Chariot

A chariot drawn by horses.

Approximate historical map of the spread of the spoke-wheeled chariot, 2000–500 BC.
A chariot is a type of carriage driven by a charioteer, usually using horses[a] to provide rapid motive power. Chariots were used by armies as transport or mobile archery platforms, for hunting or for racing, and as a conveniently fast way to travel for many ancient people.
The word "chariot" comes from the Latin term carrus, a loanword from Gaulish. A chariot of war or one used in military parades was called a car. In ancient Rome and some other ancient Mediterranean civilizations, a biga required two horses, a triga three, and a quadriga four.
The chariot was a fast, light, open, two-wheeled conveyance drawn by two or more horses that were hitched side by side, and was little more than a floor with a waist-high guard at the front and sides. It was initially used for ancient warfare during the Bronze and Iron Ages; but, after its military capabilities had been superseded by cavalry, as horses were gradually bred to be bigger, the chariot was used for travel, in processions, for games, and in races.
The critical invention that allowed the construction of light, horse-drawn chariots was the spoked wheel. The earliest spoke-wheeled chariots date to ca. 2000 BC. The use of chariots peaked around 1300 BC (see Battle of Kadesh). Chariots had lost their military importance by the 1st century AD, but chariot races continued to be popular in Constantinople until the 6th century.
Contents
1 Europe
1.1 Ancient Europe
1.1.1 Caucasus region
1.1.2 Eastern Europe
1.2 Later developments in Europe
1.2.1 Greece
1.2.2 Northern Europe
1.2.3 Western Europe and British Isles
1.2.4 Etruria
1.2.5 Urartu
1.2.6 Rome
2 Ancient Near East
2.1 Early wheeled vehicles in the Near East
2.2 Ancient Canaan and Israel
2.3 Egypt
2.4 Hittites
2.5 Persia
3 Ancient China
4 Ancient India
5 Gauge
6 See also
7 Notes
8 References
9 Further reading
10 External links
Europe
Ancient Europe
Caucasus region
Horses were introduced to Transcaucasia at the time of the Kura-Araxes culture, beginning about 3300 BC. (Archeologists have not found earlier horse bones in the area.) During the Kura-Araxes period, horses seem to become quite widespread, with signs of domestication.[1]
Eastern Europe
The domestication of the horse was an important step toward civilization. An increasing amount of evidence supports the hypothesis, that horses were domesticated in the Eurasian Steppes (Dereivka in Ukraine) approximately 4000-3500 BC.[2][3][4]
The invention of the wheel used in transportation most likely took place in Mesopotamia or the Eurasian steppes in modern-day Ukraine. Evidence of wheeled vehicles appears from the mid 4th millennium BC near-simultaneously in the Northern Caucasus (Maykop culture), and in Central Europe. The earliest vehicles may have been ox carts.[5]
Starokorsunskaya kurgan in the Kuban region of Russia contains a wagon grave (or chariot burial) of the Maikop Culture (which also had horses). The two solid wooden wheels from this kurgan have been dated to the second half of the fourth millennium. Soon thereafter the number of such burials in this Northern Caucasus region multiplied.[6][7]
As David Anthony writes in his book The Horse, the Wheel and Language, in Eastern Europe, the earliest well-dated depiction of a wheeled vehicle (a wagon with two axles and four wheels) is on the Bronocice pot (c. 3500 BC). It is a clay pot excavated in a Funnelbeaker settlement in Swietokrzyskie Voivodeship in Poland.[8]
The oldest securely dated real wheel-axle combination in Eastern Europe is the Ljubljana Marshes Wheel (c. 3150 BC).[9]
Later developments in Europe

A mosaic of the Kasta Tomb in Amphipolis depicting the abduction of Persephone by Pluto, 4th century BC.

The goddess Nike riding on a two-horse chariot, from an Apulian patera (tray), Magna Graecia, 4th century BC.

