Battle of the Ebro
The Battle of the Ebro (Spanish: Batalla del Ebro, Catalan: Batalla de l'Ebre) was the longest and largest battle of the Spanish Civil War. It took place between July and November 1938, with fighting mainly concentrated in two areas on the lower course of the Ebro River, the Terra Alta comarca of Catalonia, and the Auts area close to Fayón (Faió) in the lower Matarranya, Eastern Lower Aragon. These sparsely populated areas saw the largest array of armies in the war. The results of the battle were disastrous for the Second Spanish Republic, with tens of thousands of dead and wounded and little effect on the advance of the Nationalists.
Contents
1 Background
2 Opposing armies
2.1 Loyalist Army
2.1.1 15th Army Corps
2.1.2 5th Army Corps
2.1.3 12th Army Corps
2.1.4 18th Army Corps
2.2 Spanish Nationalist Army
2.2.1 Army of the North
2.2.2 Morocco Army Corps
2.2.3 Maestrazgo Army Corps
3 Battle
3.1 Republican assault
3.2 The Gandesa siege
3.3 Battle of attrition
3.4 Nationalist counteroffensive
4 Aftermath
5 See also
6 Notes
7 Bibliography
8 External links
Background
@media all and (max-width:720px){.mw-parser-output .mobile-float-reset{float:none!important;width:100%!important}}.mw-parser-output .stack-container{box-sizing:border-box}.mw-parser-output .stack-clear-left{float:left;clear:left}.mw-parser-output .stack-clear-right{float:right;clear:right}.mw-parser-output .stack-left{float:left}.mw-parser-output .stack-right{float:right}.mw-parser-output .stack-object{margin:1px;overflow:hidden}

Map of Spain six months before the Battle of the Ebro (Republican territory in red, Nationalist territory in blue)
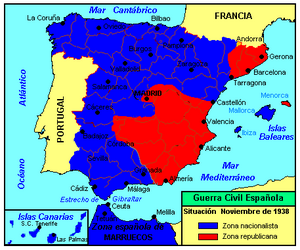
Map of Spain in November 1938, after the end of the Battle of the Ebro and immediately before the Catalonia Offensive

The Auts, low, scruffy hills south of Mequinensa where a whole Republican division was captured and slaughtered
By 1938, the Second Spanish Republic was in dire straits. The Republican Northern zone had fallen,[9] and in the winter of 1937/38 the Republican Popular Army had spent its forces in the Battle of Teruel, a series of bloody combats in subzero temperatures around the city of Teruel, which ended up being retaken by the Francoist army in February.[10]
Then, the Nationalists launched an offensive in Aragon in March without giving their enemies a chance to recover. Fighting in the middle of bitter winter temperatures, the exhausted Republican army could offer only feeble resistance. By April 15, Franco's troops reached the Mediterranean Sea at Vinaròs, cutting Republican territory in two. As a result, the Nationalist army conquered Lleida and the hydroelectric dams that provided much of the Catalan industrial areas with electricity.[11]
Nevertheless, on 17 March 1938, after the Anschluss, the French government decided to reopen the frontier.[12] The Republican Army in Catalonia received 18,000 tons of war material between March and mid-June and twelve new divisions were formed from Nationalist prisoners-of-war and an extended call-up, which included conscripts that ranged in age from sixteen years old, the so-called Quinta del Biberón (the baby-bottle call-up), to middle-aged fathers. A new army, the Ebro's army, was then formed.[13]
Meanwhile, the Francoist armies attacked the XYZ Line north of Valencia with the intention of capturing the Republican capital, instead of advancing towards Barcelona, fearing that France would enter the war in support of the ailing Republic.[14] In response to the situation, Spanish premier Juan Negrín approved a plan by General Vicente Rojo Lluch to launch attacks against the main Francoist forces advancing towards Valencia. The purpose of the attacks was to relieve the pressure on Valencia and Catalonia, as well as to show European governments that the Republican government was still viable.[15]
Opposing armies
Loyalist Army
In order to distract the Nationalist armies that were advancing towards Valencia, the Popular Republican Army decided upon an offensive in the lower Ebro basin. The size of the army was important but it lacked enough air and artillery support. The Ebro Army was formed on May 15 under Lieutenant Colonel Juan Modesto, merging the 15th and the 5th Army Corps. It would receive reinforcements from the 12th and 18th Army Corps as soon as the battle began.[1]
15th Army Corps
The 15th Army Corps XV Cuerpo del Ejército was led by Manuel Tagüeña[16] from Escaladei and was formed by the following divisions:
35th International Division led by Commander Pedro Mateo Merino, including the XI, XIII and XV International Brigades.[17]
3rd Division, led by Commander Esteban Cabezos Morente, including the 31st, 33rd and 60th mixed brigades.[17]
42nd Division, under Commander Manuel Alvarez, including the 226th, 227th and 59th brigades.- In mid-July the 15th Army Corps was reinforced by the 16th Popular Republican Army Division of the 12th Army Corps, the 3rd Cavalry Regiment, anti-aircraft guns, armoured vehicles and army engineers.
