Population density

Population density (people per km2) by country, 2006

Population density (people per km2) map of the world in 1994. In relation to the equator it is seen that the vast majority of the human population lives in the Northern Hemisphere.

Population density (people per km2) map of the world in 1994

Deserts around the world. Compare with maps above. See also this image for location of densely populated areas (cities) in various vegetation zones.
Population density (in agriculture: standing stock and standing crop) is a measurement of population per unit area or unit volume; it is a quantity of type number density. It is frequently applied to living organisms, and most of the time to humans. It is a key geographical term.[1] In simple terms population density refers to the number of people living in an area per kilometer square.
Contents
1 Biological population densities
1.1 Countries and dependent territories
1.2 Other methods of measurement
2 See also
2.1 Lists of entities by population density
3 References
4 External links
Biological population densities
Population density is population divided by total land area or water volume, as appropriate.[1]
Low densities may cause an extinction vortex and lead to further reduced fertility. This is called the Allee effect after the scientist who identified it. Examples of the causes in low population densities include:[2]
- Increased problems with locating sexual mates
- Increased inbreeding

Monaco in Southern Europe, currently holds the record for being the most densely populated nation in the world.

Mongolia is the least densely populated country in the world.
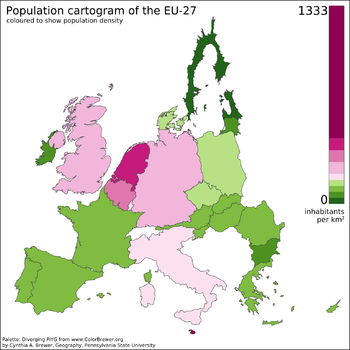
This population cartogram of the European Union (2007–2012) uses areas and colors to represent population.
For humans, population density is the number of people per unit of area, usually quoted per square kilometer or square mile (which may include or exclude, for example, areas of water or glaciers). Commonly this may be calculated for a county, city, country, another territory or the entire world.
The world's population is around 7,500,000,000[3] and Earth's total area (including land and water) is 510,000,000 square kilometers (197,000,000 sq. mi.).[4] Therefore, the worldwide human population density is around 7,500,000,000 ÷ 510,000,000 = 14.7 per km2 (38 per sq. mi). If only the Earth's land area of 150,000,000 km2 (58,000,000 sq. mi.) is taken into account, then human population density is 50 per km2 (129 per sq. mile). This includes all continental and island land area, including Antarctica. If Antarctica is also excluded, then population density rises to over 55 people per km2 (over 142 per sq. mile).[1] However, over half[citation needed] of the Earth's land mass consists of areas inhospitable to human habitation, such as deserts and high mountains, and population tends to cluster around seaports and fresh-water sources. Thus, this number by itself does not give any helpful measurement of human population density.
Several of the most densely populated territories in the world are city-states, microstates and dependencies.[5][6] These territories have a relatively small area and a high urbanization level, with an economically specialized city population drawing also on rural resources outside the area, illustrating the difference between high population density and overpopulation
The potential to maintain the agricultural aspects of deserts is extremely limited as there is not enough precipitation to support a sustainable land. The population in these areas are extremely low. Therefore cities in the Middle East, such as Dubai, have been increasing in population and infrastructure growth at a fast pace. [7]
Cities with high population densities are, by some, considered to be overpopulated, though this will depend on factors like quality of housing and infrastructure and access to resources.[8] Most of the most densely populated cities are in Southeast Asia, though Cairo and Lagos in Africa also fall into this category.[9]
City population and especially area are, however, heavily dependent on the definition of "urban area" used: densities are almost invariably higher for the central city area than when suburban settlements and the intervening rural areas are included, as in the areas of agglomeration or metropolitan area, the latter sometimes including neighboring cities. For instance, Milwaukee has a greater population density when just the inner city is measured, and the surrounding suburbs excluded.[10]
