Grand Duchy of Moscow
This article includes a list of references, but its sources remain unclear because it has insufficient inline citations. (November 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Grand Principality of Moscow Великое княжество Московское Velikoye knyazhestvo Moskovskoye | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1283–1547 | |||||||||||||||||
 Byzantine imperial eagle (adopted 1472) | |||||||||||||||||
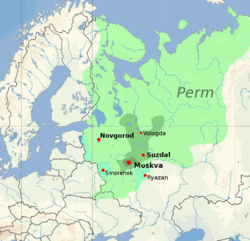 Territorial development between 1390 and 1530 | |||||||||||||||||
| Status | Vassal state of the Golden Horde (1283–1480) Sovereign state (1480–1547) | ||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Moscow | ||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Old Russian | ||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Russian Orthodoxy | ||||||||||||||||
| Government | Absolute monarchy | ||||||||||||||||
| Grand Duke | |||||||||||||||||
• 1283–1303 | Daniel (first) | ||||||||||||||||
• 1462–1505 | Ivan III the Great | ||||||||||||||||
• 1505–1533 | Vasili III | ||||||||||||||||
• 1533–1547 | Ivan IV (last) | ||||||||||||||||
| boyar | |||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||
• Established | 1283 | ||||||||||||||||
• Tsardom proclaimed | 22 October 1547 | ||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||
| 1505[1] | 2,500,000 km2 (970,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||
| Currency | ruble, denga | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
The Grand Duchy of Moscow,[2][3]Muscovite Rus'[4][5][6] or Grand Principality of Moscow[7][8] (Russian: Великое Княжество Московское, Velikoye Knyazhestvo Moskovskoye, also known in English simply as Muscovy from the Latin: Moscovia) was a Rus' principality of the Late Middle Ages centered around Moscow, and the predecessor state of the Tsardom of Russia in the early modern period.
The state originated with Daniel I, who inherited Moscow in 1283, eclipsing and eventually absorbing its parent duchy of Vladimir-Suzdal by the 1320s. It later annexed the Novgorod Republic in 1478 and the Grand Duchy of Tver in 1485.[9]
After the Mongol invasion of Rus', Muscovy was a tributary vassal to the Mongol-ruled Golden Horde (under the "Tatar Yoke") until 1480. Muscovites, Suzdalians and other inhabitans of the Rus' principality were able to maintain their Slavic, Pagan and Orthodox traditions for the most part under the Tatar Yoke. There was also strong contact and cultural exchange with the Byzantine Empire. Ivan III further consolidated the state during his 43-year reign, campaigning against his major remaining rival power, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and by 1503 he had tripled the territory of his realm, adopting the title of tsar and claiming the title of "Ruler of all Rus'". By his marriage to the niece of the last Byzantine emperor, he established Muscovy as the successor state of the Roman Empire, the "Third Rome". The emigration of the Byzantine people influenced and strengthened Moscow's identity as the heir of the Orthodox traditions. Ivan's successor Vasili III also enjoyed military success, gaining Smolensk from Lithuania in 1512, pushing Muscovy's borders to the Dniepr River. Vasili's son Ivan IV (later known as Ivan the Terrible) was an infant at his father's death in 1533. He was crowned in 1547, assuming the title of tsar together with the proclamation of Tsardom of Russia (Russian: Царство Русcкое, Tsarstvo Russkoye).