5th Army Corps
The 5th Army Corps V Cuerpo del Ejército Popular, led by Lieutenant Colonel Enrique Líster,[16] with base in Salou:
11th Division led by Commander Joaquim Rodríguez, including the 1st, 9th and 100th mixed brigades.[18]
46th Division led by Commander Valentín González "El Campesino", including the 10th, 60th and 101st mixed brigades.[18]
45th Division, international division led by Lieutenant Colonel Hans Kahle, including the 12th "Garibaldi", 14th "Marsellesa" and 139th mixed brigades.[18]
12th Army Corps
The 12th Army Corps led by Lieutenant Colonel Etelvino Vega,[1] was based at Bisbal de Falset:
16th Division led by Commander Manuel Mora Torres, including the 23rd and 24th mixed brigades.
44th Division led by Ramón Pastor, including the 140th, 144th and 145th mixed brigades.
18th Army Corps
The 18th Army Corps, led by Lieutenant Colonel José del Barrio acted as tactical reserve of the two first ones:[19]
27th Division, led by Marcelino Usatorre including the 122nd (with its 1st Battalion, "la Bruixa", 123rd and 124th mixed brigades.
60th Division led by Commander Manuel Ferràndiz, including the 95th, 84th and 224th mixed brigades.
43a División, led by Lieutenant Colonel Antonio Beltrán Casaña "l'Esquinazau", including the 72nd, 102nd and 130th mixed brigades.[20]
Spanish Nationalist Army
The Morocco Army Corps was positioned on the right bank of the Ebro. Later, the Maestrazgo Army Corps was sent as reinforcements, led by General Rafael García Valiño.[citation needed]
Army of the North
General Fidel Davila[citation needed]
Morocco Army Corps
The Morocco Army Corps Cuerpo del Ejército de Marruecos led by General Juan Yagüe:[3]
- 40a División
50a División, led by Colonel Campos.[3]
- 105a División
Except for the 50a División, made up of relatively inexperienced soldiers, all other divisions were battle-hardened Legionarios, Regulares, African mercenaries from Ifni and Western Sahara, as well as Carlist and Falangist militias.[citation needed]
Maestrazgo Army Corps
The Maestrazgo Army Corps Cuerpo del Ejército del Maestrazgo was led by General Rafael García Valiño.[21][22]
1a División de Navarra, led by Mohammed el Mizzian.[23]
74a División la Leona, led by Coronel Arias.[23]
84a División. led by Coronel Galera.[23]
13a División, led by Fernando Barron.
