South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands | |
|---|---|
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
Motto: "Leo Terram Propriam Protegat" (Latin) "Let [or May] the Lion protect his own land" | |
Anthem: "God Save the Queen" | |
 Location of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands in the southern Atlantic Ocean | |
| Status | British Overseas Territory |
| Capital | King Edward Point 54°17′S 36°30′W / 54.283°S 36.500°W / -54.283; -36.500 |
| Largest settlement | Grytviken |
| Official languages | English |
| Demonym |
|
| Government | Dependency under a constitutional monarchy |
• Monarch | Elizabeth II |
• Commissioner | Nigel Phillips |
• UK government minister[a] | Tariq Ahmad |
| Area | |
• Total | 3,903 km2 (1,507 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• Estimate | 35 (summer) 16 (winter) |
| Currency | Falkland Islands pound[1][b] (FKP) |
| Time zone | UTC−2 (GST) |
| Calling code | +500 |
| ISO 3166 code | GS |
| Internet TLD | .gs |
Website www.gov.gs | |
| |
UK Postcode SIQQ 1ZZ | |
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (SGSSI) is a British Overseas Territory in the southern Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote and inhospitable collection of islands, consisting of South Georgia and a chain of smaller islands known as the South Sandwich Islands. South Georgia is 165 km (103 mi) long and 1 to 35 km (1 to 22 mi) wide[3] and is by far the largest island in the territory. The South Sandwich Islands lie about 700 km (430 mi) southeast of South Georgia.[3] The territory's total land area is 3,903 km2 (1,507 sq mi).[4] The Falkland Islands are about 1,300 km (810 mi) north-west from its nearest point.
No permanent native population lives in the territory although a very small non-permanent population does reside in South Georgia.[5] The present inhabitants are three officers of the Government of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands along with scientists and support staff from the British Antarctic Survey who maintain scientific bases at Bird Island and at the capital, King Edward Point along with postal staff, as well as three museum staff at Grytviken. With an estimated minimum non-permanent population of around sixteen people in the winter months to a maximum of around thirty five people in the summer months it is the least populated of all the British Overseas Territories. There are no scheduled passenger flights or ferries to or from the territory, although visits by cruise liners to South Georgia are increasingly popular, with several thousand visitors each summer.
The United Kingdom claimed sovereignty over South Georgia in 1775 and the South Sandwich Islands in 1908. The territory of "South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands" was formed in 1985; previously, it had been governed as part of the Falkland Islands Dependencies. Argentina claimed South Georgia in 1927 and claimed the South Sandwich Islands in 1938.
Argentina maintained a naval station, Corbeta Uruguay, on Thule Island in the South Sandwich Islands from 1976 until 1982 when it was closed by the Royal Navy. The Argentine claim over South Georgia contributed to the 1982 Falklands War, during which Argentine forces briefly occupied the island. Argentina continues to claim sovereignty over South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands.
Toothfish are vital to the islands' economy; as a result, Toothfish Day is celebrated on 4 September as a bank holiday in the territory.[6][7]
Contents
1 History
1.1 South Georgia
1.1.1 17th–19th centuries
1.1.2 20th and 21st centuries
1.2 South Sandwich Islands
2 Geography
2.1 South Georgia group
2.1.1 Islands within the South Georgia group
2.2 South Sandwich Islands
2.3 Extreme points
3 Climate
4 Government
5 Economy
5.1 Fishing
5.2 Tourism
5.3 Postage stamps
5.4 Currency
5.5 Internet domain registration
6 Flora and fauna
6.1 Plants
6.2 Birds
6.3 Mammals
6.4 Marine ecosystem
7 Military
8 See also
9 References
10 Further reading
11 External links
History
South Georgia
17th–19th centuries
 Central South Georgia Cumberland Bay – Thatcher Peninsula with King Edward Cove (Grytviken) – Allardyce Range, featuring the summit of Mount Paget. (NASA imagery) | |
 Map by James Cook (1777, south facing upwards) | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Antarctic |
| Highest elevation | 2,934 m (9,626 ft) |
| Highest point | Mount Paget |
| Administration | |
| Demographics | |
| Ethnic groups | Britons |
The Island of South Georgia is said to have been first sighted in 1675 by Anthony de la Roché, a London merchant,[8] and was named Roche Island on a number of early maps.[citation needed] It was sighted by the commercial Spanish ship León operating out of Saint-Malo on 28 June or 29 June 1756.[9] At one time it was confused with Pepys Island, which was "discovered" by Dampier and Cowley in 1683 but later proved to be a phantom island.[citation needed]
Captain James Cook circumnavigated the island in 1775 and made the first landing. He claimed the territory for the Kingdom of Great Britain, and named it "the Isle of Georgia" in honour of King George III. British arrangements for the government of South Georgia were established under the 1843 British Letters Patent.
In 1882–1883, a German expedition for the First International Polar Year was stationed at Royal Bay on the southeast side of the island. The scientists of this group observed the transit of Venus and recorded waves produced by the 1883 eruption of Krakatoa.
Seal hunting at South Georgia began in 1786 and continued throughout the 19th century. The waters proved treacherous and a number of vessels were wrecked there, such as Earl Spencer, in late 1801.[10]
20th and 21st centuries
South Georgia became a base for whaling beginning in the 20th century, until whaling ended in the 1960s. A Norwegian, Carl Anton Larsen, established the first land-based whaling station and first permanent habitation at Grytviken in 1904. It operated through his Argentine Fishing Company, which settled in Grytviken.[11][9] The station operated until 1965.
