External carotid artery
| External carotid artery | |
|---|---|
 The external carotid artery arises from the common carotid artery and supplies structures in the face and neck. | |
| Details | |
| Source | common carotid artery |
| Branches | superior thyroid, lingual, facial, ascending pharyngeal, occipital, posterior auricular, maxillary, superficial temporal |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria carotis externa |
| MeSH | D002342 |
| TA | A12.2.05.001 |
| FMA | 10635 |
Anatomical terminology [edit on Wikidata] | |
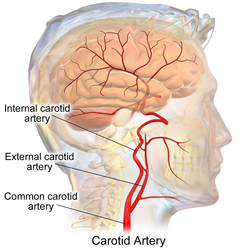
The external carotid artery is a major artery of the head and neck. It arises from the common carotid artery when it splits into the external and internal carotid artery. It supplies blood to the face and neck.[1]
Contents
1 Structure
1.1 Development
1.2 Relations
2 Function
3 Additional images
4 References
5 External links
Structure
The external carotid artery begins at the upper border of thyroid cartilage, and curves, passing forward and upward, and then inclining backward to the space behind the neck of the mandible, where it divides into the superficial temporal and maxillary artery within the parotid gland.
It rapidly diminishes in size as it travels up the neck, owing to the number and large size of its branches.
At its origin, this artery is closer to the skin and more medial than the internal carotid, and is situated within the carotid triangle.
Development
In children, the external carotid artery is somewhat smaller than the internal carotid; but in the adult, the two vessels are of nearly equal size.
Relations
The external carotid artery is covered by the skin, superficial fascia, Platysma, deep fascia, and anterior margin of the Sternocleidomastoideus; it is crossed by the hypoglossal nerve, by the lingual, ranine, common facial, and superior thyroid veins; and by the Digastricus and Stylohyoideus; higher up it passes deeply into the substance of the parotid gland, where it lies deep to the facial nerve and the junction of the temporal and internal maxillary veins.
Medial to it are the hyoid bone, the wall of the pharynx, the superior laryngeal nerve, and a portion of the parotid gland.
Lateral to it, in the lower part of its course, is the internal carotid artery.
Posterior to it, near its origin, is the superior laryngeal nerve; and higher up, it is separated from the internal carotid by the Styloglossus and Stylopharyngeus, the glossopharyngeal nerve, the pharyngeal branch of the vagus, and part of the parotid gland.
Function
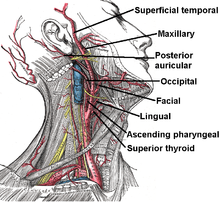
Branches of external carotid artery.
As the artery travels upwards, it supplies:
- In the carotid triangle:[2]
Superior thyroid artery, arising from its anterior aspect
Ascending pharyngeal artery - arising from medial, or deep, aspect
Lingual artery - arising from its anterior aspect
Facial artery - arise from its anterior aspect
Occipital artery - arising from its posterior aspect
Posterior auricular artery - arising from posterior aspect
The external carotid artery terminates as two branches:
- Maxillary artery
- Superficial temporal artery
Several mnemonics are commonly used to remember the main branches of the external carotid artery.
Mnemonic — Some Anatomists Like Freaking Out Poor Medical Students .
Mnemonic — Sister Lucy's Face Often Powdered Attracts Medical Students .
Additional images

Branches of external carotid artery

Magnetic Resonance Angiography
References
^ "Carotid artery". WebMD. Retrieved 28 July 2015..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Human Anatomy - Lab 25 Step 12
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to External carotid artery. |
lesson5 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
lesson4 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (infratempfossaart)- Diagram at umich.edu

