Galegine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
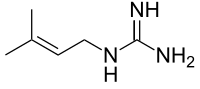
IUPAC name 2-(3-Methylbut-2-enyl)guanidine | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
ChEBI |
|
ChEMBL |
|
ChemSpider |
|
KEGG |
|
PubChem CID |
|
UNII |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C6H13N3 |
Molar mass | 7002127191000000000♠127.191 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Infobox references | |
Gelagine is a toxic chemical compound that has been isolated from Goat's rue (Galega officinalis).[1] It has also been found to be the principle cause of the toxicity of poison sedge (Schoenus asperocarpus).[2]
Galegine was used in the 1920s as a pharmaceutical treatment for diabetes;[3] however, because of its toxicity, its use was soon supplanted by superior alternatives. Research based upon the effects of galegine eventually led to the development of metformin which is used today for treatment of type 2 diabetes.[3]
References
^ Oldham, Michelle; Ransom, Corey V.; Ralphs, Michael H.; Gardner, Dale R. (2011). "Galegine Content in Goatsrue (Galega officinalis) Varies by Plant Part and Phenological Growth Stage". Weed Science. 59 (3): 349–352. doi:10.1614/WS-D-10-00169.1..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Huxtable, C. R.; Dorling, P. R.; Colegate, S. M. (1993). "Identification of galegine, an isoprenyl guanidine, as the toxic principle of Schoenus asperocarpus (poison sedge)". Australian Veterinary Journal. 70 (5): 169–71. doi:10.1111/j.1751-0813.1993.tb06120.x. PMID 8343085.
^ ab Bailey, CJ; Day, C. (2004). "Metformin: Its botanical background". Practical Diabetes International. 21 (3): 115–117. doi:10.1002/pdi.606.