Procession of chariots on a Late Geometric amphora from Athens (ca. 720–700 BC).
Greece

The Charioteer of Delphi was dedicated to the god Apollo in 474 BC by the tyrant of Gela in commemoration of a Pythian racing victory at Delphi.
The earliest records of chariots are the arsenal inventories of the palatial centres in Mycenaean Greece, as described in Linear B tablets from the 15th-14th centuries BC. The tablets distinguish between "assembled" and "dismantled" chariots.
The latter Greeks of the first millennium BC had a (still not very effective) cavalry arm, and the rocky terrain of the Greek mainland was unsuited for wheeled vehicles. Consequently, in historical Greece the chariot was never used to any extent in war. Nevertheless, the chariot retained a high status and memories of its era were handed down in epic poetry. Linear B tablets from Mycenaean palaces record large inventories of chariots, sometimes with specific details as to how many chariots were assembled or not (i.e. stored in modular form). Later the vehicles were used in games and processions, notably for races at the Olympic and Panathenaic Games and other public festivals in ancient Greece, in hippodromes and in contests called agons. They were also used in ceremonial functions, as when a paranymph, or friend of a bridegroom, went with him in a chariot to fetch the bride home.
Herodotus (Histories, 5. 9) Reports that chariots were widely used in the Pontic–Caspian steppe by the Sigynnae.
Greek chariots were made to be drawn by two horses attached to a central pole. If two additional horses were added, they were attached on each side of the main pair by a single bar or trace fastened to the front or prow of the chariot, as may be seen on two prize vases in the British Museum from the Panathenaic Games at Athens, Greece, in which the driver is seated with feet resting on a board hanging down in front close to the legs of the horses. The biga itself consists of a seat resting on the axle, with a rail at each side to protect the driver from the wheels. Greek chariots appear to have lacked any other attachment for the horses, which would have made turning difficult.
The body or basket of the chariot rested directly on the axle (called beam) connecting the two wheels. There was no suspension, making this an uncomfortable form of transport. At the front and sides of the basket was a semicircular guard about 3 ft (1 m) high, to give some protection from enemy attack. At the back the basket was open, making it easy to mount and dismount. There was no seat, and generally only enough room for the driver and one passenger.
The reins were mostly the same as those in use in the 19th century, and were made of leather and ornamented with studs of ivory or metal. The reins were passed through rings attached to the collar bands or yoke, and were long enough to be tied round the waist of the charioteer to allow for defense.
The wheels and basket of the chariot were usually of wood, strengthened in places with bronze or iron. They had from four to eight spokes and tires of bronze or iron. Due to the widely spaced spokes, the rim of the chariot wheel was held in tension over comparatively large spans. Whilst this provided a small measure of shock absorption, it also necessitated the removal of the wheels when the chariot was not in use, to prevent warping from continued weight bearing.[10] Most other nations of this time had chariots of similar design to the Greeks, the chief differences being the mountings.
According to Greek mythology, the chariot was invented by Erichthonius of Athens to conceal his feet, which were those of a dragon.[11]
The most notable appearance of the chariot in Greek mythology occurs when Phaëton, the son of Helios, in an attempt to drive the chariot of the sun, managed to set the earth on fire. This story led to the archaic meaning of a phaeton as one who drives a chariot or coach, especially at a reckless or dangerous speed. Plato, in his Chariot Allegory, depicted a chariot drawn by two horses, one well behaved and the other troublesome, representing opposite impulses of human nature; the task of the charioteer, representing reason, was to stop the horses from going different ways and to guide them towards enlightenment.
The Greek word for chariot, ἅρμα, hárma, is also used nowadays to denote a tank, properly called άρμα μάχης, árma mákhēs, literally a "combat chariot".
Northern Europe