Whaling stations operated under leases granted by the (British) Governor of the Falkland Islands. The seven stations, all on the north coast with its sheltered harbours, were, from the west to east:
Prince Olav Harbour (from 1911–1916 factory ship and small land-based station 1917–1931)
Leith Harbour (1909–1965)
Stromness (from 1907 factory ship, land-based station 1913–1931, repair yard to 1960/1961)
Husvik (from 1907 factory ship, land-based station 1910–1960, not in operation 1930–1945)
Grytviken (1904–1964)
Godthul (1908–1929, only a rudimentary land base, main operations on factory ship)
Ocean Harbour (1909–1920)
The whaling stations' tryworks were unpleasant and dangerous places to work. One was called "a charnel house boiling wholesale in vaseline" by an early 20th-century visitor. Tim Flannery wrote that its "putrid vapors [resembled] the pong of bad fish, manure, and a tanning works mixed together", and noted one bizarre peril: "A rotting whale could fill with gas to bursting, ejecting a fetus the size of a motor vehicle with sufficient force to kill a man."[12] (See Coffin birth and Exploding whale)
With the end of the whaling industry, the stations were abandoned. Apart from a few preserved buildings such as the museum and church at Grytviken, only their decaying remains survive.
From 1905, the Argentine Meteorological Office cooperated in maintaining a meteorological observatory at Grytviken under the British lease requirements of the whaling station until these changed in 1949.

The church at Grytviken

A panoramic view of South Georgia taken by Frank Hurley during the Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition
In 1908, the United Kingdom issued further letters patent that established constitutional arrangements for its possessions in the South Atlantic. The letters covered South Georgia, the South Orkneys, the South Shetlands, the South Sandwich Islands, and Graham Land. (The claim was extended in 1917 to include a sector of Antarctica reaching to the South Pole.)
In 1909, an administrative centre and residence were established at King Edward Point on South Georgia, near the whaling station of Grytviken. A permanent local British administration and resident magistrate exercised effective possession, enforcement of British law, and regulation of all economic, scientific, and other activities in the territory, which was then governed as the Falkland Islands Dependencies.
In about 1912, what is according to some accounts the largest whale ever caught, a blue whale of 34 m (110 ft), was landed at Grytviken.[13][14]
In April 1916, Ernest Shackleton's Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition became stranded on Elephant Island, some 800 mi (1,300 km) southwest of South Georgia. Shackleton and five companions set out in a small boat to summon help, and on 10 May, after an epic voyage, they landed at King Haakon Bay on South Georgia's south coast. While three stayed at the coast, Shackleton and the two others, Tom Crean and Frank Worsley, went on to cover 22 mi (35 km) over the spine of the mountainous island to reach help at Stromness whaling station. The remaining 22 members of the expedition, who had stayed on Elephant Island, were subsequently rescued. In January 1922, during a later expedition, Shackleton died on board ship while moored in King Edward Cove, South Georgia. He is buried at Grytviken. The ashes of another noted Antarctic explorer, Frank Wild, who had been Shackleton's second-in-command on the Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition, were interred next to Shackleton in 2011.
Argentina claimed South Georgia in 1927.[15]
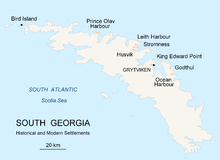
Historical and modern settlements of South Georgia Island
During the Second World War, the Royal Navy deployed an armed merchant vessel to patrol South Georgian and Antarctic waters against German raiders, along with two four-inch shore guns (still present) protecting Cumberland Bay and Stromness Bay, which were manned by volunteers from among the Norwegian whalers. The base at King Edward Point was expanded as a research facility in 1949/1950 by the British Antarctic Survey, which until 1962 was called the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey.

Topography of South Georgia Island
The Falklands War was precipitated on 19 March 1982 when a group of Argentinians (most of them Argentine Marines in mufti), posing as scrap-metal merchants, occupied the abandoned whaling station at Leith Harbour on South Georgia. On 3 April, the Argentine troops attacked and occupied Grytviken. Among the commanding officers of the Argentine garrison was Alfredo Astiz, a captain in the Argentine Navy who was convicted years later of crimes against humanity committed during the Dirty War in Argentina.
The island was recaptured by British forces on 25 April in Operation Paraquet. In 1985, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands ceased to be administered as a Falkland Islands Dependency and became a separate territory. The King Edward Point base, which had become a small military garrison after the Falklands War, returned to civilian use in 2001 and is now operated by the British Antarctic Survey.
South Sandwich Islands
Captain James Cook discovered the southern eight islands of the Sandwich Islands Group in 1775, although he lumped the southernmost three together, and their status as separate islands was not established until 1820 by Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen.[16] The northern three islands were discovered by Bellingshausen in 1819. The islands were tentatively named "Sandwich Land" by Cook, although he also commented that they might be a group of islands rather than a single body of land. The name was chosen in honour of John Montagu, 4th Earl of Sandwich, First Lord of the Admiralty. The word "South" was later added to distinguish them from the "Sandwich Islands", now known as the Hawaiian Islands.
Argentina claimed the South Sandwich Islands in 1938, and challenged British sovereignty in the Islands on several occasions. From 25 January 1955 to mid-1956, Argentina maintained the summer station Teniente Esquivel at Ferguson Bay on the southeastern coast of Thule Island. Argentina maintained a naval base (Corbeta Uruguay) from 1976 to 1982, in the lee (southern east coast) of the same island. Although the British discovered the presence of the Argentine base in 1976,[17] protested and tried to resolve the issue by diplomatic means, no effort was made to remove them by force until after the Falklands War. The base was removed on 20 June 1982.
