Duchy of Nassau
Duchy of Nassau Herzogtum Nassau (de) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1806–1866 | |||||||||||||
 Flag  Coat of arms | |||||||||||||
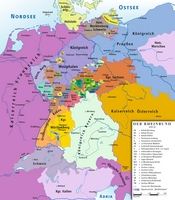
 The Duchy of Nassau in 1815. | |||||||||||||
| Status | State of the Confederation of the Rhine (1806–1813) State of the German Confederation (1815–1866) | ||||||||||||
| Capital | Weilburg (1806–1816) Wiesbaden (1816–1866) | ||||||||||||
| Common languages | Moselle Franconian | ||||||||||||
| Government | Constitutional monarchy | ||||||||||||
| Duke of Nassau | |||||||||||||
• 1806–1816 | Frederick Augustus | ||||||||||||
• 1816–1839 | William | ||||||||||||
• 1839–1866 | Adolph | ||||||||||||
| Historical era | Modern era | ||||||||||||
• Established | 30 August 1806 | ||||||||||||
• Annexed by Prussia | 23 August 1866 | ||||||||||||
| Currency | Kronenthaler | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
The Duchy of Nassau (German: Herzogtum Nassau) was an independent state between 1806 and 1866, located in what is now the German states of Rhineland-Palatinate and Hesse. It was a member of the Confederation of the Rhine and later of the German Confederation. Its ruling dynasty, now extinct, was the House of Nassau. The duchy was named for its historical core city, Nassau, although Wiesbaden rather than Nassau was its capital. In 1865, the Duchy of Nassau had 465,636 inhabitants. After being occupied and annexed into the Kingdom of Prussia in 1866 following the Austro-Prussian War, it was incorporated into the Province of Hesse-Nassau. The area today is a geographical and historical region, Nassau, and Nassau is also the name of the Nassau Nature Park within the borders of the former duchy.
Today, the Grand Duke of Luxembourg still uses "Duke of Nassau" as his secondary title (of pretense), and "Prince" or "Princess of Nassau" is used as a title of pretense by other members of the grand ducal family. Nassau is also part of the name of the Dutch royal family, which styles itself Orange-Nassau.
History

The ancestral and core coat of arms of Nassau, which formed the heart shield of the greater coat of arms. It is almost identical to the coat of arms of the Netherlands and is also included as the third and fourth field in the coat of arms of the Grand Duke of Luxembourg.
On 17 July 1806, the remaining counties of Nassau-Usingen and Nassau-Weilburg joined the Confederation of the Rhine. Under pressure from Napoleon I both counties merged to form the Duchy of Nassau on 30 August 1806, under the joint rule of Frederick Augustus, and his younger cousin Frederick William. As Frederick August had no heirs, he agreed that Frederick William should become sole ruler after his death. However Frederick William died from a fall on the stairs at Schloss Weilburg on 9 January 1816, and it was his son William who became Duke of Nassau.
At the Congress of Vienna, the Principality of Orange-Nassau was partly incorporated into the Duchy of Nassau and subsequently, the unified Duchy joined the German Confederation with Wiesbaden as its new capital. Through the extinction of most lines, the Nassau-Usingen branch of the Nassau-Weilburg line under Duke William became the reigning house of Nassau until the Austro-Prussian War in 1866, when it was annexed by the Kingdom of Prussia and incorporated as the Wiesbaden Region into the Province of Hesse-Nassau. William's son Adolphe, the last Duke of Nassau, received Luxembourg after the male line of Orange-Nassau became extinct in 1890.[1]
References
^ "Image Gallery of the Coins of Nassau". Retrieved 5 April 2017..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}