A petroglyph in a double burial, c. 1000 BC (the Nordic Bronze Age)
The Trundholm sun chariot is dated to c. 1400 BC (see Nordic Bronze Age). The horse drawing the solar disk runs on four wheels, and the Sun itself on two. All wheels have four spokes. The "chariot" comprises the solar disk, the axle, and the wheels, and it is unclear whether the sun is depicted as the chariot or as the passenger. Nevertheless, the presence of a model of a horse-drawn vehicle on two spoked wheels in Northern Europe at such an early time is astonishing.
In addition to the Trundholm chariot, there are numerous petroglyphs from the Nordic Bronze Age that depict chariots. One petroglyph, drawn on a stone slab in a double burial from c. 1000 BC, depicts a biga with two four-spoked wheels.
The use of the composite bow in chariot warfare is not attested in northern Europe.
Western Europe and British Isles
The Celts were famous for their chariots and modern English words like car, carriage and carry are ultimately derived from the native Brythonic language (Modern Welsh: Cerbyd). The word chariot itself is derived from the Norman French charriote and shares a Celtic root (Gaulish: karros). Some 20 iron-aged chariot burials have been excavated in Britain, roughly dating from between 500 BC and 100 BC. Virtually all of them were found in East Yorkshire - the exception was a find in 2001 in Newbridge, 10 km west of Edinburgh.
The Celtic chariot, which may have been called karbantos in Gaulish (compare Latin carpentum),[12][13] was a biga that measured approximately 2 m (6.56 ft) in width and 4 m (13 ft) in length.
British chariots were open in front. Julius Caesar provides the only significant eyewitness report of British chariot warfare:
.mw-parser-output .templatequote{overflow:hidden;margin:1em 0;padding:0 40px}.mw-parser-output .templatequote .templatequotecite{line-height:1.5em;text-align:left;padding-left:1.6em;margin-top:0}
Their mode of fighting with their chariots is this: firstly, they drive about in all directions and throw their weapons and generally break the ranks of the enemy with the very dread of their horses and the noise of their wheels; and when they have worked themselves in between the troops of horse, leap from their chariots and engage on foot. The charioteers in the meantime withdraw some little distance from the battle, and so place themselves with the chariots that, if their masters are overpowered by the number of the enemy, they may have a ready retreat to their own troops. Thus they display in battle the speed of horse, [together with] the firmness of infantry; and by daily practice and exercise attain to such expertness that they are accustomed, even on a declining and steep place, to check their horses at full speed, and manage and turn them in an instant and run along the pole, and stand on the yoke, and thence betake themselves with the greatest celerity to their chariots again.[14]
Chariots play an important role in Irish mythology surrounding the hero Cú Chulainn.

Sculpture by Thomas Thornycroft of Boudica and her daughters in her chariot, addressing her troops before the battle.

Procession of chariots and warriors on the Vix krater (c. 510), a vessel of Archaic Greek workmanship found in a Gallic burial.

Modern reconstruction of a Hussite war wagon.
Chariots could also be used for ceremonial purposes. According to Tacitus (Annals 14.35), Boudica, queen of the Iceni and a number of other tribes in a formidable uprising against the occupying Roman forces, addressed her troops from a chariot in 61 AD:
- "Boudicca curru filias prae se vehens, ut quamque nationem accesserat, solitum quidem Britannis feminarum ductu bellare testabatur"
- Boudicca, with her daughters before her in a chariot, went up to tribe after tribe, protesting that it was indeed usual for Britons to fight under the leadership of women.
The last mention of chariot use in battle seems to be at the Battle of Mons Graupius, somewhere in modern Scotland, in 84 AD. From Tacitus (Agricola 1.35–36) "The plain between resounded with the noise and with the rapid movements of chariots and cavalry." The chariots did not win even their initial engagement with the Roman auxiliaries: "Meantime the enemy's cavalry had fled, and the charioteers had mingled in the engagement of the infantry."
Later through the centuries, the chariot, became commonly known as the "war wagon". The "war wagon" was a medieval development used to attack rebel or enemy forces on battle fields. The wagon was given slits for archers to shoot enemy targets, supported by infantry using pikes and flails and later for the invention of gunfire by hand-gunners; side walls were use for protection against archers, crossbowmen, the early use of gunpowder and cannon fire.
It was especially useful during the Hussite Wars, ca. 1420, by Hussite forces rebelling in Bohemia. Groups of them could form defensive works, but they also were used as hardpoints for Hussite formations or as firepower in pincer movements. This early use of gunpowder and innovative tactics helped a largely peasant infantry stave off attacks by the Holy Roman Empire's larger forces of mounted knights.
Etruria