On 10 February 2008, a 6.5 magnitude earthquake had its epicentre 205 km (127 mi; 111 nmi) south-southeast of Bristol Island.[18] On 30 June 2008 at 06:17:53 UTC, a 7.0-magnitude earthquake struck the region. Its epicentre was at 58.160S 21.893W, 283 km (176 mi; 153 nmi) ENE (73 degrees) of Bristol Island.[19] The United States Geological Survey reported that a 7.3-magnitude earthquake had occurred at 10:04 EDT on 15 Jul 2013, 216 km (134 mi; 117 nmi) south-southeast of Bristol Island, South Sandwich Islands, at a depth of 31.3 km (19.4 mi). The epicentre was located 2,230 km (1,390 mi; 1,200 nmi) southeast of Stanley, Falkland Islands.[20]
Geography

CIA map of the islands
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands are a collection of islands in the South Atlantic Ocean. Most of the islands, rising steeply from the sea, are rugged and mountainous. At higher elevations, the islands are permanently covered with ice and snow.
South Georgia group
The South Georgia group lies about 1,390 km (864 mi; 751 nmi) east-southeast of the Falkland Islands, at 54°–55°S, 36°–38°W. It comprises South Georgia Island itself (by far the largest island in the territory), and the islands that immediately surround it and some remote and isolated islets to the west and east-southeast. It has a total land area of 3,756 km2 (1,450 sq mi), including satellite islands (but excluding the South Sandwich Islands which form a separate island group).
Islands within the South Georgia group
South Georgia Island lies at 54°15′S 36°45′W / 54.250°S 36.750°W / -54.250; -36.750Coordinates: 54°15′S 36°45′W / 54.250°S 36.750°W / -54.250; -36.750 and has an area of 3,528 km2 (1,362 sq mi). It is mountainous and largely barren. Eleven peaks rise to over 2,000 m (6,562 ft) high, their slopes furrowed with deep gorges filled with glaciers; the largest is Fortuna Glacier. The highest peak is Mount Paget in the Allardyce Range at 2,934 m (9,626 ft).
Geologically, the island consists of gneiss and argillaceous schists with occasional tufts and other sedimentary layers from which fossils have been recovered.[21] The island is a fragment of some greater land-mass now vanished and was probably a former extension of the Andean system.
Smaller islands and islets off the coast of South Georgia Island include:

View of Grytviken
- Annenkov Island
- Bird Island
- Cooper Island
- Grass Island
- Jomfruene
- Pickersgill Islands
- Welcome Islands
- Willis Islands
- Trinity Island
These remote rocks are also considered part of the South Georgia group:
Shag Rocks 185 km (115 mi; 100 nmi) west-northwest of South Georgia Island
Black Rock 169 km (105 mi; 91 nmi) west-northwest of South Georgia Island and 16 km (9.9 mi; 8.6 nmi) southeast of the Shag Rocks
Clerke Rocks 56 km (35 mi; 30 nmi) east-southeast of South Georgia Island
South Sandwich Islands

NASA satellite photograph of Montagu Island
The South Sandwich Islands (Spanish: Islas Sandwich del Sur) comprise 11 mostly volcanic islands (excluding tiny satellite islands and offshore rocks), with some active volcanoes. They form an island arc running north-south in the region 56°18'–59°27'S, 26°23'–28°08'W, between about 350 and 500 mi (300 and 430 nmi; 560 and 800 km) southeast of South Georgia.
The northernmost of the South Sandwich Islands form the Traversay Islands and Candlemas Islands groups, while the southernmost make up Southern Thule. The three largest islands – Saunders, Montagu, and Bristol – lie between the two. The Islands' highest point is Mount Belinda (1,370 m or 4,495 ft) on Montagu Island.
The South Sandwich Islands are uninhabited, though a permanently manned Argentine research station was located on Thule Island from 1976 to 1982 (for details, see § History above). Automatic weather stations are on Thule Island and Zavodovski. To the northwest of Zavodovski Island is the Protector Shoal, a submarine volcano.