Battle
Republican assault
The Republican Army spent a week preparing to cross the Ebro. The commandos of the XIV Corps slipped across the river in order to obtain information about the Nationalist positions and the Republican troops rehearsed the crossing in ravines, and rivers on the coast. The Nationalist intelligence assets passed back reports to the Nationalist High Command, detailing troop movements and the concentration of the International Brigades, as well as the presence of rafts and pontoon bridges on the other side of the river, but Franco thought that the Republican Army would not be ready to undertake an offensive across the Ebro.[24]
For the crossing, the Republicans chose the bend of the Ebro River between Fayon and Benifallet, an area held by the 50th Division of the Nationalist Army.[25] The Republican army started the crossing on the night of 24–25 July during a no moon period.[26] Republican commandos crossed the river, killed the Nationalist guards and fastened lines for the assault boats, then the first Republican troops crossed in ninety boats (each of which carried ten men). The remaining troops of the V and XV Corps crossed the next day, using three pontoon bridges and another 12. The surprise was total and Republican forces were initially successful. Nevertheless, a secondary assault near Amposta, carried out by the XIV International Brigade, failed after 18 hours of combat, and the XIV International Brigade retreated, after suffering huge losses.[27]
During the first day, Republican troops surrounded the troops of the Colonel Campos’s 50th Division, taking 4,000 prisoners, and many other Nationalist soldiers deserted. By the evening, Tagueña had advanced three miles in the north and Lister twenty one in the center.[28] By 26 July, the Republican troops had occupied 800 square kilometres and reached the outskirts of Gandesa; nevertheless the Nationalists deployed Barron’s 13th Division in the town and the Republican troops failed to occupy it.[29]
Then, Franco decided to send heavy reinforcements to the Ebro’s front (eight divisions, more than 140 bombers and 100 fighters) and passed the order for the dams at Tremp and Camarasa to be opened. The flood water destroyed the pontoon bridges, although the Republican engineers managed to repair them within two days. Furthermore, the Condor Legion and the Aviazione Legionaria started to bomb and destroy the pontoon bridges each day, although the Republican engineers managed to repair them each night. Because of this, only 22 tanks and a handful of artillery managed to cross the Ebro River, and Republican troops began running low on supplies, ammunition and drinking water.[30]

Positions of the Republican and nationalist armies before the battle (Nationalists in blue, Republicans in red)
The Gandesa siege
The key target for the Republicans was the town of Gandesa, some 25 km west of the Ebro, a crossroads to Catalonia and the north-south roads running parallel to the Ebro. The terrain around the town was extremely hilly, being dominated by the Cavalls, Pandols and Fatarella mountain ranges whose hard and bold limestone rocks and scant forest cover provided little shelter against Francoist fire.
On 27 July, Modesto ordered an attack on Gandesa with T-26 tanks and on 30 July decided to concentrate his tanks and artillery around Gandesa and launched an infantry assault against the city. On 1 August, the XV International Brigade launched a fierce attack against Hill 481 in front of Gandesa, suffering huge casualties; nevertheless, the Republican assault had failed due the Nationalist air and artillery superiority and Modesto ordered the Army of the Ebro to go on the defensive.[31]
Battle of attrition
After the end of the Republican offensive, the Republican army of the Ebro was trapped in a pocket with its back to a river[32] and Nationalist officers wanted to attack across the unprotected Segre River and advance to Barcelona, but Franco wanted to destroy the Republican Army of the Ebro and to recover the lost territory. The Nationalists concentrated most of their artillery and air forces in the Ebro's Front. On the other hand, the Republican high command ordered their troops to resist and not to retreat. Officers and men were executed for retreating.[33]
The battle was fought by both sides as a World War I Western Front style battle, with each side launching bloody frontal assaults on enemy positions in what became a war of attrition. The Nationalist tactic was to use artillery and aerial bombardment in small areas to soften resistance and then to launch a frontal assault with one or two infantry battalions to occupy the area.[34][35] Each day 500 cannons fired more than 13,000 rounds at the Republican troops and more than 200 Nationalist aircraft dropped 10,000 pounds of bombs.[36] Nevertheless, the Republican troops fought with stubborn bravery[37] and repelled the Nationalist assaults with barrages of machine-gun and mortar fire.[38] In many zones, the terrain was too hard to dig trenches or foxholes, and as the August heat became unbearable (on 4 August it was 37 degrees in the shade), the shortages of water and food grew worse for the Republican troops.[39] The situation was made more desperate by the relentless bombing that the Republican troops endured from dawn to dusk, which made it impossible for bodies to be buried, and meant that the wounded could only be evacuated at night, by small boats.[40]
The key to the battle was Nationalist air superiority, provided by the Italian Aviazione Legionaria and German Condor Legion squadrons that flew under the Aviación Nacional markings. Some 500 first class planes were available on the Nationalist side (Savoia 79, Savoia SM-81, Breda 20, Heinkel 111, Dornier 20, Junker 52 and 6 Ju 87 bombers,[39] and Bf 109 and CR-42 fighters)[41] against only some 35 modern fighters and some 40 second class aircraft of the Spanish Republican Air Force. In July, the Legion Condor had destroyed 76 Republican planes and by August the Republican Air Force had lost air superiority in the area. The Republican planes were outnumbered by at least two to one, and most of the experienced Soviet pilots had been withdrawn. Republican anti-aircraft defenses proved to be inadequate and many planes were destroyed on ground.[36] The Nationalists used their bombers to cut the pontoon bridges on the Ebro, and as a flying artillery to smash the Republican positions in the sierras, and to destroy their supply lines: "Republican communications were bombed to oblivion and, as so many international brigader memoirs testify, their troops were blasted off the bare and rocky hillsides by the sheer force of the incendiary materiel launched."[42]
Nationalist counteroffensive

Ebro's battlefield. In pink maximum republican advance.
