Argolis
Argolis Περιφερειακή ενότητα Αργολίδας | |
|---|---|
Regional unit | |
 Municipalities of Argolis | |
 Argolis within Greece | |
| Coordinates: 37°40′N 22°50′E / 37.667°N 22.833°E / 37.667; 22.833Coordinates: 37°40′N 22°50′E / 37.667°N 22.833°E / 37.667; 22.833 | |
| Country | Greece |
| Region | Peloponnese |
| Capital | Nafplio |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,154 km2 (832 sq mi) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 97,044 |
| • Density | 45/km2 (120/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Postal codes | 21x xx |
| Area codes | 275x0 |
| ISO 3166 code | GR-11 |
| Car plates | ΑΡ |
| Website | www.argolida.gr |
Argolis or the Argolid (Greek: Αργολίδα Argolída, [arɣoˈliða]; Ἀργολίς Argolís in ancient Greek and Katharevousa) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Peloponnese, situated in the eastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula and part of the tripoint area of Argolis, Arcadia and Corinthia. Much of the territory of this region is situated in the Argolid Peninsula.
Contents
1 Geography
2 History
2.1 Modern history
3 Administration
3.1 Prefecture
3.2 Provinces
4 Transport
5 Communications
5.1 Newspapers
5.2 Radio
5.3 Television
6 See also
7 References
8 Sources
Geography
Most arable land lies in the central part of Argolis. Its primary agricultural resources are oranges and olives. Argolis has a coastline on the Saronic Gulf in the northeast and on the Argolic Gulf in the south and southeast. Notable mountains ranges are the Oligyrtos in the northwest, Lyrkeio and Ktenia in the west, and Arachnaio and Didymo in the east.
Argolis has land borders with Arcadia to the west and southwest, Corinthia to the north, and the Islands regional unit (Troezen area) to the east. Ancient Argolis included Troezen.
History

Map of ancient Argolis

Argolic Gulf

Mycenae

View of Argos

Nafplion

Ermioni
Parts of the history of the area can be found in the articles on Argos, Mycenae, Epidaurus, Nafplio, Troezen, Ermioni, Kranidi, and Tolo.
Modern history
From 1833 to 1899, Argolis was part of Argolidocorinthia, which included present Corinthia, Hydra, Spetses and Kythira. It joined Corinthia to form Argolidocorinthia again in 1909. Forty years later, in 1949, Argolis was finally separated from Corinthia.
Administration
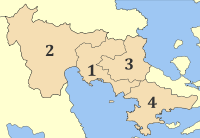
The regional unit Argolis is subdivided into 4 municipalities. These are (number as in the map in the infobox):[1]
Argos-Mykines (2)
Epidaurus (Epidavros, 3)
Ermionida (4)
Nafplio (1)
Prefecture
As a part of the 2011 Kallikratis government reform, the regional unit Argolis was created out of the former prefecture Argolis (Greek: Νομός Αργολίδας). The prefecture had the same territory as the present regional unit. At the same time, the municipalities were reorganised, according to the table below.[1]
| New municipality | Old municipalities | Seat |
|---|---|---|
| Argos-Mykines | Argos | Argos |
Achladokampos | ||
Alea | ||
Koutsopodi | ||
Lerna | ||
Lyrkeia | ||
Mykines | ||
Nea Kios | ||
Epidaurus (Epidavros) | Epidaurus | Lygourio |
Asklipieio | ||
| Ermionida | Ermioni | Kranidi |
Kranidi | ||
| Nafplio | Nafplio | Nafplio |
Asini | ||
Midea | ||
Nea Tiryntha |
Provinces
The provinces of Argolis were:
Argos Province – Argos
Ermionida Province – Kranidi
Nafplia Province – Nafplio
Transport
The area is connected by highways:
E65 (northwest)- Greek National Road 7
Greek National Road 70 (east)
Communications
Newspapers
- Argeiakon Bima – Argos
- Ta Nea tis Argolidos – Nafplio
Radio
- Argaiki Radiofonia – Argos
- Argos Radio Deejay – Argos – 96.2 FM
- Cool FM – Argos, Kefalari – 90.7 FM
- Dimotiko Radiofoniou Nafpliou – Nafplio
- Orange FM - Argos - 91.1 FM
- Radio Argolida – Nafplio – 90.2 FM
- Radio Ermionida – Ermioni
- Radio Kranidi – Kranidi
- Style 89.6 – Argos – 89.6 FM
Television
- Max TV
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Argolis. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Argolis. |
- List of settlements in Argolis
- List of traditional Greek place names
References
^ ab "Kallikratis reform law text" (PDF)..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
Sources
Jameson, Michael H.; Runnels, Curtis Neil; van Andel, Tjeerd Hendrik (1994). A Greek Countryside: The Southern Argolid from Prehistory to the Present Day. Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0-804716086.
Sutton, Susan Buck, ed. (2000). Contingent Countryside: Settlement, Economy, and Land Use in the Southern Argolid Since 1700. Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0-804733151.
