Lysorophia
| Lysorophians Temporal range: Pennsylvanian–Cisuralian PreЄ Є O S D C P T J K Pg N | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Life restoration of Brachydectes newberryi | |
Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
Clade: | Reptiliomorpha |
| Subclass: | †Lepospondyli |
| Order: | †Lysorophia Romer, 1930 |
| Family: | †Molgophidae Cope, 1875 |
| Genera | |
| |
Synonyms | |
| |
Lysorophia is an order of aquatic Carboniferous and Permian tetrapods within the extinct subclass Lepospondyli. Lysorophians resembled small snakes, as their bodies are extremely elongate. There is a single family, the Molgophidae (previously known as Lysorophidae). Currently there are around five genera included within Lysorophia, although many may not be valid.[1]
Contents
1 Description
2 Distribution
3 Paleoecology
4 References
5 General references
6 External links
Description

The skull of Brachydectes in multiple views[1]
The skull is heavily built but with large lateral openings to accommodate jaw musculature, with small orbits restricted to the anterior edge of the large fenestrae. The intertemporal, supratemporal, postfrontal, and jugal bones of the skull have disappeared. The mandibles are short and robust with a small number of large triangular teeth. Although it was initially thought that the maxilla and premaxilla were freely movable, detailed anatomical studies show that this is not the case.[2] The braincase is extremely robust[1], suggesting that lysorophians may have engaged in headfirst burrowing.
The torso is very elongate, the limbs diminutive or absent, and the tail short. There are up to 99 pre-sacral (i.e. not including the hips and tail) vertebrae.
Based on morphology of the cranio-vertebral articulation and internal structure of the head, lysorophians are usually considered to be related to the Microsauria, although the pattern of bones of the skull is somewhat different.[3]
Distribution
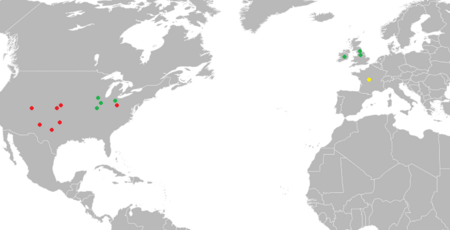
Lysorophians are known mainly from the Pennsylvanian and Early Permian of North America.[4] In North America, fossils of lysorophians have been found from places such as the Chinle Formation in San Juan County, Utah and the Mazon Creek fossil beds in Grundy County, Illinois. Carboniferous lysorophians are also known from Europe, having been found from England and Ireland. Possible remains of a lysorophian have also been found from La Machine, France, although they may belong to an aïstopod.[3][5]
Paleoecology
Swim traces referrable to lysorophians have been found at the Robledo mountains of New Mexico, an area famous for its Permian tetrapod trackways. Designated as the ichnogenus Serpentichnus, these marks occur as a series of L-shaped grooves, which are divided into two shafts: a long, diagonal shaft preceded by a shorter, forward-pointing shaft offset at a 150% angle. What seem to be tiny foot impressions occur on either side of the series of groves. When originally described in 2003, Serpentichnus tracks were argued to have been formed by a long-bodied animal with small limbs, moving in a "sidewinding" motion along a riverbed. Lysorophians such as Brachydectes were considered to be the most likely candidates for these swim traces.[6]
However, some paleontologists have argued that Serpentichnus traces were not actually formed by animals.These sources argue that the grooves were "tool marks", meaning that they were formed by rocks or vegetation brushing against the riverbed while being carried by a current.[7]
References
^ abc Pardo, Jason D.; Anderson, Jason S. (2016-08-26). "Cranial Morphology of the Carboniferous-Permian Tetrapod Brachydectes newberryi (Lepospondyli, Lysorophia): New Data from µCT". PLOS ONE. 11 (8): e0161823. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0161823. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 5001628. PMID 27563722..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Bolt, John R.; Wassersug, Richard J. (1975). "Functional Morphology of the Skull in Lysorophus: A Snake-Like Paleozoic Amphibian (Lepospondyli)". Paleobiology. 1 (3): 320–332. JSTOR 2400372.
^ ab Wellstead, C. F. (1991). "Taxonomic revision of the Lysorophia, Permo-Carboniferous lepospondyl amphibians" (PDF). Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History. 209: 1–90.
^ Cannatella, D.C.; Vieites D.R.; ZHang P.; Wake M.H.; Wake D.B. (2009). "Amphibians (Lissamphibia)". In Hedges S.B. & Kumar S. The Timetree of Life. Oxford University Press. p. 354. ISBN 9780191608988. Retrieved 3 December 2012.
^ Baird, D. (1964). "The aïstopod amphibians surveyed". Breviora. 206: 1–17.
^ Braddy, Simon J.; Morrissey, Lance B.; Yates, Adam M. (24 November 2003). "Amphibian swimming traces from the Lower Permian of southern New Mexico". Palaeontology. 46 (4): 671–683. doi:10.1111/1475-4983.00315. ISSN 0031-0239.
^ Voigt, Sebastian; Lucas, Spencer G. (2015). "Permian tetrapod ichnodiversity of the Prehistoric Trackways National Monument (south-central New Mexico, U.S.A.)". New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin. 65: 153–167.
General references
.mw-parser-output .refbegin{font-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul{list-style-type:none;margin-left:0}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>dd{margin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100{font-size:100%}
- Carroll, RL (1988), Vertebrate Paleontology and Evolution, WH Freeman & Co. p. 180
- von Zittel, K.A (1932), Textbook of Paleontology, C.R. Eastman (transl. and ed), 2nd edition, vol.2, p. 225-6, Macmillan & Co.
External links
- Lysorophia - Palaeos
- Lysorophia - phylogeny