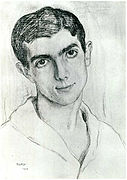Léon Bakst
Léon Bakst | |
|---|---|
 Bakst's Self-portrait, 1893, oil on cardboard, 34 x 21 cm., The State Russian Museum, St. Petersburg, Russia | |
| Born | Leyb-Khaim Izrailevich Rosenberg 27 January, 1866 Grodno (now in Belarus) |
| Died | 28 December 1924 Rueil-Malmaison, near Paris |
| Residence | Saint Petersburg, Moscow, Paris (1893 to 1897) |
| Nationality | Russian |
| Education | St. Petersburg Academy of Arts |
| Movement | Modernist, Orientalist themes |
Léon Bakst (Russian: Леон (Лев) Николаевич Бакст, Leon (Lev) Nikolaevich Bakst) – born as Leyb-Khaim Izrailevich (later Samoylovich) Rosenberg, Лейб-Хаим Израилевич (Самойлович) Розенберг (27 January (8 February) 1866[1][2] – 28 December 1924) was a Russian painter and scene and costume designer. He was a member of the Sergei Diaghilev circle and the Ballets Russes, for which he designed exotic, richly coloured sets and costumes.[3]
Contents
1 Early life
2 Rise to fame
3 Cultural depictions
4 Gallery of selected works
5 See also
6 References
7 Sources
8 External links
Early life

Bakst in 1916
Leyb-Khaim Izrailevich (later Samoylovich) Rosenberg was born in Grodno (now in Belarus), into a middle-class Jewish family. As his grandfather was an exceptional tailor, the Tsar gave him a very good position, and he had a huge and wonderful house in Saint Petersburg[citation needed]. Later, when Leyb's parents moved to the capital, the boy Leyb would visit his grandfather's house every Saturday. He said that he had been very impressed as a youth by that house, always returning with pleasure. At the young age of twelve, Lejb won a drawing contest and decided to become a painter, but his parents did not approve of this.
After graduating from gymnasium, he studied at the St. Petersburg Academy of Arts as a noncredit student, because he had failed the entry. He also worked part-time as a book illustrator, gaining admission into the Imperial Academy in 1883.
At the time of his first exhibition (1889) he took the surname of "Bakst," based on his mother's maiden name. The surname "Rosenberg" was thought to be "too Jewish" and not good for business. At the beginning of the 1890s, Bakst exhibited his works with the Society of Watercolourists. From 1893 to 1897 he lived in Paris, where he studied at the Académie Julian.[4] He still often visited Saint Petersburg. After the mid-1890s, Bakst became a member of the circle of writers and artists formed by Sergei Diaghilev and Alexandre Benois,[5] who in 1899 founded the influential periodical Mir iskusstva, meaning "World of Art." His graphics for this publication brought him fame.
Rise to fame
Bakst continued painting, producing portraits of Filipp Malyavin (1899), Vasily Rozanov (1901), Andrei Bely (1905), Zinaida Gippius (1906). He also worked as an art teacher for the children of Grand Duke Vladimir Alexandrovich of Russia. In 1902, he took a commission from Tsar Nicholas II to paint Admiral Avellan and Russian sailors meeting in Paris, a painting he started there, during the celebrations from the 17 to 25 October 1893. However, it took him 8 years to finish this work.
In 1898, he showed his works in the Diaghilev-organized First Exhibition of Russian and Finnish Artists; in World of Art exhibitions, as well as the Munich Secession, exhibitions of the Union of Russian Artists, etc.
During the Russian Revolution of 1905, Bakst worked for the magazines Zhupel, Adskaja Pochta, and Satyricon, then for an art magazine called Apollon.