The South Sandwich Islands from north to south are:
Island (Spanish name) | Area | Highest peak | Location | |
Traversay Islands | ||||
Protector Shoal | — | −27 m (−89 ft) | 55°54′S 28°06′W / 55.900°S 28.100°W / -55.900; -28.100 (Protector Shoal) | |
Zavodovski | 25 km2 (9.7 sq mi) | Mount Asphyxia 550 m (1,800 ft) | 56°18′S 27°34′W / 56.300°S 27.567°W / -56.300; -27.567 (Zavodovski) | |
Leskov | 0.3 km2 (0.12 sq mi) | Rudder Point 190 m (620 ft) | 56°40′S 28°08′W / 56.667°S 28.133°W / -56.667; -28.133 (Leskov) | |
Visokoi | 35 km2 (14 sq mi) | Mount Hodson 915 m (3,002 ft) | 56°42′S 27°13′W / 56.700°S 27.217°W / -56.700; -27.217 (Visokoi) | |
Candlemas Islands (sometimes included with Traversay Islands) | ||||
Candlemas (Candelaria) | 14 km2 (5.4 sq mi) | Mount Andromeda 550 m (1,800 ft) | 57°05′S 26°39′W / 57.083°S 26.650°W / -57.083; -26.650 (Candlemas) | |
Vindication (Vindicación) | 5 km2 (1.9 sq mi) | Quadrant Peak 430 m (1,410 ft) | 57°06′S 26°47′W / 57.100°S 26.783°W / -57.100; -26.783 (Vindication) | |
Central islands | ||||
Saunders | 40 km2 (15 sq mi) | Mount Michael 990 m (3,250 ft) | 57°48′S 26°28′W / 57.800°S 26.467°W / -57.800; -26.467 (Saunders) | |
Montagu (Jorge) | 110 km2 (42 sq mi) | Mount Belinda 1,370 m (4,490 ft) | 58°25′S 26°23′W / 58.417°S 26.383°W / -58.417; -26.383 (Montagu) | |
Bristol (Blanca) | 46 km2 (18 sq mi) | Mount Darnley 1,100 m (3,600 ft) | 59°03′S 26°30′W / 59.050°S 26.500°W / -59.050; -26.500 (Bristol) | |
Southern Thule (Tule del Sur) | ||||
Bellingshausen | 1 km2 (0.39 sq mi) | Basilisk Peak 255 m (837 ft) | 59°25′S 27°05′W / 59.417°S 27.083°W / -59.417; -27.083 (Bellingshausen) | |
Cook | 20 km2 (7.7 sq mi) | Mount Harmer 1,115 m (3,658 ft) | 59°26′S 27°09′W / 59.433°S 27.150°W / -59.433; -27.150 (Cook) | |
Thule (or Morrell) Island | 14 km2 (5.4 sq mi) | Mount Larsen 710 m (2,330 ft) | 59°27′S 27°18′W / 59.450°S 27.300°W / -59.450; -27.300 (Thule) | |
| Vysokaya Bank | — | −89 m (−292 ft) | 59°43′S 27°58′W / 59.717°S 27.967°W / -59.717; -27.967 (Vysokaya Bank) | |
South Sandwich Islands (entire) | 310 km2 (120 sq mi) | Mount Belinda 1,370 m (4,490 ft) | ||
A series of six passages separates each of the islands or island groups in the chain. They are, from north to south: Zavodovski Isl. – Traverse passage – Visokoi Isl. – Brown's passage – Candlemas Isl. – Shackleton's passage – Saunders Isl. – Larsen's passage – Montagu Isl. – Biscoe's passage – Bristol Isl. – Forsters Passage – Southern Thule. Nelson Channel is the passage between Candlemas and Vindication Island.
Extreme points
- Northernmost point –
- Southernmost point –
- Westernmost point –
- Easternmost point –
- Highest point – Mount Paget: 2,934 m
- Lowest point – Atlantic Ocean: 0
Climate

NASA satellite image of South Georgia Island covered with snow

The South Sandwich Islands connect with air currents to make wave patterns in clouds.

Royal Bay and South Georgia Island
The climate is classified as polar, and the weather is highly variable and harsh; making a tundra (ET) in Köppen climate classification. Typical daily maximum temperatures in South Georgia at sea level are around 0 °C (32 °F) in winter (August) and 8 °C (46.4 °F) in summer (January). Winter minimum temperatures are typically about −5 °C (23 °F) and rarely dip below −10 °C (14 °F). Annual precipitation in South Georgia is about 1,500 mm (59.1 in), much of which falls as sleet or snow, which is possible the entire year. Inland, the snow line in summer is at an altitude of about 300 m (984 ft).
Westerly winds blow throughout the year interspersed with periods of calm—indeed, in 1963, 25% of winds were in the calm category at King Edward point, and the mean wind speed of around 8 knots (9.2 mph; 15 km/h) is around half that of the Falkland Islands. This gives the eastern side of South Georgia (leeward side) a more pleasant climate than the exposed western side. The prevailing weather conditions generally make the islands difficult to approach by ship, though the north coast of South Georgia has several large bays which provide good anchorage.
Sunshine, as with many South Atlantic Islands, is low, at a maximum of just 21.5%. This amounts to around 1,000 hours of sunshine annually. The local topography, however, also contributes significantly to the low insolation. A study published during the early 1960s[22] indicated that sunshine recording instruments remained significantly obscured throughout the year and entirely obscured during June. It was estimated that the theoretical sunshine exposure minus obstructions would be around 14% at Bird Island and 35% at King Edward Point – or, in hourly terms, ranging from around 650 hours in the west to 1,500 hours in the east. This illustrates the effect the Allardyce range has in breaking up cloud cover.
Mountain winds blow straight up the western side and straight down the eastern side of the mountains and become much warmer and drier due to the Föhn effect; this produces the most pleasant conditions when temperatures can occasionally rise over 20 °C (68 °F) on summer days. The highest recorded temperature was 28.8 °C (83.8 °F) at Grytviken.[23] and 26.3 °C (79.3 °F) at nearby King Edward point, both on the sheltered east side of the Islands. Conversely, the highest recorded temperature at Bird Island on the windward western side is a mere 14.5 °C (58.1 °F). As one might expect, the sheltered eastern side can also record lower winter temperatures—the absolute minimum for Grytviken being −19.4 °C (−2.9 °F), King Edward Point −18.9 °C (−2.0 °F), but Bird Island just −11.4 °C (11.5 °F).
The seas surrounding South Georgia are cold throughout the year due to the proximity of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current. They usually remain free of pack ice in winter, though thin ice may form in sheltered bays, and icebergs are common.[24] Sea temperatures drop to 0 °C (32 °F) in late August and rise to around 4 °C (39.2 °F) only in early April.