Detail of the Monteleone Chariot at the Met (c. 530 BC)
The only intact Etruscan chariot dates to c. 530 BC and was uncovered as part of a chariot burial at Monteleone di Spoleto. Currently in the collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art,[15] it is decorated with bronze plates decorated with detailed low-relief scenes, commonly interpreted as depicting episodes from the life of Achilles.[16]
Urartu
In Urartu (860–590 BC), the chariot was used by both the nobility and the military. In Erebuni (Yerevan), King Argishti of Urartu is depicted riding on a chariot which is dragged by two horses. The chariot has two wheels and each wheel has about eight spokes. This type of chariot was used around 800 BC.
Rome

A winner of a Roman chariot race
In the Roman Empire, chariots were not used for warfare, but for chariot racing, especially in circuses, or for triumphal processions, when they could be drawn by as many as ten horses or even by dogs, tigers, or ostriches[citation needed]. There were four divisions, or factiones, of charioteers, distinguished by the colour of their costumes: the red, blue, green and white teams. The main centre of chariot racing was the Circus Maximus,[17] situated in the valley between the Palatine and Aventine Hills in Rome. The track could hold 12 chariots, and the two sides of the track were separated by a raised median termed the spina. Chariot races continued to enjoy great popularity in Byzantine times, in the Hippodrome of Constantinople, even after the Olympic Games had been disbanded, until their decline after the Nika riots in the 6th century. The starting gates were known as the Carceres.
An ancient Roman car or chariot drawn by four horses abreast together with the horses drawing it was called a Quadriga, from the Latin quadriugi (of a team of four). The term sometimes meant instead the four horses without the chariot or the chariot alone. A three-horse chariot, or the three-horse team drawing it, was a triga, from triugi (of a team of three). A two-horse chariot, or the two-horse team drawing it, was a biga, from biugi.
Ancient Near East
Some scholars argue that the horse chariot was most likely a product of the ancient Near East early in the 2nd millennium BCE.[18] Archaeologist Joost Crouwel writes that "Chariots were not sudden inventions, but developed out of earlier vehicles that were mounted on disk or cross-bar wheels. This development can best be traced in the Near East, where spoke-wheeled and horse-drawn chariots are first attested in the earlier part of the second millennium BCE..." and were illustrated on a Syrian cylinder seal dated to either the 18th or 17th century BC.[19]
Early wheeled vehicles in the Near East

Relief of early war wagons on the Standard of Ur, c. 2500 BC
It is widely believed that wheeled transport was invented in Mesopotamia. Nevertheless, recent archaeological evidence seems to indicate otherwise, pointing to Neolithic Europe.[7]
According to Christoph Baumer, the earliest discoveries of wheels in Mesopotamia come from the first half of the third millennium BC – more than half a millennium later than the first finds from the Kuban region. At the same time, in Mesopotamia, some intriguing early pictograms of a sled that rests on wooden rollers or wheels have been found. They date from about the same time as the early wheel discoveries in Europe and may indicate knowledge of the wheel.[6]
The earliest fully developed spoke-wheeled horse chariots are from the chariot burials of the Andronovo (Timber-Grave) sites of the Sintashta-Petrovka Proto-Indo-Iranian culture in modern Russia and Kazakhstan from around 2000 BC. This culture is at least partially derived from the earlier Yamna culture. It built heavily fortified settlements, engaged in bronze metallurgy on an industrial scale and practiced complex burial rituals reminiscent of Hindu rituals known from the Rigveda and the Avesta.
Over the next few centuries, the Andronovo culture spread across the steppes from the Urals to the Tien Shan, likely corresponding to the time of early Indo-Iranian cultures.
Chariots figure prominently in Indo-Iranian mythology. Chariots are also an important part of both Hindu and Persian mythology, with most of the gods in their pantheon portrayed as riding them. The Sanskrit word for a chariot is rátha- (m.), which is cognate with Avestan raθa- (also m.), and in origin a substantiation of the adjective Proto-Indo-European *rot-h₂-ó- meaning "having wheels", with the characteristic accent shift found in Indo-Iranian substantivisations. This adjective is in turn derived from the collective noun *rot-eh₂- "wheels", continued in Latin rota, which belongs to the noun *rót-o- for "wheel" (from *ret- "to run") that is also found in Germanic, Celtic and Baltic (Old High German rad n., Old Irish roth m., Lithuanian rãtas m.).[20]
The earliest depiction of vehicles in the context of warfare is on the Standard of Ur in southern Mesopotamia, c. 2500 BCE. These are more properly called wagons or carts and were double-axled and pulled by oxen or a hybrid of a donkey and a female onager,[21] named Kunga in the city of Nagar which was famous for breeding them.[22] The hybrids were used by the Eblaite,[22]early Sumerian, Akkadian and Ur III armies.[23] Although sometimes carrying a spearman with the charioteer (driver), such heavy wagons, borne on solid wooden wheels and covered with skins, may have been part of the baggage train (e.g., during royal funeral processions) rather than vehicles of battle in themselves.
The Sumerians had a lighter, two-wheeled type of cart, pulled by four asses, and with solid wheels. The spoked wheel did not appear in Mesopotamia until the mid-2000s BCE.[24]