Contents
1 Name
2 Origin
3 Dmitri Donskoi
4 Vasily I and Vasily II
5 Ivan III
6 Court
7 Relations with the Horde
8 Assessment
9 See also
10 References
11 Sources
12 Further reading
13 External links
Name

The seal of Simeon the Proud (1340s), reads: "The seal of the Grand Duke Simeon of all Rus'"

The seal of Ivan III the Great (1490s), reads: "Ioan (John), by God's grace, the Sovereign of all Rus' and the Grand Duke"

Blaeu's map of Russia (1645), Moscovia is Moscow and the vicinities
As with many medieval states the country had no particular "official" name, but rather official titles of the ruler. "The Duke (Knyaz) of Moscow" (Московский князь) or "the Sovereign of Moscow" (Московский государь) were common short titles. After the unification with the Duchy of Vladimir in the mid-14th century, the dukes of Moscow might call themselves also "the Duke of Vladimir and Moscow", as Vladimir was much older than Moscow and much more "prestigious" in the hierarchy of possessions, although the principal residence of the dukes had been always in Moscow. In rivalry with other duchies (especially the Grand Duchy of Tver) Moscow dukes also designated themselves as the "Grand Dukes", claiming a higher position in the hierarchy of Russian dukes. During the territorial growth and later acquisitions, the full title became rather lengthy.[10] In routine documents and on seals, though, various short names were applied: "the (Grand) Duke of Moscow", "the Sovereign of Moscow" (Московский государь), "the Grand Duke of all Rus'" (Великий князь всея Руси), "the Sovereign of all Rus'" (Государь всея Руси), or simply ""the Grand Duke" (Великий князь) or "the Great (or Grand) Sovereign" (Великий государь).
In spite of feudalism the collective name of the Eastern Slavic land, Rus', was not forgotten,[11] though it then became a cultural and geographical rather than political term, as there was no single political entity on the territory. Since the 14th century various Moscow dukes added "of all Rus'" (всея Руси) to their titles, after the title of Russian metropolitans, "the Metropolitan of all Rus'".[12]Dmitry Shemyaka (died 1453) was the first Moscow duke who minted coins with the title "the Sovereign of all Rus'". Although initially both "Sovereign" and "all Rus'" were supposed to be rather honorific epithets,[12] since Ivan III it transformed into the political claim over the territory of all the former Kievan Rus', a goal that the Moscow duke came closer to by the end of that century, uniting eastern Rus'.[11]
Such claims raised much opposition and hostility from its main rival, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, which controlled a large (western) portion of the land of ancient Rus' and hence denied any claims and even the self-name of the eastern neighbour.[11][12] Under the Polish-Lithuanian influence the country began to be called Muscovy (Latin: Moscovia, Muscovy, French: Moscovie) in Western Europe.[11] The first appearances of the term were in an Italian document of 1500.[11] Initially Moscovia was the Latinized name of the city of Moscow itself, not of the state;[11] later it acquired its wider meaning (synecdoche) and has been used alongside of the older name, Russia. The term Muscovy persisted in the West until the beginning of the 18th century and is still used in historical contexts.
Origin
When the Mongols invaded the lands of Kievan Rus' in the 13th century, Moscow was an insignificant trading outpost in the principality of Vladimir-Suzdal. Although the Mongols burnt down Moscow in the winter of 1238 and pillaged it in 1293, the outpost's remote, forested location offered some security from Mongol attacks and occupation, while a number of rivers provided access to the Baltic and Black Seas and to the Caucasus region.[13]

During the reign of Daniel, Moscow was little more than a small timber fort in the forest of Central Rus'.
More important to the development of the state of Moscow, however, was its rule by a series of princes who expanded its borders and turned a small principality in the Moscow River Basin into the largest state in Europe of the 16th century.[14] The first ruler of the principality of Moscow, Daniel I (d. 1303), was the youngest son of Alexander Nevsky of Vladimir-Suzdal. He started to expand his principality by seizing Kolomna and securing the bequest of Pereslavl-Zalessky to his family. Daniel's son Yuriy (also known as Georgiy; ruled 1303-1325) controlled the entire basin of the Moskva River and expanded westward by conquering Mozhaisk. He then forged an alliance with the overlord of the Rus' principalities, Uzbeg Khan of the Golden Horde, and married the khan's sister. The Khan allowed Yuriy to claim the title of Grand Duke of Vladimir-Suzdal, a position which allowed him to interfere in the affairs of the Novgorod Republic to the north-west.
Yuriy's successor, Ivan I (ruled 1325–1340), managed to retain the title of Grand Duke by cooperating closely with the Mongols and by collecting tribute and taxes from other Rus' principalities on their behalf. This relationship enabled Ivan to gain regional ascendancy, particularly over Moscow's chief rival, the northern city of Tver, which rebelled against the Horde in 1327. The uprising was subdued by the joint forces of the Grand Duchy of Suzdal, the Grand Duchy of Moscow (which competed with Tver for the title of the Grand Duke of Vladimir), and Tatars.[15] Ivan was reputed to be the richest person in Rus', as his moniker "Kalita" (literally, the "moneybag") testifies.[16] He used his treasures to purchase land in other principalities and to finance the construction of stone churches in the Moscow Kremlin.