The South Sandwich Islands are much colder than South Georgia, being farther south and more exposed to cold outbreaks from the Antarctic continent. They are also surrounded by sea ice from the middle of May to late November (even longer at their southern end).[25] Recorded temperature extremes at South Thule Island have ranged from −29.8 to 17.7 °C (−21.6 to 63.9 °F).
| Climate data for Bird Island, South Georgia, 1961–1990 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 5.5 (41.9) | 5.6 (42.1) | 4.4 (39.9) | 1.9 (35.4) | −0.5 (31.1) | −1.8 (28.8) | −2.4 (27.7) | −1.9 (28.6) | −0.2 (31.6) | 1.6 (34.9) | 3.4 (38.1) | 4.5 (40.1) | 1.7 (35) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 0.7 (33.3) | 1.4 (34.5) | 0.6 (33.1) | −1 (30) | −3.8 (25.2) | −4.6 (23.7) | −5.4 (22.3) | −4.8 (23.4) | −3.4 (25.9) | −1.9 (28.6) | −1.5 (29.3) | −0.6 (30.9) | −2 (28.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 84 (3.31) | 80 (3.15) | 95 (3.74) | 123 (4.84) | 108 (4.25) | 108 (4.25) | 120 (4.72) | 114 (4.49) | 107 (4.21) | 98 (3.86) | 88 (3.46) | 77 (3.03) | 1,204 (47.4) |
| Source: Climatic Research Unit, UEA[26] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Grytviken/King Edward Point, South Georgia, 1901–1950 (Sunshine 1931–1960) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 24.5 (76.1) | 26.5 (79.7) | 28.8 (83.8) | 19.1 (66.4) | 17.5 (63.5) | 14.0 (57.2) | 13.6 (56.5) | 13.2 (55.8) | 17.0 (62.6) | 20.0 (68) | 22.5 (72.5) | 21.5 (70.7) | 28.8 (83.8) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 8.4 (47.1) | 9.1 (48.4) | 8.4 (47.1) | 5.6 (42.1) | 2.9 (37.2) | 0.9 (33.6) | 1.2 (34.2) | 1.5 (34.7) | 3.5 (38.3) | 5.4 (41.7) | 6.5 (43.7) | 7.5 (45.5) | 5.1 (41.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 1.4 (34.5) | 1.7 (35.1) | 1.0 (33.8) | −0.8 (30.6) | −3.1 (26.4) | −4.6 (23.7) | −4.7 (23.5) | −4.9 (23.2) | −3.3 (26.1) | −1.8 (28.8) | −0.5 (31.1) | 0.4 (32.7) | −1.6 (29.1) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −4.1 (24.6) | −3.7 (25.3) | −6.3 (20.7) | −9.8 (14.4) | −11.4 (11.5) | −14.6 (5.7) | −15.2 (4.6) | −19.2 (−2.6) | −18.4 (−1.1) | −11 (12) | −6.4 (20.5) | −5.4 (22.3) | −19.2 (−2.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 92.0 (3.622) | 114.0 (4.488) | 136.0 (5.354) | 139.0 (5.472) | 137.0 (5.394) | 135.0 (5.315) | 149.0 (5.866) | 149.0 (5.866) | 92.0 (3.622) | 80.0 (3.15) | 93.0 (3.661) | 88.0 (3.465) | 1,394 (54.882) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 152 | 160 | 127 | 66 | 34 | 12 | 22 | 74 | 123 | 171 | 174 | 167 | 1,282 |
| Source #1: Globalbioclimatics/S.Rivas-Martínez[27] | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: DMI/Danish Meteorology Institute[28] | |||||||||||||
Government
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands |
|---|
 |
This article is part of a series on the politics and government of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands |
The Crown
|
Government
|
History
|
South Georgia
|
South Sandwich Islands
|
Research Stations British Antarctic Survey
|
Other
|
|
Executive power is vested in the Monarch of the United Kingdom and is exercised by the commissioner, a post held by the Governor of the Falkland Islands. The current commissioner is Nigel Phillips, who became commissioner on 12 September 2017. A chief executive officer (Martin Collins) deals with policy matters and is director of SGSSI Fisheries, responsible for the allocation of fishing licences. An executive officer (Richard McKee) deals with administrative matters relating to the territory. Also, an environmental officer (Jennifer Lee) and a marine and Fisheries officer (Katherine Ross) are appointed. The financial secretary and attorney general of the territory are appointed ex officio similar appointments in the Falkland Islands' government.
As no permanent inhabitants live on the islands, no legislative council and no elections are needed. The UK Foreign Office manages the foreign relations of the territory. Since 1982, the territory celebrates Liberation Day on 14 June.
The constitution of the territory (adopted 3 October 1985), the manner in which its government is directed and the availability of judicial review were discussed in a series of litigations between 2001 and 2005 (see, in particular, Regina v. Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs (Appellant) ex parte Quark Fishing Limited [2005] UKHL 57[29]). Although its government is entirely directed by the UK Foreign Office, it was held that, since it was acting as an agent of the Crown in right of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands rather than in right of the UK, its decisions under that direction could not be challenged as if they were in law decisions of a UK government department;[clarification needed] thus the European Convention on Human Rights did not apply.
Economy
Commercial sealing occurred on the islands between 1817 and 1909. During that period 20 visits are recorded by sealing vessels.[30]
Economic activity in South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands is limited. The territory has revenues of £4.5 million, 80% of which is derived from fishing licences (2011 figures).[31] Other sources of revenue are the sale of postage stamps and coins, tourism and customs and harbour dues.[32]
Fishing
Fishing takes place around South Georgia and in adjacent waters in some months of the year, with fishing licences sold by the territory for Patagonian toothfish, cod icefish and krill. Fishing licences bring in millions of pounds a year, most of which is spent on fishery protection and research. All fisheries are regulated and managed in accordance with the Convention for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR) system.
