South Bohemian Region
South Bohemia Jihočeský kraj | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Region | |||
 Jindřichův Hradec castle | |||
| |||
 | |||
| Country | Czech Republic | ||
| Capital | České Budějovice | ||
| Districts | Český Krumlov District, Jindřichův Hradec District, Písek District, Prachatice District, Strakonice District, Tábor District | ||
| Government | |||
| • Governor | Ivana Stráská (ČSSD) | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 10,056.79 km2 (3,882.95 sq mi) | ||
| Highest elevation | 1,378 m (4,521 ft) | ||
| Population (09/2013) | |||
| • Total | 636,459 | ||
| • Density | 63/km2 (160/sq mi) | ||
| ISO 3166 code | CZ-JC | ||
| Vehicle registration | C | ||
| Website | http://www.kraj-jihocesky.cz/ | ||
South Bohemia (Czech: Jihočeský kraj, German: Südböhmische Region) is an administrative unit (kraj) of the Czech Republic, located mostly in the southern part of its historical land of Bohemia, with a small part in southwestern Moravia. The western part of the South Bohemian Region is former Prachens (Prácheňsko), a huge archaic region with distinctive features with its capital, Písek. In 2011, there were 623 municipalities in the region, whereof 54 had a status of town.
The region borders (from the west clockwise) the regions Plzeň, Central Bohemia, Vysocina and South Moravia. To the south it borders Austria and Germany. Until 30 May 2001, the region was named as Budějovický kraj or Českobudějovický kraj, after its capital, České Budějovice.
Due to its geographical location and natural surroundings the region belongs the first settlements appeared in the distant past. Over the past centuries, the South Bohemian region has been famous for fishpond cultivation and forestry. The region has been industrialized since the beginning of the twentieth century. Nowadays, it is an attractive destination due to its natural and historical richness and the fastest growing industry has been the travel industry.[1]
Contents
1 Administrative divisions
2 Population and area
3 Geography
4 Climate
5 Economy
6 Architecture
7 Photo gallery
8 External links
9 References
Administrative divisions
The South Bohemian Region was established with constitutional lax No. 347/97 of Collections concerning the formation of higher territorial administrative units. The region and its authorities are specified by Act No. 129-2000 of Collections concerning regions, which came into effect on the day of the regional authorities elections, January 1, 2001.[2]
The region is divided into 7 districts:
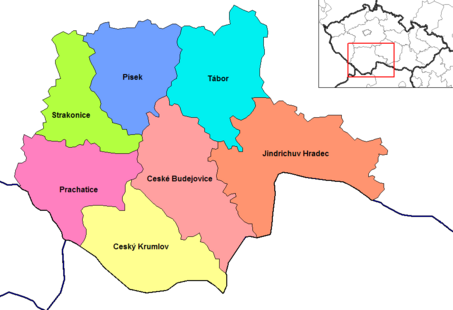 | |||||||||||||||||
Districts of South Bohemia Region
| |||||||||||||||||
Population and area
The total area of the region is 10,056 km² which is 12.8% of the total area of the Czech Republic. As of September 2013, South Bohemia's population is 636,459 and with only 63 people per 1 km² the region has the lowest population density in the whole country.
64.2% of region’s population lives in towns or cities. One third of the inhabitants live in the five largest municipalities. Only 4% of region’s population lives in municipalities with less than 200 inhabitants.
In 2011, the average age in the region is 41.2 years. Approximately 11% of inhabitants who were 15 years or older had a university degree (in 2001 this was 8%). According to 2011 census, 20.6% of inhabitants in the region believe in God (however, almost half of the people did not answer this question). The table below gives an overview of town and cities in the region that have more than 8,000 inhabitants.
| Name | Population[3] | Area (km²) | District |
|---|---|---|---|
| 93,285 | 56 | České Budějovice District | |
| 34,716 | 62 | Tábor District | |
| 29,824 | 63 | Písek District | |
| 23,020 | 35 | Strakonice District | |
| 21,569 | 74 | Jindřichův Hradec District | |
| 13,193 | 22 | Český Krumlov District | |
| 11,139 | 39 | Prachatice District | |
| 8,649 | 42 | Písek District | |
| 8,391 | 98 | Jindřichův Hradec District | |
| 8,053 | 43 | České Budějovice District |
Other significant towns are: Vimperk, Dačice, Kaplice, Soběslav, Sezimovo Ústí, Vodňany, Blatná, Veselí nad Lužnicí, Bechyně and Protivín. The following table provides more details on the districts of the South Bohemia:
| District | Population | Area | Pop. Dens. | No.of Settlements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
České Budějovice (CB) | 184,531 | 1,638.30 | 113 | 109 |
Český Krumlov (CK) | 61,346 | 1,615.03 | 38 | 45 |
Jindřichův Hradec (JH) | 92,719 | 1,943.69 | 48 | 106 |
Písek (PI) | 70,290 | 1,126.84 | 62 | 75 |
Prachatice (PT) | 51,461 | 1,375.03 | 37 | 65 |
Strakonice (ST) | 70,823 | 1,032.10 | 69 | 112 |
Tábor (TA) | 102,580 | 1,326.01 | 77 | 110 |
Geography