In 1325 the Orthodox Metropolitan Peter (died 1326) transferred his residence from Kiev to Vladimir and then to Moscow, further enhancing the prestige of the new principality.[17]
Dmitri Donskoi

Dmitry Donskoi in the Battle of Kulikovo
Ivan's successors continued gathering the lands of Rus' to increase the population and wealth under their rule. In the process, their interests clashed with the expanding Grand Duchy of Lithuania, whose subjects were predominantly East Slavic and Orthodox. Grand Duke Algirdas of Lithuania allied himself by marriage with Tver and undertook three expeditions against Moscow (1368, 1370, 1372) but was unable to take it. The main bone of contention between Moscow and Vilnius was the large city of Smolensk.
In the 1350s, the country and the royal family were hit by the Black Death. Dmitry Ivanovich was aged nine when his parents died and the title of Grand Duke slipped into the hands of his distant relative, Dmitry of Suzdal. Surrounded by Lithuanians and Muslim nomads, the ruler of Moscow cultivated an alliance with the Rus' Orthodox Church, which experienced a resurgence in influence, due to the monastic reform of St. Sergius of Radonezh.
Educated by Metropolitan Alexis, Dmitri posed as a champion of Orthodoxy and managed to unite the warring principalities of Rus' in his struggle against the Horde. He challenged the Khan's authority and defeated his commander Mamai in the epic Battle of Kulikovo (1380). However, the victory did not bring any short-term benefits; Tokhtamysh in 1382 sacked Moscow hoping to reassert his vested authority over his vassal, the Grand Prince, and his own Mongol hegemony, killing 24,000 people.
Nevertheless, Dmitri became a national hero. The memory of Kulikovo Field made the Rus' population start believing in their ability to end Tatar domination and become a free people. In 1389, he passed the throne to his son Vasily I without bothering to obtain the Khan's sanction.
Vasily I and Vasily II
Vasily I (1389–1425) continued the policies of his father. After the Horde was attacked by Tamerlane, he desisted from paying tribute to the Khan, but was forced to pursue a more conciliatory policy after Edigu's incursion on Moscow in 1408. Married to the only daughter of the Grand Duke Vytautas of Lithuania, he attempted to avoid open conflicts with his powerful father-in-law, even when the latter annexed Smolensk. The peaceful years of his long reign were marked by the continuing expansion to the east (annexation of Nizhny Novgorod and Suzdal, 1392) and to the north (annexation of Vologda, Veliky Ustyug, and Perm of Vychegda, 1398). Nizhny Novgorod was given by the Khan of the Golden Horde as a reward for Muscovite help against a rival.[18]

Andrei Rublev's famous icon of the Trinity
The reforms of St. Sergius triggered a cultural revival, exemplified by the icons and frescoes of the monk Andrei Rublev. Hundreds of monasteries were founded by disciples of St. Sergius in distant and inhospitable locations, including Beloozero and Solovki. Apart from their cultural function, these monasteries were major landowners that could control the economy of an adjacent region. In fact they served as outposts of Moscow influence in the neighboring principalities and republics. Another factor responsible for the expansion of the Grand Duchy of Moscow was its favorable dynastic situation, in which each sovereign was succeeded by his son, while rival principalities were plagued by dynastic strife and splintered into ever smaller polities. The only lateral branch of the House of Moscow, represented by Vladimir of Serpukhov and his descendants, was firmly anchored to the Moscow Duchy.