The area of the spoke-wheeled chariot finds within the Sintashta-Petrovka Proto-Indo-Iranian culture is indicated in purple.
Ancient Canaan and Israel
Chariots are frequently mentioned in the Hebrew Tanakh and the Greek Old Testament, respectively, particularly by the prophets, as instruments of war or as symbols of power or glory. First mentioned in the story of Joseph (Genesis 50:9), "Iron chariots" are mentioned also in Joshua (17:16,18) and Judges (1:19,4:3,13) as weapons of the Canaanites and Israelites. 1 Samuel 13:5 mentions chariots of the Philistines, who are sometimes identified with the Sea Peoples or early Greeks.
Examples from The Jewish Study Bible[25] of Tanakh (Jewish Bible) include:
Isaiah 2:7 Their land is full of silver and gold, there is no limit to their treasures; their land is full of horses, there is no limit to their chariots.[26]
Jeremiah 4:13 Lo, he[I.e., the invader of v.7.] ascends like clouds, his chariots are like a whirlwind, his horses are swifter than eagles. Woe to us, we are ruined![27]
Ezekiel 26:10 From the cloud raised by his horses dust shall cover you; from the clatter of horsemen and wheels and chariots, your walls shall shake−when he enters your gates as men enter a breached city.[28]
Psalms 20:8 They [call] on chariots, they [call] on horses, but we call on the name of the LORD our God.[29]
Song of Songs 1:9 I have likened you, my darling, to a mare in Pharaoh's chariots [30]
Examples from the King James Version of Christian Bible include:
2 Chronicles 1:14 And Solomon gathered chariots and horsemen: and he had a thousand and four hundred chariots, and twelve thousand horsemen, which he placed in the chariot cities, and with the king at Jerusalem.
Judges 1:19 And the LORD was with Judah; and he drave out the inhabitants of the mountain; but could not drive out the inhabitants of the valley, because they had chariots of iron.[31]
Acts 8:37–38 Then Philip said, "If you believe with all your heart, you may." And he answered and said, "I believe that Jesus Christ is the Son of God." So he commanded the chariot to stand still. And both Philip and the eunuch went down into the water, and he baptized him.
Jezreel (city) has been identified as the chariot base of King Ahab.[32] And the decorated lynchpin of Sisera's chariot was identified at a site identified as his fortress Harosheth Haggoyim.[33]
Egypt

