ ab "Autorità Portuale di Genova — Traffico porto". Porto.genova.it. Archived from the original on 2 December 2008. Retrieved 26 December 2008.
^ "Inf_07_05_Statistiche dei trasporti marittimi 2002–2004" (PDF). Retrieved 26 December 2008.
^ "Regional Unemployment by NUTS2 Region". Eurostat.
^ "Regione Liguria – - sito ufficiale". Regione.liguria.it. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
[permanent dead link]
^ Della Gatta, Andrea. "La Ricetta del Pesto Genovese" (in Italian). Consorzio del Pesto Genovese. Retrieved 13 May 2016.
^ abc "The Food and Cuisine of Liguria". Made in Italy. Retrieved 13 May 2016.
External links
![]() Liguria travel guide from Wikivoyage
Liguria travel guide from Wikivoyage
- Official Region website
- Video Introduction to Liguria
Coordinates: 44°27′00″N 8°46′00″E / 44.45000°N 8.76667°E / 44.45000; 8.76667