Territorial growth from 1300 to 1462
The situation changed with the ascension of Vasily I's successor, Vasily II (r. 1425–62). Before long his uncle, Yuri of Zvenigorod, started to advance his claims to the throne and Monomakh's Cap. A bitter family conflict erupted and rocked the country during the whole reign. After Yuri's death in 1432, the claims were taken up by his sons, Vasily Kosoy and Dmitry Shemyaka, who pursued the Great Feudal War well into the 1450s. Although he was ousted from Moscow on several occasions, taken prisoner by Olug Moxammat of Kazan, and blinded in 1446, Vasily II eventually managed to triumph over his enemies and pass the throne to his son. At his urging, a native bishop was elected as Metropolitan of Moscow, which was tantamount to declaration of independence of the Russian Orthodox Church from the Patriarch of Constantinople (1448).
Ivan III

Great stand on the Ugra river, 1480
Outward expansion of the Grand Duchy in the 14th and 15th centuries was accompanied by internal consolidation. By the 15th century, the rulers of Moscow considered the entire Rus' territory their collective property. Various semi-independent princes of Rurikid stock still claimed specific territories, but Ivan III (the Great; r. 1462–1505) forced the lesser princes to acknowledge the grand prince of Moscow and his descendants as unquestioned rulers with control over military, judicial, and foreign affairs.
Moscow gained full sovereignty over a significant part of the ethnically Rus' lands by 1480, when the overlordship of the Tatar Golden Horde officially ended after its defeat in the Great standing on the Ugra river. By the beginning of the 16th century virtually all those lands were united, including the Novgorod Republic (annexed in 1478) and the Grand Duchy of Tver (annexed in 1485). Through inheritance, Ivan was able to control the important Principality of Ryazan, and the princes of Rostov and Yaroslavl' subordinated themselves to him. The northwestern city of Pskov, consisting of the city and a few surrounding lands, remained independent in this period, but Ivan's son, Vasili III (r. 1505–33), later conquered it.
Having consolidated the core of Russia under his rule, Ivan III became the first Moscow ruler to adopt the titles of tsar[19] and "Ruler of all Rus'".[13] Ivan competed with his powerful northwestern rival, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, for control over some of the semi-independent former principalities of Kievan Rus' in the upper Dnieper and Donets river basins. Through the defections of some princes, border skirmishes, and a long, inconclusive war with Lithuania that ended only in 1503, Ivan III was able to push westward, and the Moscow state tripled in size under his rule.
The reign of the Tsars started officially with Ivan the Terrible, the first monarch to be crowned Tsar of Russia, but in practice it started with Ivan III, who completed the centralization of the state (traditionally known as the gathering of the Russian lands).
Court
The court of the Moscow princes combined ceremonies and customs inherited from Kievan Rus' with those imported from the Byzantine Empire and Golden Horde. Some traditional Russian offices, like that of tysyatsky and veche, were gradually abolished in order to consolidate power in the hands of the ruling prince. A new elaborate system of court precedence, or mestnichestvo, predicated the nobleman's rank and function on the rank and function of his ancestors and other members of his family. The highest echelon of hereditary nobles was composed of boyars. They fell into three categories:

The Dormition Cathedral in the Moscow Kremlin
Rurikid princes of Upper Oka towns, Suzdal, Rostov, Yaroslavl, etc. that lived in Moscow after their hereditary principalities had been incorporated into Duchy of Moscow (e.g., Shuisky, Vorotynsky, Repnin, Romodanovsky);- Foreign princes from Lithuania and Golden Horde, claiming descent either from Grand Duke Gediminas or from Genghis Khan (e.g., Belsky, Mstislavsky, Galitzine, Trubetskoy);
- Ancient families of Moscow nobility that have been recorded in the service of Grand Dukes from the 14th century (e.g., Romanov, Godunov, Sheremetev).
Rurikid and Gediminid boyars, whose fathers and grandfathers were independent princelings, felt that they were kin to the grand prince and hence almost equal to him. During the times of dynastic troubles (such as the years of Ivan IV's minority), boyardom constituted an internal force that was a permanent threat to the throne. An early form of the monarch's conflict with the boyars was the oprichnina policy of Ivan the Terrible.
During such conflicts, Ivan, Boris Godunov, and some later monarchs felt the necessity to counterbalance the boyardom by creating a new kind of nobility, based on personal devotion to the tsar and merits earned by faithful service, rather than by heredity. Later these new nobles were called dvoryans (singular: dvoryanin). The name comes from the Russian word dvor, meaning tsar's dvor, i.e., The Court. Hence the expression pozhalovat ko dvoru, i.e., to be called to (serve) The Court.