The Nationalist forces launched six counter-offensives in order to retake the territory seized by the Republicans. The first counteroffensive was launched on 6 August against the northern republican held pocket between Mequinenza and Fayón. The Legion Condor dropped 50 tons of bombs and by the 10 August the Republican troops were forced back across the river.[37] The Republicans had lost 900 men and 200 machine-guns.[36] On 11 August the Nationalists led by Camilo Alonso Vega launched an attack against the Pandols Range held by the Lister's 11th Division.[37] By 14 August the Nationalists had occupied the high point of Santa Magdalena, but the Republicans held the Sierra.[36] On 18 August the Nationalists opened again the dams on the Segre River, destroying the pontoon bridges at the Ebro and on 19 August General Juan Yagüe with six divisions and supported by the Legion Condor advanced from Villalba del Arcs and captured the heights of Gaeta after five days of fierce fighting.[41] The slow advance of the Nationalists infuriated Mussolini: "Today 29 August, I predict the defeat of Franco. That man does not know to make war or doesn't want to".[43]
Then Franco decided to send Garcia Valiño's Maestrazgo Corps to the front and on 31 August the Nationalists launched an attack against the Cavalls Range in order to advance towards Corbera. The mountain range was held by the 35th, 11th and the 43rd Republican divisions, and the Nationalists attacked with eight divisions, 300 guns, 500 aircraft and 100 tanks. On 3 September the Nationalists launched a new attack from Gandesa supported by German 88 mm guns and by 4 September the Nationalists had occupied Corbera. Then Yagüe's forces broke the Republican lines, but Modesto sealed the breach with the 35th Division and ordered their troops to hold on: "Not a single position must be lost. If the enemy takes one, there must be a rapid counterattack and as much fighting as necessary, but always making sure that it remains in republican hands. Not a metre of ground to the enemy!"[44] After six weeks of combat the Nationalists had recovered 120 square miles.[36] On the other hand, on 21 September the Republican prime minister, Juan Negrin, announced the unconditional withdrawal of the International Brigades.[45]

Republican antiaircraft artillery in the Battle of the Ebro.
On 2 October the Nationalists occupied the heights of Lavall and two weeks later Point 666, the key of the Pandols Range.[46] On 30 October the troops of the Garcia Valiño's Army Corps of the Maestrazgo, led by Mohammed el Mizzian, attacked the heights of the Cavalls Range, supported by 175 guns and 100 aircraft. The Republicans lost the heights after one day of combat, suffering huge casualties (1,000 prisoners and 500 dead), despite the support of 100 fighters. On 2 November the Nationalists occupied the Pandols Range and on 3 November the right flank of the Nationalist forces reached the river Ebro. On 7 November Móra la Nova fell and by 10 November the Nationalists had occupied Mount Picossa.[47] On 16 November the last men of the 35th recrossed the Ebro at Flix and the battle ended.[41]
Aftermath

Monument to those who died in the battle located on Hill 705, on the Pandols Range.
