Tagbanwa script
Tagbanwa, also known as Apurahuano, is one of the suyat[1]writing systems of the Philippines used by the Tagbanwa people as their ethnic writing system and script.
| Tagbanwa .mw-parser-output .nobold{font-weight:normal} .mw-parser-output .script-tagbanwa{font-family:"Tagbanwa","Quivira","Noto Sans Tagbanwa",Code2000} ᝦᝤᝪᝨᝯ | |
|---|---|
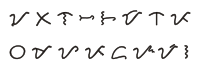 | |
| Type | Abugida |
| Languages | Palawan languages |
Time period | c. 1300–present |
Parent systems | Proto-Sinaitic alphabet
|
Sister systems | In the Philippines: Baybayin Buhid Hanunó'o Kulitan In other countries: Balinese Batak Javanese Lontara Sundanese Rencong Rejang |
| Direction | Left-to-right |
| ISO 15924 | Tagb, 373 |
Unicode alias | Tagbanwa |
Unicode range | U+1760–U+177F |
The Tagbanwa languages (Aborlan, Calamian and Central), which are Austronesian languages with about 25,000 total speakers in the central and northern regions of Palawan, are dying out as the younger generations of Tagbanwa are learning and using non-traditional languages, such as Cuyonon and Tagalog, thus becoming less knowledgeable of their own indigenous cultural heritage. There are proposals to revive the script by teaching it in public and private schools with Tagbanwa populations.[1]
Contents
1 Origin
2 Features
2.1 Vowels
2.2 Consonants
3 Unicode
4 See also
5 References
6 External links
Origin
The Tagbanwa script was used in the Philippines until the 17th century. Closely related to Baybayin, it is believed to have come from the Kawi script of Java, Bali and Sumatra, which in turn, descended from the Pallava script, one of the southern Indian scripts derived from Brahmi.[2]
Features
Tagbanwa is a syllabic alphabet in which each consonant has an inherent vowel /a/. Other vowels are indicated by a diacritic above (for /i/) or below (for /u/) the consonant.[3] Vowels at the beginning of syllables are represented by their own, independent characters. Syllables ending in a consonant are written without the final consonant.[4]
Tagbanwa is traditionally written on bamboo in vertical columns from bottom to top and left to right. Though it is read from left to right in horizontal lines.[2]
 |
Vowels
| Tagbanwa Vowels[4] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Dependent | ||||
| transcription | a | i | u | i | u |
| letter | ᝠ | ᝡ | ᝢ | ᝲ | ᝳ |
Consonants
Tagbanwa Syllables[4] | ||||||||||||||||
| transcription | k | g | ng | t | d | n | p | b | m | y | l | w | s | |||
| consonant + a | ᝣ | ᝤ | ᝥ | ᝦ | ᝧ | ᝨ | ᝩ | ᝪ | ᝫ | ᝬ | ᝮ | ᝯ | ᝰ | |||
| consonant + i | ᝣᝲ | ᝤᝲ | ᝥᝲ | ᝦᝲ | ᝧᝲ | ᝨᝲ | ᝩᝲ | ᝪᝲ | ᝫᝲ | ᝬᝲ | ᝮᝲ | ᝯᝲ | ᝰᝲ | |||
| consonant + u | ᝣᝳ | ᝤᝳ | ᝥᝳ | ᝦᝳ | ᝧᝳ | ᝨᝳ | ᝩᝳ | ᝪᝳ | ᝫᝳ | ᝬᝳ | ᝮᝳ | ᝯᝳ | ᝰᝳ | |||
Tagbanwa writing makes use of single (᜵) and double (᜶) punctuation marks.[4]
Unicode
Tagbanwa script was added to the Unicode Standard in March, 2002 with the release of version 3.2.
The Unicode block for Tagbanwa is U+1760–U+177F:
Tagbanwa[1][2] Official Unicode Consortium code chart (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| U+176x | ᝠ | ᝡ | ᝢ | ᝣ | ᝤ | ᝥ | ᝦ | ᝧ | ᝨ | ᝩ | ᝪ | ᝫ | ᝬ | ᝮ | ᝯ | |
| U+177x | ᝰ | ᝲ | ᝳ | |||||||||||||
Notes
| ||||||||||||||||
See also
- Suyat
- Baybayin
- Buhid script
- Hanunó'o script
- Kulitan
- Kawi script
- Filipino orthography
References
^ ab http://newsinfo.inquirer.net/985669/protect-all-ph-writing-systems-heritage-advocates-urge-congress
^ ab Omniglot: Tagbanwa. Accessed October 13, 2016.
^ Everson, Michael (1998-11-23). "N1933 Revised proposal for encoding the Philippine scripts in the UCS" (PDF)..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ abcd "Chapter 17: Indonesia and Oceania" (PDF). Unicode Consortium. June 2018.
External links
- Tagbanwa font
This writing system-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