Relations with the Horde
Relations between the Moscow principality and the Horde were mixed.[20] In the first two decades of the 13th century Moscow gained support of one of the rivaling Mongol statesmen, Nogai, against the principalities that were oriented towards Sarai khans. After the restoration of unity in the Golden Horde in the early 14th century, it generally enjoyed the favour of khans until 1317, but lost it in 1322–1327.[20] The following thirty years, when the relations between the two states improved, allowed Moscow to achieve a sufficient economic and political potential. Further attempts to deprive its rulers of the status of grand dukes of Vladimir were unsuccessful after the Khanate sank into internecine war and proved to be fruitless during the reign of a relavetively powerful khan such as Mamai, whereas Tokhtamysh had no other choice but to recognise the supremacy of Moscow over northern and eastern Russian lands.[20] The traditional Mongol principle of breaking up larger concentrations of power into smaller ones resulted in a failure, and the following period is characterised by the lack of support from the Horde.[20] Although Moscow recognized khans as the legitimate authority in the early years of the Tatar yoke, despite certain acts of resistance and disobedience, it refused to acknowledge their suzerainty in the years 1374–1380, 1396–1411, 1414–1416 and 1417–1419, even in spite of the growing might of the Golden Horde.[21] The power of the Horde over Moscow was greatly limited in the reign of Dmitri Donskoi, who gained recognition of the Grand Duchy of Vladimir as a hereditary possession of Moscow princes: while the Horde collected tribute from his land, it could no longer have a serious impact on the internal structure of northern Russian lands.[22] In the years of Vasily II and Ivan III, the Grand Duchy of Moscow acquired the idea of tsardom from the fallen Byzantine empire, which was incompatible with the recognition of the suzerainty of the khan, and started to declare its independence in diplomatic relations with other countries.[23] Eventually, the country was liberated in the reign of Ivan III.[21]
Assessment
The development of the modern day Russian state is traced from Kievan Rus' through Vladimir-Suzdal and the Grand Duchy of Moscow to the Tsardom of Russia, and then the Russian Empire. The Moscow Duchy drew people and wealth to the northeastern part of Kievan Rus'; established trade links to the Baltic Sea, White Sea, Caspian Sea, and to Siberia; and created a highly centralized and autocratic political system. The political traditions established in Muscovy, therefore, exerted a powerful influence on the future development of Russian society.
See also
- Foreign policy of the Russian Empire
- List of Russian rulers
- Tsardom of Russia
- Muscovite Manorialism
- Muscovite–Lithuanian Wars
References
^ Rein Taagepera (September 1997). "Expansion and Contraction Patterns of Large Polities: Context for Russia". International Studies Quarterly. 41 (3): 498. doi:10.1111/0020-8833.00053. Retrieved 16 September 2016..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ A Short History of the USSR. Progress Publishers. 1965.
^ Florinsky, Michael T. (1965). Russia: a History and an Interpretation.
^ Plokhy, Serhii (2006-09-07). The Origins of the Slavic Nations: Premodern Identities in Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781139458924.
^ Isham, Heyward; Pipes, Richard (2016-09-16). Remaking Russia: Voices from within: Voices from within. Routledge. ISBN 9781315483078.
^ Dewey, Horace W. (1987). "Political Poruka in Muscovite Rus'". The Russian Review. 46 (2): 117–133. doi:10.2307/130622.
^ "Moscow, Grand Principality of". Encyclopædia Britannica. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica. 2012.
^ Perrie, Maureen, ed. (2006). The Cambridge History of Russia. 1. Cambridge University Press. p. 751. ISBN 978-0-521-81227-6.