In comparison, based on a world population of seven billion, the world's inhabitants, as a loose crowd taking up ten square feet (one square metre) per person (Jacobs Method), would occupy a space a little larger than Delaware's land area.[citation needed]
Countries and dependent territories
| Pos. | Country (or dependent territory) | Area (km2) | Area (mi2) | Population | Density (pop./km2) | Density (pop./mi2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30.5 | 12 | 650,834 | 21,339 | 55,268 | |
| 2 | 2.02 | 0.78 | 37,550 | 18,589 | 48,145 | |
| 3 | 719.9 | 278 | 5,612,300 | 7,796 | 20,192 | |
| 4 | 1,106.3 | 427 | 7,409,800 | 6,698 | 17,348 | |
| 5 | 6.8 | 2.6 | 33,140 | 4,874 | 12,624 | |
| 6 | 757 | 292 | 1,451,200 | 1,917 | 4,965 | |
| 7 | 0.44 | 0.17 | 800 | 1,818 | 4,709 | |
| 8 | 315 | 122 | 475,701 | 1,510 | 3,911 | |
| 9 | 298 | 115 | 378,114 | 1,269 | 3,287 | |
| 10 | 52 | 20 | 63,779 | 1,227 | 3,178 |
The Gaza Strip (blockaded exclave of Palestine) has a population of 1.85 million and a population density of 5,046 pop/km.
Other methods of measurement
Although arithmetic density is the most common way of measuring population density, several other methods have been developed to provide a more accurate measure of population density over a specific area.
Arithmetic density: The total number of people / area of land (measured in square miles or square kilometers)
Physiological density: The total population / area of arable land
Agricultural density: The total rural population / area of arable land
Residential density: The number of people living in an urban area / area of residential land
Urban density: The number of people inhabiting an urban area / total area of urban land
Ecological optimum: The density of population that can be supported by the natural resources
See also
- Demography
- Human geography
- Idealized population
- Optimum population
- Population genetics
- Population health
- Population momentum
- Population pyramid
- Rural transport problem
- Small population size
- Distance sampling
- List of population concern organizations
Lists of entities by population density
- List of countries by population density
- List of cities by population density
- List of city districts by population density
- List of English districts by population density
- List of European cities proper by population density
- List of United States cities by population density
- List of islands by population density
- List of U.S. states by population density
- List of Australian suburbs by population density
References
^ abc Matt Rosenberg Population Density. Geography.about.com. March 2, 2011. Retrieved on December 10, 2011.
^ Minimum viable population size. Eoearth.org (March 6, 2010). Retrieved on December 10, 2011.
^ U.S. & World Population Clocks. Census.gov. Retrieved on December 10, 2011.
^ World. CIA World Handbook
^ Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division (2009). "World Population Prospects, Table A.1" (PDF). 2008 revision. United Nations. Retrieved March 12, 2009..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ The Monaco government uses a smaller surface area figure resulting in a population density of 18,078 per km2
^ 1923-2009., Portnov, B. A. (Boris Adolʹfovich) Hare, A. Paul (Alexander Paul), (1999). Desert regions : population, migration, and environment. Springer. ISBN 3540657800. OCLC 41320143.
^ Human Population. Global Issues. Retrieved on December 10, 2011.
^ The largest cities in the world by land area, population and density. Citymayors.com. Retrieved on December 10, 2011.
^ The Population of Milwaukee County. Wisconline.com. Retrieved on December 10, 2011.
^ Territory claimed by Spain.
External links
- Selected Current and Historic City, Ward & Neighborhood Density
| Pos. | Country (or dependent territory) | Area (km2) | Area (mi2) | Population | Density (pop./km2) | Density (pop./mi2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 143,998 | 55,598 | 165,001,946 | 1,146 | 2,968 | |
| 19 | 36,193 | 13,974 | 23,572,049 | 651 | 1,686 | |
| 25 | 100,210 | 38,691 | 51,635,256 | 515 | 1,334 | |
| 27 | 26,338 | 10,169 | 12,001,136 | 456 | 1,181 | |
| 31 | 41,526 | 16,033 | 17,271,819 | 416 | 1,077 | |
| 33 | 27,065 | 10,450 | 11,112,945 | 411 | 1,064 | |
| 34 | 3,287,240 | 1,269,210 | 1,335,543,957 | 406 | 1,052 | |
| 36 | 27,816 | 10,740 | 10,681,186 | 384 | 995 | |
| 38 | 30,528 | 11,787 | 11,414,214 | 374 | 969 | |
| 39 | 300,000 | 115,831 | 106,302,840 | 354 | 917 |
Global human population | |
|---|---|
| Major topics |
|
| Biological and related topics |
|
| Human impact on the environment |
|
Population ecology |
|
| Literature |
|
| Publications |
|
| Lists |
|
Events and organizations |
|
| Related topics |
|
| |