Ramses II fighting from a chariot at the Battle of Kadesh with two archers, one with the reins tied around the waist to free both hands (relief from Abu Simbel)
The chariot and horse were introduced to Egypt by the Hyksos invaders in the 16th century BCE and undoubtedly contributed to the military success of the Egyptians. In the remains of Egyptian and Assyrian art, there are numerous representations of chariots, which display rich ornamentation. The chariots of the Egyptians and Assyrians, with whom the bow was the principal arm of attack, were richly mounted with quivers full of arrows. The Egyptians invented the yoke saddle for their chariot horses in c. 1500 BCE. As a general rule, the Egyptians used chariots as mobile archery platforms; chariots always had two men, with the driver steering the chariot with his reins while the main archer aimed his bow and arrow at any targets within range. The best preserved examples of Egyptian chariots are the four specimens from the tomb of Tutankhamun. Chariots can be carried by two or more horses.
Hittites
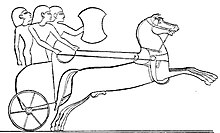
Hittite chariot (drawing of an Egyptian relief)
The oldest testimony of chariot warfare in the ancient Near East is the Old Hittite Anitta text (18th century BCE), which mentions 40 teams of horses (in the original cuneiform spelling: 40 ṢÍ-IM-TI ANŠE.KUR.RAḪI.A) at the siege of Salatiwara. Since the text mentions teams rather than chariots, the existence of chariots in the 18th century BCE is uncertain. The first certain attestation of chariots in the Hittite empire dates to the late 17th century BCE (Hattusili I). A Hittite horse-training text is attributed to Kikkuli the Mitanni (15th century BCE).
The Hittites were renowned charioteers. They developed a new chariot design that had lighter wheels, with four spokes rather than eight, and that held three rather than two warriors. It could hold three warriors because the wheel was placed in the middle of the chariot and not at the back as in Egyptian chariots. Typically one Hittite warrior steered the chariot while the second man was usually the main archer; the third warrior would either wield a spear or sword when charging at enemies or hold up a large shield to protect himself and the others from enemy arrows.
Hittite prosperity largely depended on their control of trade routes and natural resources, specifically metals. As the Hittites gained dominion over Mesopotamia, tensions flared among the neighboring Assyrians, Hurrians, and Egyptians. Under Suppiluliuma I, the Hittites conquered Kadesh and, eventually, the whole of Syria. The Battle of Kadesh in 1274 BCE is likely to have been the largest chariot battle ever fought, involving over 5,000 chariots.[34]
Persia

A golden chariot made during Achaemenid Empire (550–330 BCE).
The Persians succeeded Elam in the mid 1st millennium. They may have been the first to yoke four horses to their chariots. They also used scythed chariots. Cyrus the Younger employed these chariots in large numbers at the Battle of Cunaxa.
Herodotus mentions that the Ancient Libyan and the Ancient Indian (Sattagydia, Gandhara and Hindush) satrapies supplied cavalry and chariots to Xerxes the Great's army. However, by this time, cavalry was far more effective and agile than the chariot, and the defeat of Darius III at the Battle of Gaugamela (331 BCE), where the army of Alexander simply opened their lines and let the chariots pass and attacked them from behind, marked the end of the era of chariot warfare (barring the Seleucid and Pontic powers, India, China, and the Celtic peoples).
Ancient China
Bronze Chinese charioteer from the Warring States period (403–221 BCE).

Powerful landlord in chariot (Eastern Han, 25–220 AD, Anping County, Hebei).
The earliest archaeological evidence of chariots in China, a chariot burial site discovered in 1933 at Hougang, Anyang in Henan province, dates to the rule of King Wu Ding of the late Shang Dynasty (c. 1200 BCE). Oracle bone inscriptions suggest that the western enemies of the Shang used limited numbers of chariots in battle, but the Shang themselves used them only as mobile command-vehicles and in royal hunts.[35]
During the Shang Dynasty, members of the royal family were buried with a complete household and servants, including a chariot, horses, and a charioteer. A Shang chariot was often drawn by two horses, but four-horse variants are occasionally found in burials.
Jacques Gernet claims that the Zhou dynasty, which conquered the Shang ca. 1046 BC, made more use of the chariot than did the Shang and "invented a new kind of harness with four horses abreast".[36] The crew consisted of an archer, a driver, and sometimes a third warrior who was armed with a spear or dagger-axe. From the 8th to 5th centuries BCE the Chinese use of chariots reached its peak. Although chariots appeared in greater numbers, infantry often defeated charioteers in battle.
Massed-chariot warfare became all but obsolete after the Warring-States Period (476–221 BC). The main reasons were increased use of the crossbow, use of long halberds up to 18 feet long and pikes up to 22 feet long, and the adoption of standard cavalry units, and the adaptation of mounted archery from nomadic cavalry, which were more effective. Chariots would continue to serve as command posts for officers during the Qin dynasty (221-206 BC) and the Han Dynasty (206 BCE-220 AD), while armored chariots were also used during the Han Dynasty against the Xiongnu Confederation in the Han–Xiongnu War (133 BC to 89 AD), specifically at the Battle of Mobei (119 BC).
Before the Han Dynasty, the power of Chinese states and dynasties was often measured by the number of chariots they were known to have. A country of a thousand chariots ranked as a medium country, and a country of ten thousand chariots ranked as a huge and powerful country.[37][38]
Ancient India