^ Davies B. Warfare, State and Society on the Black Sea Steppe, 1500–1700. Routledge, 2014, P. 5
^ The full title of Vasily III (the father of the first Russian tsar Ivan IV) in a 1517 document: By God's will and our own desire, We, the Great Sovereign Vasily, by God's grace, the Tsar (sic!) and the Sovereign of all Rus' and the Grand Duke of Vladimir, Moscow, Novgorod, Pskov, Smolensk, Tver, Yugra, Perm, Vyatka, Bolgar, and others, and the Grand Duke of Novgorod of the lower lands (i. e. Nizhny Novgorod), Chernigov, Ryazan, Volok, Rzhev, Bely, Rostov, Yaroslavl, Belozersk, Udora, Obdora, Konda, and others... (Сборник Русского исторического общества. 53. СПб. 1887. p. 19.)
^ abcdef Хорошкевич, А. Л. (1976). "Россия и Московия: Из истории политико-географической терминологии" [Khoroshkevich A. L. Russia and Muscovy: from the history of politico-geographic terminology]. Acta Baltico-slavica. X: 47–57.
^ abc Филюшкин, А. И. (2006). Титулы русских государей [Filyushkin A. I. The titles of the Russian rulers]. pp. 152–193. ISBN 5-98874-011-1.
^ ab Library of Congress Country Studies -Russia
^ Gorskij, A.A. (2000). Moskva i Orda (in Russian) (Naučnoe izd. ed.). Moskva: Nauka. pp. 3–4. ISBN 5-02-010202-4. Retrieved 5 December 2016.
^ Martin J. Medieval Russia, 980-1584. 2007. Cambridge University Press. P. 196
^ Moss (2005)
^
Compare: Trepanier, Lee (2010). "2: Muscovite Russia (ca. 1240-ca. 1505)". Political Symbols in Russian History: Church, State, and the Quest for Order and Justice. G - Reference, Information and Interdisciplinary Subjects Series. Lanhan, Maryland: Lexington Books. p. 31. ISBN 9780739117897. Retrieved 2016-12-14.But the crucial year was 1326, when [Metropolitan] Peter became a resident of Moscow and began to build his own burial vault. On December 20, 1326. Metropolitan Peter died and was buried by one of the bishops in the presence of Ivan I. Due to his residency and burial place, Metropolitan Peter had confirmed on Moscow the future haven of the Russian Orthodox Church, although this official transfer would not take place until the reign of Alexis.
^ Richard Pipes, Russia under the Old Regime (1995), p.80.
^ Trepanier L. Political Symbols in Russian History: Church, State, and the Quest for Order and Justice. Lexington Books. 2010. P. 39
^ abcd Gorskij, A.A. (2000). Moskva i Orda (in Russian) (Naučnoe izd. ed.). Moskva: Nauka. p. 187. ISBN 5-02-010202-4. Retrieved 5 December 2016.
^ ab Gorskij, A.A. (2000). Moskva i Orda (in Russian) (Naučnoe izd. ed.). Moskva: Nauka. pp. 188–189. ISBN 5-02-010202-4. Retrieved 5 December 2016.
^ Gorskij, A.A. (2000). Moskva i Orda (in Russian) (Naučnoe izd. ed.). Moskva: Nauka. p. 189. ISBN 5-02-010202-4. Retrieved 5 December 2016.
^ Gorskij, A.A. (2000). Moskva i Orda (in Russian) (Naučnoe izd. ed.). Moskva: Nauka. p. 188. ISBN 5-02-010202-4. Retrieved 5 December 2016.
Sources
- Moss, Walter G (2005). "History of Russia - Volume 1: To 1917", Anthem Press, p. 80
Further reading
Chester Dunning, The Russian Empire and the Grand Duchy of Muscovy: A Seventeenth Century French Account
Romaniello, Matthew (September 2006). "Ethnicity as social rank: Governance, law, and empire in Muscovite Russia". Nationalities Papers. 34 (4): 447–469. doi:10.1080/00905990600842049.
Marshall Poe, Foreign Descriptions of Muscovy: An Analytic Bibliography of Primary and Secondary Sources, Slavica Publishers, 1995,
ISBN 0-89357-262-4
 This article incorporates public domain material from the Library of Congress Country Studies website http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/. - Russia
This article incorporates public domain material from the Library of Congress Country Studies website http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/. - Russia
|
|
|
External links
 Media related to Muscovy at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Muscovy at Wikimedia Commons