Plešné jezero (Plešné Lake)
South Bohemia consists of the South Bohemian Basin, České Budějovice Basin and Třeboň Basin. The Bohemian Forest (Czech: Šumava) is a low range of mountains situated in the south-west. Other highlands that can be found in the region are the Brdy Highlands (in the very northern part of the region), the Central-Bohemian Highlands (Czech: Středočeská vrchovina, in the northern part of the region), the Bohemian-Moravian Highlands (Czech: Českomoravská vrchovina, eastern part of the region) and the Novohradské Mountains (in the south of the region). The highest elevation in the region is the 1,378-metre (4,521 ft) high Plechý in the Bohemian Forest, the lowest elevation with 350 metres above sea level is at the Orlík Dam.
The region is located in the drainage basin of Vltava river. Other significant rivers are Malše, Lužnice, Otava, Nežárka and Lomnice. South Bohemia is famous for its countless ponds. In the past, more than seven thousand ponds were established across the region. With its 489 ha Rožmberk is the largest one, followed by Bezdrev (450 ha) and Horusice pond (415 ha). In the 20th century, a series of dams was constructed on Vltava river. Lipno Dam is the largest dam in the Czech Republic and has area of 4,870ha. Other dams in the region are Orlík Dam, Římov Dam and Hněvkovice Dam.[4]
A big part of the Šumava National Park is situated in South Bohemia. The Bohemian Forest is a popular holiday destination because it is excellent hiking country. Most interesting natural and cultural sights are connected with more than 500 km of summer marked trails and many bike trails.
Climate
The climate in South Bohemia is of a transitional Central European type. It is affected alternatively by an oceanic influence from the west, and a continental influence from the east. Therefore, the weather can be variable. Most of the South Bohemian region belongs to the mild, warm and wet zone and at altitudes above 750 m this passes to mild and cool. The warmest month is usually July, with temperatures averaging between 17 and 18 °C in valley areas. In higher localities (over 900 m) the temperatures can drop below 14 °C. Days with temperatures above 25 °C are most frequently in valley-basins, and the area around the confluence of the rivers Lužnice and Vltava (Moldau): on average there are 40-50 such days a year.[5]
Economy

500ml bottle of Budweiser Budvar, as marketed in the UK
In 2010, the region produced 5% of the national GDP. The GDP per capita is 84% of the national average, which is the 8th highest among all regions. In 2011, the business sector in the South Bohemian Region comprises 159,000 entities, 114,000 of which were sole traders. There are more than 300 thousand people employed in the region, whereof 31% in industry, 13% in trade and 10% in construction sector. The average salary in the region in September 2013 was CZK 21,768 (approximately EUR 850). The unemployment rate in September 2013 was 6.05%.
The Region does not rank among key industrial areas of the Czech Republic. The industrial production is concentrated particularly in the area of České Budějovice and in Tábor District and Strakonice District. Food and drink processing industries plays a significant role in the region. Other important sectors are the automotive industry, production of machinery and appliances, and also the textile and clothing industries. Recently, the travel industry has become an important sector in the region.
The Czech Academy of Sciences, whose institutes operate all over the region, provides a good base for the development of science. These institutes focus mostly on biology and ecology. Scientific work is also part of the activities of the University of South Bohemia (Czech: Jihočeská univerzita) with its headquarters in České Budějovice and Jindřichův Hradec.
Approximately 11% of the national agricultural production is produced in the South Bohemian Region. The agricultural sector focuses on plant production, mostly on growing cereals, oil plants and potatoes. In animal husbandry, the breeding of cattle and pigs prevails. Fishpond cultivation has a long tradition in South Bohemia. Fish husbandry in the total area of 25 000 ha makes up about 50% of the total national production.[6]
Architecture

Rustic baroque in Holašovice
The region is famous for its small villages with a pond in the middle. These are generally built in the style of the Rustic Baroque, also known as South Bohemian Baroque:
"Rustic Baroque is a term for the unique architecture of South Bohemia. The local folk bricklayer masters Martin Paták and František Šoch created a new type of South Bohemian farmhouse with an ornate frontispiece in the middle of the 19th century. A typical building of this style is a massive rustic farmhouse with two richly decorated frontispieces, which are joined by an arched gate with small doors. The marshland frontispieces are beautifully decorated, they have lavish contours, the surface is usually divided by allusive decorative columns, completed by arches, stylised hearts, four-leafed clovers, meadow flowers."
Photo gallery
Chauteau in Bechyně

Přemysl Otakar II Square in České Budějovice
Castle in Český Krumlov
Chalupská slať near Borová Lada (Šumava)

Dačice

Monument of Jan Hus in town of Husinec

Holy Trinity´s sculpture in Jindřichův Hradec
The Lipno nad Vltavou dam

Buquoy tomb in the town of Nové Hrady

Jewish cemetery in Milevsko

Velké Square in Písek
Prachatice

Historical view at Prachatice (around 1900)
Rožmberk nad Vltavou
Strakonice pedestrian bridge

Memorial of Jan Žižka in Žižka Square in Tábor
Sculptural group on square and town hall in Volyně
External links
(in Czech) Official website
(in English) (in Czech) Tourist Information System Of South Bohemia
(in English) Bohemian Forest
- Region Statistics
(in English) [permanent dead link] Rustic Barocco
(in English) Photo gallery made by a UNESCO photographer
References
^ Characteristics of the South Bohemian Region; Available at: http://www.kraj-jihocesky.cz/foreign/eng/region.php
^ Welcome to South Bohemian Region's websites Archived 14 August 2016 at the Wayback Machine (English)
^ Data as of 1 January 2015 from the Czech Statistical Office[permanent dead link]
^ Characteristics of the South Bohemian Region; Available at: http://www.kraj-jihocesky.cz/foreign/eng/region.php Archived 17 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine
^ Climate; Available at: "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 19 April 2015. Retrieved 8 October 2013.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link).mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Population, Economy; Available at: http://www.kraj-jihocesky.cz/foreign/eng/more2.php Archived 1 June 2012 at the Wayback Machine
Coordinates: 49°05′N 14°40′E / 49.083°N 14.667°E / 49.083; 14.667


