In 2001 the South Georgia government was cited by the Marine Stewardship Council for its sustainable Patagonian toothfish fishery, certifying that South Georgia met the MSC's environmental standards. The certificate places limits on the timing and quantity of Patagonian toothfish that may be caught.[33]
Tourism
Tourism has become a larger source of income in recent years, with many cruise ships and sailing yachts visiting the area (the only way to visit South Georgia is by sea; there are no airstrips on the Islands). The territory gains income from landing charges and the sale of souvenirs. Cruise ships often combine a Grytviken visit with a trip to the Antarctic Peninsula.
Charter yacht visits usually begin in the Falkland Islands, last between four and six weeks, and enable guests to visit remote harbours of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands. Sailing vessels are now required to anchor out and can no longer tie up to the old whaling piers on shore. One exception to this is the recently upgraded/repaired yacht berth at Grytviken. All other jetties at former whaling stations lie inside a 200 m (656 ft) exclusion zone; and berthing, or putting ropes ashore, at these is forbidden. Yachts visiting South Georgia are normally expected to report to the Government Officers at King Edward Point before moving round the island.
The island has featured in the Warren Miller video Storm.
Postage stamps

This postage stamp depicting a fin whale was issued in 1963.
A large source of income from abroad also comes from the issue of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands postage stamps which are produced in the UK.
A reasonable issue policy (few sets of stamps are issued each year) along with attractive subject matter (especially whales) makes them popular with topical stamp collectors.
There are only four genuine first day cover sets from 16 March 1982 in existence. They were stamped at the South Georgia Post Office; all those in circulation were stamped elsewhere and sent out, but the only genuine ones were kept at the Post Office on South Georgia. These four sets were removed during the Falklands War by a member of staff of the British Antarctic Survey in the few moments the Argentinians allowed them to gather their belongings. Everything else was burnt, but these four sets were saved and brought to the UK by Robert Headland, BAS.
Currency
The pound sterling is the official currency of the islands, and the same notes and coins are used as in the United Kingdom. For more information on British currency in the wider region, see Pound sterling in the South Atlantic and the Antarctic.
Internet domain registration
The Internet country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands is .gs. Although the territory has no permanent residents, the domain suffix has some popularity for website registrations, with approximately 6 million instances as of November 2018.[34]
Flora and fauna
 Southern giant petrel on South Georgia Island |  A colony of 200,000 king penguins (Aptenodytes patagonicus) on Salisbury Plain |  King penguins at St Andrews Bay, South Georgia Island, 1996 |
Plants
The parts of the islands that are not permanently covered in snow or ice are part of the Scotia Sea Islands tundra ecoregion. In total there are 26 species of vascular plant native to South Georgia; six species of grass, four rushes, a single sedge, six ferns, one clubmoss and nine small forbs. There are also about 125 species of moss, 85 of liverworts and 150 lichens, as well as about 50 species of macrofungi.[35] A number of introduced species have become naturalised; many of these were introduced by whalers in cattle fodder, and some are considered invasive.[36] There are no trees or shrubs on the islands.[37]
The largest plant is the tussock grass Poa flabellata. This grows mostly on raised beaches and steep slopes near the shore and may reach 2 m (7 ft). Other grasses include the tufted fescue (Festuca contracta), the Alpine cat's-tail (Phleum alpinum) and Antarctic hair-grass (Deschampsia antarctica), and one of the commonest flowering plants is the greater burnet (Acaena magellanica).[35]
Birds
South Georgia supports many sea birds, including albatross, a large colony of king penguins, Macaroni penguins[38] and penguins of various other species, along with petrels, prions, shags, skuas, gulls and terns. Birds unique to the archipelago are the South Georgia shag, South Georgia pipit, and the South Georgia pintail. Both South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands have been identified as Important Bird Areas (IBA) by BirdLife International.[39]
Mammals
Wikispecies has information related to South Georgia Island nonmarine fauna |
Seals frequent the islands, and whales may be seen in the surrounding waters. There are no native land mammals, though reindeer, brown rats and mice were introduced to South Georgia through human activities.