The Nationalist superiority in manpower and equipment meant they were better able to withstand the losses and exhaust the Republicans. The Ebro saw the Republican army destroyed as an effective force while the Republican air force was no longer capable of offering further resistance.[48][49]
Both sides had suffered huge losses, with estimates ranging from 50,000–60,000[48] to 110,000 casualties,[50] as well as the loss of large numbers of aircraft (the Republicans between 130 and 150).[48] The Nationalists had lost most of their best officers and most of their tanks and lorries needed repairs or spare parts,[51] and the Republican army had lost most of their weapons and experienced units.[52] Nevertheless, after Franco signed a new mining law making huge concessions to the German government,[53] Germany sent new weapons to the Nationalist forces and in December, Franco launched an offensive against Catalonia.[54]
Antony Beevor has argued that Negrín's "active war policy", attacking rather than adopting strong defences and hoping for a wider European conflict or harrying the Nationalist forces, was driven primarily by the PCE's desire for propaganda victories, and, at the Ebro, destroyed the Republican army for no great purpose.[55] The Republicans were unable to accomplish any of their strategic objectives and, according to Beevor, were unwilling to apply the theory of the deep operation to their attacks—meaning their forces spent a long time clearing Nationalist secondary defensive positions, allowing the highly mechanised Nationalist forces to quickly deploy in strong defensive positions.[39]
Nevertheless, Paul Preston and Helen Graham said that the Republicans, by launching the Battle of the Ebro, stopped the Nationalist assault on Valencia, inflicted huge losses on the Nationalist army and prolonged the war several months. However the Munich Agreement removed any hope of aid from the Western democracies and turned the political victory into a resounding military defeat.[56][57]
A well-known Republican song, ¡Ay Carmela!, commemorates the battle.
See also
- Hill 705
- Si me quieres escribir
Notes
^ abcde Thomas, Hugh. The Spanish Civil War. Penguin Books. 2001. London. p.813
^ ab Beevor, Antony. The Battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War 1936–1939. Penguin Books. London. 2006. p.350
^ abc Thomas, Hugh. The Spanish Civil War. Penguin Books. 2001. London. p.816
^ abcd Beevor, Antony. The battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War 1936–1939. Penguin Books. London. 2006. p.357
^ Beevor, Antony. The battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War 1936–1939. Penguin Books. London. 2006. p.358
^ ab Thomas, Hugh. The Spanish Civil War. Penguin Books. 2001. London. p.833
^ ab Jackson, Gabriel. The Spanish Republic and the Civil War, 1931–1939. Princeton University Press. Princeton. 1967. p. 528
^ ab Preston, Paul. The Spanish Civil War. Reaction, Revolution & Revenge. Harper Perennial. London. 2006. p.291
^ Thomas, Hugh. (2001). The Spanish Civil War. Penguin Books. London. p.712
^ Beevor, Antony. (2006). The Battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War, 1936–1939. Penguin Books. London. pp.321–322
^ Thomas, Hugh. (2001). The Spanish Civil War. Penguin Books. London. p.781
^ Thomas, Hugh. (2001). The Spanish Civil War. Penguin Books. London. pp.782–783
^ Beevor, Antony. (2006). The Battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War, 1936–1939. Penguin Books. London. pp.359–350
^ Hugh Thomas, The Spanish Civil War (2001), pages 780–781
^ Graham, Helen. (2005). The Spanish Civil War. A Very Short Introduction. Oxford University Press. p.109
^ ab Beevor, Antony. (2006). The Battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War, 1936–1939. Penguin Books. London. p. 350.
^ ab Henry, Chris. (1999). The Ebro, 1938: Death Knell of the Republic. Osprey Publishing. p.22
^ abc Henry, Chris. (1999). The Ebro, 1938: Death Knell of the Republic. Osprey Publishing. p.21
^ Thomas, Hugh. (2001). The Spanish Civil War. Penguin Books. London. p. 812
^ Beevor, Antony. (2006). The Battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War, 1936–1939. Penguin Books. London. p. 357
^ Thomas, Hugh. The Spanish Civil War. Penguin Books. 2001. London. p.821
^ (in Spanish) Requetes.com Rafael García Valiño
^ abc Henry, Chris. (1999). The Ebro, 1938: Death Knell of the Republic. Osprey Publishing. p.18
^ Beevor, Antony. (2006). The Battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War, 1936–1939. Penguin Books. London. p. 350
^ Jackson, Gabriel. (1965). The Spanish Republic and the Civil War, 1931–1939. Priceton University Press. Princeton. p. 454
^ Thomas, Hugh. (2001). The Spanish Civil War. Penguin Books. London. p. 816
^ Preston, Paul. (2006). The Spanish Civil War. Reaction, Revolution & Revenge. Harper Perennial. London. p. 289
^ Thomas, Hugh. (2001). The Spanish Civil War. Penguin Books. London. p. 817
^ Beevor, Antony. (2006). The Battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War, 1936–1939. Penguin Books. London. p. 352.