Waddesdon Manor holds a 'Bakst room' which holds seven Sleeping Beauty panels commissioned from Bakst in 1913.
Beginning in 1909, Bakst worked mostly as a stage-designer, designing sets for Greek tragedies. In 1908, he gained attention as a scene-painter for Diaghilev with the Ballets Russes. He produced scenery for Cleopatra (1909), Scheherazade (1910), Carnaval (1910), Narcisse (1911), Le Spectre de la Rose (1911), L'après-midi d'un faune (1912) and Daphnis et Chloé (1912).[6] During this time, Bakst lived in western Europe because, as a Jew, he did not have the right to live permanently outside the Pale of Settlement in the Russian Empire. Despite being known for his work as a stage designer, art was also commissioned by various English families during the Art Deco era. During this time, he produced such works as the Sleeping Beauty series for James and Dorothy de Rothschild at Waddesdon Manor in 1913. The story is depicted in seven panels that line the walls of an oval, theatrical styled space in the Buckinghamshire manor house.
During his visits to Saint Petersburg, he taught in Zvantseva's school, where one of his students was Marc Chagall (1908–1910). Bakst described Chagall as a favorite, because when told to do something, he would listen carefully, but then he would take his paint and his brushes and do something completely different from the assignment.
In 1914, Bakst was elected a member of the Imperial Academy of Arts.
In 1922, Bakst broke off his relationship with Diaghilev and the Ballets Russes. During this year, he visited Baltimore and, specifically Evergreen House - the residence of his American friend and patron, art philanthropist Alice Warder Garrett (1877–1952). Having met in Paris in 1914, when Mrs. Garrett was accompanying her diplomat husband in Europe, Bakst soon depended upon Garrett as both a confidante and agent. Alice Garrett became Bakst's representative in the United States upon her return home in 1920, organizing two exhibitions of the artist's work at New York's Knoedler Gallery, as well as subsequent traveling shows. When in Baltimore, Bakst re-designed the dining room of Evergreen into a shocking acidic yellow and 'Chinese' red confection. The artist transformed the house's small c. 1885 gymnasium into a colorfully Modernist private theatre. This is believed to be the only extant private theatre designed by Bakst.
Bakst died on 27 December 1924, in a clinic in Rueil Malmaison, near Paris, from lung problems (oedema). His many admirers amongst the most famous artists of the time, poets, musicians, dancers and critiques, formed a funeral procession to accompany his body to his final resting place, in the Cimetière des Batignolles, in Paris, during a very moving ceremony.[5]
In late 2010, the Victoria and Albert Museum in London presented an exhibit of Bakst's costumes and prints.[7]
Cultural depictions
Anna Pavlova, film by Emil Loteanu; portrayed by Igor Dmitriev (1983).
Gallery of selected works

Dmitry Filosofov, 1897

Supper, 1902

Model, 1905

Andrei Bely, 1905

Zinaida Gippius, 1906

Sergei Diaghilev, 1906

Terror Antiquus, 1908

Costume of Cléopâtre for Ida Rubinstein, 1909

The Firebird, ballet costume, 1910

Nijinsky in the ballet L'après-midi d'un faune, 1912
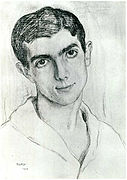
Léonide Massine, 1914
See also
- List of Orientalist artists
- Orientalism
- Place des États-Unis
References
^ БАКСТ, ЛЕВ САМОЙЛОВИЧ
^ Бакст Лев Самойлович
^ Леон Бакст
^ Bakst
^ ab Бакст Л. С.
^ Thomas J Mikotowicz "Bakst, Léon" in Thomas J Mikotowicz, Theatrical designers: and International Biographic Dictionary. New York: Greenwood, 1992 .mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
ISBN 0313262705. p.17
^ "Biography of Léon Bakst - Victoria and Albert Museum". Vam.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 2009-04-11. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
Sources
Marc Chagall, My Life, St.-Petersburg, Azbuka, 2000,
ISBN 5-267-00200-3
- Léon Bakst, Serov et moi en Grèce, traduction et introduction d'Olga Medvedkova, préface de Véronique Schiltz, TriArtis Editions, 2015, 128 p., 24 illustrations (
ISBN 978-2-916724-56-0)
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Léon Bakst. |
External links
- The seven Sleeping Beauty panels at Waddesdon Manor
Léon Bakst at FMD
Working for Diaghilev Exhibition at the Groninger Museum- Léon Bakst (1866–1924) Artwork Images, Exhibitions, Reviews at wwar.com
- Works by Léon Bakst at the Russian Art Gallery
Video on YouTube
- Art Signature Dictionary - See Léon Bakst's signature, although the police seizure of counterfeit
Bakst theatre and performance collection at the Victoria and Albert Museum
Evergreen Museum and Library - Collection includes original stage sets, costume designs, and other related works.
Leon Bakst designs, circa 1911-1923, held by the Billy Rose Theatre Division, New York Public Library for the Performing Arts
Diaghilev and the Ballets Russes, 1909–1929: When Art Danced with Music 2013 exhibition at the National Gallery of Art in Washington, DC
Bakst collection at the McNay Art Museum