Rats, brought to the island as stowaways on sealing and whaling ships in the late 18th century,[40] have caused much damage to native wildlife, destroying tens of millions of ground-nesting birds' eggs and chicks. While previously the island's glaciers formed a natural barrier to the spread of rats, these glaciers are now slowly melting as the climate warms.[41] In 2011, scientists instituted a four-year programme to entirely eradicate the rats and mice, in what would be by far the largest rodent eradication attempt in the world to date.[42][43][44] The project was led by zoologist Anthony Martin of The University of Dundee who stated, "This is a man-induced problem and it's about time that man put right earlier errors."[45] In July 2013, the success of the main phase of the extermination of the rats, which took place in May that year, was announced. 180 tonnes of rat poison, brodifacoum, were dropped over 70% of the island, in what was the world's largest ever operation of this kind.[46] Another 95t of rat poison was planned to be dropped by three helicopters in January 2015.[47] In June 2015 the eradication programme concluded, apparently successfully, with the island believed "very likely" to be rat free. In 2017/18, an intensive 6-month search by the South Georgia Heritage Trust, using sniffer dogs and baited traps, found no evidence of rodent presence.[48] Monitoring will continue for a further two or three years.[49]
Reindeer were introduced to South Georgia in 1911 by Norwegian whalers for meat and for sport hunting. In February 2011, the authorities announced that due to the reindeer's detrimental effect on native species and the threat of their spreading to presently pristine areas, a complete cull would take place, leading to the eradication of reindeer from the island.[50] The eradication began in 2013 with 3,500 reindeer killed. Nearly all the rest were killed in early 2014, with the last (about 50) cleared in the 2014/15 southern summer.[51]
Marine ecosystem
The seas around South Georgia have a high level of biodiversity. In a recent study (2009–2011), South Georgia has been discovered to contain one of the highest levels of biodiversity among all the ecosystems on Earth.[52] In respect to species, marine inhabitants endemic to this ecosystem outnumber and (in respect to biodiversity) surpass well-known regions such as the Galápagos or Ecuador.[53] The marine ecosystem is thought to be vulnerable because its low temperatures mean that it can repair itself only very slowly.[54] On 23 February 2012, to protect marine biodiversity, the territory's government created the South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Marine Protected Area – comprising 1.07 million km2 (410,000 sq mi).[55][56][57]
 Wandering albatross at South Georgia Island |  Antarctic Pearlwort at St. Andrews Bay, South Georgia |  South Georgia glacier and penguin colony |
Military

HMS Protector
After the Falklands War in 1982, a full-time British military presence was maintained at King Edward Point on South Georgia. This was scaled down during the 1990s until the last detachment left South Georgia in March 2001, after a new station had been built and occupied by the British Antarctic Survey.[58]
The main British military facility in the region is at RAF Mount Pleasant and the adjacent Mare Harbour naval base on East Falkland, and three Remote Radar Heads on the Falklands: RRH Mount Kent, RRH Byron Heights and RRH Mount Alice. A handful of British naval vessels patrol the region, visiting South Georgia a few times each year and sometimes deploying small infantry patrols. Flights by RAF C-130 Hercules and Vickers VC10 (replaced by Voyager) aircraft also occasionally patrol the territory.
A Royal Navy destroyer or frigate and a Royal Fleet Auxiliary vessel carry out the Atlantic Patrol Task (South) mission in the surrounding area.
HMS Endurance, the Royal Navy ice-patrol ship, operated in the South Georgia area during part of most southern summer seasons until her near loss due to flooding in 2008. She carried out hydrological and mapping work as well as assisting with scientific fieldwork for the British Antarctic Survey, film and photographic units, and youth expedition group BSES Expeditions. While the final decision on the fate of Endurance was pending, the Royal Navy chartered a Norwegian icebreaker, renamed HMS Protector, to act as replacement for three years.[59] In September 2013 the British Ministry of Defence purchased the ship outright.[60] It was announced on 7 October 2013 that Endurance would be sold for scrap.[61]
See also
- Bibliography of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- British Overseas Territories
- Index of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands-related articles
- List of Antarctic and subantarctic islands
- Lists of islands
- South Orkney Islands
- South Shetland Islands
References
^ Tony Wheeler (2004). The Falklands & South Georgia Island. Lonely Planet. pp. 172–. ISBN 978-1-74059-643-5..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "Foreign travel advice South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands". UK Government. Retrieved 1 November 2016.
^ ab "Google Maps".
^ South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, CIA World Factbook, 2002.
^ "South Georgia & the South Sandwich Islands – Current Status". Government of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (GSGSSI). Retrieved 31 May 2016.There are no permanent residents in the Territory but the British Antarctic Survey (BAS) operates two bases on South Georgia. The base at King Edward Point (KEP) is operated under contract to GSGSSI and the FCO and is staffed by eight BAS personnel, plus three GSGSSI Officers and their spouses. Bird Island has a year round complement of four BAS personnel who undertake long-term monitoring of seabirds and marine mammals. The South Sandwich Islands are uninhabited, though an originally undetected, and subsequently allowed, manned Argentinean research station was located on Thule from 1976 to 1982.
^ http://en.mercopress.com/2015/09/04/toothfish-day-celebration-in-south-georgia-and-south-sandwich-islands
^ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GlnegoEzeL0
^ Carroll, Paul. "The Living Edens -- South Georgia Island -- Ice and Isolation". www.pbs.org. Retrieved 23 August 2017.
^ ab "Iberoamerica – Bienvenido --". Archived from the original on 2012-06-29.
^ Wheeler (2004), pp.26–27.
^ La Infanteria de Marina en el conflicto del Atlántico Sur, Jorge Alberto Erecaborde. The original quote in Spanish is: "La Compañia Argentina de Pesca SA, al amparo de las leyes argentinas y bajo su bandera, se instala en Grytviken".
^ "On the Minds of the Whales" by Tim Flannery, NYRB, 9 February 2012
^ The Island of South Georgia, The Whaling Museum, Sandefjord, Norway Archived 16 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine.
^ Whaling, South Georgia Heritage Trust Archived 12 December 2009 at the Wayback Machine.
^ Headland, R. K. The Island of South Georgia, Cambridge University Press, 1984. p. 238.
^ Mills, William James. Exploring polar frontiers: a historical encyclopedia, Volume 2, p. 157, 2003.
^ Lawrence Freedman (2005). The Official History of the Falklands Campaign: The origins of the Falklands war. Psychology Press. p. 76. ISBN 978-0-7146-5206-1.
^ 2008 February 10: Magnitude 6.5 – South Sandwich Islands region: USGS Archived 1 June 2008 at the Wayback Machine.
^ Earthquake Hazards Program Archived 16 September 2008 at the Wayback Machine. at U.S. Geological Survey
^ Summary of earthquake 2013-07-15 14:03:43 UTC at U.S. Geological Survey
^ Trendall, A. 1953 The Geology of South Georgia. Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey: Scientific Reports: Number 7. pdf
^ "British Antarctic Survey" (PDF). British Antarctic Survey. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 September 2012. Retrieved 10 July 2011.