^ Beevor, Antony. (2006). The Battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War, 1936–1939. Penguin Books. London. pp. 352–353
^ Beevor, Antony. (2006). The Battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War, 1936–1939. Penguin Books. London. p. 354
^ Jackson, Gabriel. (1965). The Spanish Republic and the Civil War, 1931–1939. Princeton University Press. Princeton. p.457
^ Thomas, Hugh. (2001). The Spanish Civil War. Penguin Books. London. p.820
^ Thomas, Hugh. (2001). The Spanish Civil War. Penguin Books. London. p.820
^ Preston, Paul. (2006). The Spanish Civil War. Reaction, revolution & revenge. Harper Perennial. London. p.291
^ abcde Thomas, Hugh. (2001). The Spanish Civil War. Penguin Books. London. p.821
^ abc Beevor, Antony. (2006). The Battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War, 1936–1939. Penguin Books. London. p.355
^ Jackson, Gabriel. The Spanish Republic and the Civil War, 1931–1939. Princeton University Press. Princeton. 1967. p. 458
^ abc Beevor, Antony. (2006). The Battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War, 1936–1939. Penguin Books. London. p.354
^ Jackson, Gabriel. (1965). The Spanish Republic and the Civil War, 1931–1939. Princeton University Press. Princeton. p.456
^ abc Beevor, Antony. (2006). The Battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War, 1936–1939. Penguin Books. London. p.356
^ Graham, Helen. (2005). The Spanish Civil War. A Very Short Introduction. Oxford University Press. pp.109–110
^ Beevor, Antony. (2006). The Battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War, 1936–1939. Penguin Books. London. p.357
^ Beevor, Antony. (2006). The Battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War, 1936–1939. Penguin Books. London. pp.357–358
^ Beevor, Antony. (2006). The Battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War, 1936–1939. Penguin Books. London. p.362
^ Beevor, Antony. (2006). The Battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War, 1936–1939. Penguin Books. London. pp.358
^ Thomas, Hugh. (2001). The Spanish Civil War. Penguin Books. London. p.832
^ abc Thomas, Hugh. (2001). The Spanish Civil War. Penguin Books. London. p.833
^ Preston, Paul. (2006). The Spanish Civil War. Reaction, revolution & revenge. Harper Perennial. London. pp.291–292
^ Preston, Paul. (2006). The Spanish Civil War. Reaction, revolution & revenge. Harper Perennial. London. p.290
^ Jackson, Gabriel. (1965). The Spanish Republic and the Civil War, 1931–1939. Princeton University Press. Princeton. p.461
^ Preston, Paul. The Spanish Civil War. Reaction, Revolution & Revenge. Harper Perennial. London. 2006. p. 292
^ Thomas, Hugh. (2001). The Spanish Civil War. Penguin Books. London. p.807
^ Beevor, Antony. (2006). The Battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War 1936–1939. Penguin Books. p. 374
^ Antony Beevor (2006) [1982]. The Battle for Spain. Orion. ISBN 978-0-7538-2165-7..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Preston, Paul. (2006). The Spanish Civil War. Reaction, revolution & revenge. Harper Perennial. London. p.292
^ Graham, Helen. (2005). The Spanish Civil War. A Very Short Introduction. Oxford University Press. p.110
Bibliography
- Beevor, Antony. (2006). The Battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil war, 1936–1939. Penguin Books. London.
ISBN 978-0-14-303765-1. - Henry, Chris. (1999). The Ebro 1938: Death Knell of the Republic. Osprey Campaign Series #60. Osprey Publishing. Consultant Editor: David G. Chandler.
ISBN 1-85532-738-4
- Jackson, Gabriel. (1967) The Spanish Republic and the Civil War, 1931–1939. Princeton University Press. Princeton.
ISBN 978-0-691-00757-1. - Preston, Paul. (2006). The Spanish Civil War. Reaction, Revolution & Revenge. Harper Perennial. London.
ISBN 978-0-00-723207-9.
ISBN 0-00-723207-1. - Ranzato, Gabrielle. The Spanish Civil War
- Thomas, Hugh. (2001). The Spanish Civil War. Penguin Books. London.
ISBN 978-0-14-101161-5.
External links
- Spartacus Educational — Battle of the Ebro
- Maps of the Civil War in Catalonia
Coordinates: 41°09′50″N 0°28′30″E / 41.16389°N 0.47500°E / 41.16389; 0.47500