^ "Extreme Temperatures Around the World- world highest lowest recorded temperatures".
^ "South Georgia official website – environment – ocean".
^ General Survey of Climatology V12, 2001, Edited by Landsberg, Elsevier publishing
^ "Climate Normals". Climatic Research Unit, UEA. July 2011. Retrieved 10 July 2011.
^ "Temp/Rain 1901–1950". Globalbioclimatics. Apr 2012. Retrieved 24 April 2012.
^ "Sunshine 1931–1960 [page 242]" (PDF). DMI.DK. Apr 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 April 2013. Retrieved 24 April 2012.
^ "Quark Fishing Ltd, R (on the application of) v Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs [2005] UKHL 57 (13 October 2005)".
^ R.K. Headland (ed.) Historical Antarctic sealing industry, Scott Polar Research Institute, University of Cambridge, 2018, p.169
ISBN 978-0-901021-26-7
^ Commonwealth Secretariat website Archived 20 August 2006 at the Wayback Machine.
^ "Healthy Surplus in South Georgia Finances, Spurred by Fishing, Tourism and Stamps". MercoPress. May 12, 2010. Retrieved January 19, 2017.
^ Whole Foods Market (2006), Welcome Back Chilean Sea Bass!, Whole Foods Market
^ Retrieved 11/5/2018.[1]
^ ab Headland, Robert (1992). The Island of South Georgia. CUP Archive. pp. 195–197. ISBN 978-0-521-42474-5.
^ "South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands". Department of Plant Sciences, University of Oxford. 2014. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
^ "Native flora – South Georgia Heritage Trust".
^ Attenborough, D. 1998. The Life of Birds. BBC Books.
ISBN 0563-38792-0
^ "South Georgia & the South Sandwich Islands". BirdLife International. 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
^ "Eradication of Rodents". South Georgia and South Sandwich Islands. Archived from the original on 3 August 2015. Retrieved 8 July 2013.
^ "Climate Change – Overview". British Antarctic Survey. Archived from the original on 8 July 2015. Retrieved 8 July 2013.
^ Hastings, Chris (7 March 2010). "South Georgia to poison millions of rats". Times Online. London.
^ Connor, Steve (8 March 2010). "Ecologists turn exterminators in the great rat hunt". The Independent. London.
^ Amos, Jonathan (4 May 2011). "'Success' in South Georgia rat eradication". BBC.
^ Hogenboom, Melissa (4 July 2013). "South Georgia rat removal hits milestone". BBC News. Retrieved 3 July 2013.
^ Cookson, Clive (3 July 2013). "Rats removed from South Georgia in biggest mass poisoning". Financial Times.
^ Sarsfield, Kate (3 December 2014), "Habitat Restoration Project gears up for final phase of airborne rodent eradication programme", Flightglobal, Reed Business Information, retrieved 4 December 2014
^ "Rats driven from South Georgia's wildlife paradise", BBC Website, 9 May 2018
^ "Rare birds return to remote South Georgia island after successful rat eradication programme", The Independent, 25 June 2015
^ Management of introduced reindeer on South Georgia Archived 16 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine., Office of the Commissioner, 19 February 2011.
^ Doyle, Alister (18 March 2013). "Hunters slay 3,500 reindeer on island near Antarctica". Reuters.
^ "Which has more biodiversity, the Galápagos or the sub-Antarctic island South Georgia? Surprise, surprise". George Wright Society. 25 May 2011. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
^ Merco Press (27 May 2011). "South Georgia marine biodiversity richer than the Galápagos Islands".
^ "The Antarctic island that's richer in biodiversity than the Galapagos". 27 May 2011.
^ Marine Protected Areas Order 2012 Archived 6 May 2012 at the Wayback Machine., South Georgia and South Sandwich Islands Gazette, 29 February 2012.
^ "SGSSI Marine Protection Area (Management Plan)" (PDF).
^ Good Planet: Denmark. Archived 12 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine. Largest protected area in the world.
^ "King Edward Point Research Station, King Edward Point, Cumberland East Bay, South Georgia".
^ Powell, Michael. HMS Protector will be Endurance replacement, The News. Portsmouth, 11 January 2011.
^ "UK purchases Arctic patrol vessel HMS Protector". IHS Jane's 360. 26 September 2013. Retrieved 2 August 2014.
^ "HMS Endurance: Former ice patrol ship to be scrapped". BBC News. 7 October 2013. Retrieved 8 October 2013.
Further reading
- Forster, George (1777). A Voyage Round the World in His Britannic Majesty's Sloop Resolution Commanded by Capt. James Cook, during the Years 1772, 3, 4 and 5 (2 vols.). London.
- Headland, R. K. (1984). The Island of South Georgia. Cambridge University Press.
ISBN 0-521-25274-1. - Wheeler, Tony (2004). The Falklands & South Georgia Island. Lonely Planet.
ISBN 978-1740596435.
External links
- Government
South Georgia government website♠
"South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands at Curlie
 Wikimedia Atlas of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
Wikimedia Atlas of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- Map of the Argentine claim over Islas Georgias del Sur y Sandwich del Sur
- Others
- South Georgia Association website
- South Georgia Heritage Trust
- Live picture from the South Georgia webcam
- Operation Paraquat
- Argentine invasion of South Georgia
- South Georgia Wiki
- Constitution of South Georgia