Coach driver 2000 BCE in Daimabad, Indus Valley Civilization.

Bronze Chariot with Lord Krishna and Arjuna during the Kurukshetra war.

Chariot detail at Airavatesvara Temple built by Rajaraja Chola II of the Chola Empire in the 12th century CE.

Stone chariot at Hampi, build under the Vijayanagara Empire.
Chariots figure prominently in the Rigveda, evidencing their presence in India in the 2nd millennium BCE. Among Rigvedic deities, notably Ushas (the dawn) rides in a chariot, as well as Agni in his function as a messenger between gods and men.
There are some depictions of chariots among the petroglyphs in the sandstone of the Vindhya range. Two depictions of chariots are found in Morhana Pahar, Mirzapur district. One depicts a biga and the head of the driver. The second depicts a quadriga, with six-spoked wheels, and a driver standing up in a large chariot box. This chariot is being attacked. One figure, who is armed with a shield and a mace, stands in the chariot's path; another figure, who is armed with bow and arrow, threatens the right flank. It has been suggested (speculated) that the drawings record a story, most probably dating to the early centuries BCE, from some center in the area of the Ganges–Yamuna plain into the territory of still Neolithic hunting tribes.[39] The very realistic chariots carved into the Sanchi stupas are dated to roughly the 1st century.
The scythed chariot was invented by the King of Magadha, Ajatashatru around 475 BCE. He used these chariots against the Licchavis.[citation needed] A scythed war chariot had a sharp, sickle-shaped blade or blades mounted on each end of the axle. The blades, used as weapons, extended horizontally for a metre on the sides of the chariot.
There is a chariot displayed at the AP State Archaeology Museum, Hyderabad, Telangana.
Gauge
A popular legend that has been around since at least 1937 traces the origin of the 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in standard railroad gauge to Roman times,[40] suggesting that it was based on the distance between the ruts of rutted roads marked by chariot wheels dating from the Roman Empire.[b] This is encouraged by the fact that the otherwise peculiar distance is almost exactly 5 Roman feet but there is no evidence to span the millennium and a half between the departure of the Romans from Britain and the adoption of the gauge on the Stockton and Darlington railroad in 1825.
See also
- Cavalry
- Chariot burial
- Chariot clock
- Chariot tactics
- Chuckwagon racing
- Merkava
- Ratha
- South-pointing chariot
- Tachanka
- Tanks
- Temple car
Notes
^ Although there were rare exceptions to the use of horses to pull chariots. For instance, the lion-pulled chariot described by Plutarch in his "Life of Antony".
^ The gaps in the pedestrian crossings in Pompeii could give credence or otherwise to this statement, but no relevant studies appear to have been made.
References
^ David W. Anthony, The Horse, the Wheel, and Language: How Bronze-Age Riders from the Eurasian Steppes Shaped the Modern World. Princeton University Press, 2010 .mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
ISBN 1400831105 p298.
^ Matossian Shaping World History p. 43
^ "What We Theorize – When and Where Did Domestication Occur". International Museum of the Horse. Archived from the original on 2010-12-17. Retrieved 2010-12-12.
^ "Horsey-aeology, Binary Black Holes, Tracking Red Tides, Fish Re-evolution, Walk Like a Man, Fact or Fiction". Quirks and Quarks Podcast with Bob Macdonald. CBC Radio. 2009-03-07. Retrieved 2010-09-18.
^ David W. Anthony, The Horse, the Wheel, and Language: How Bronze-Age Riders from the Eurasian Steppes Shaped the Modern World. Princeton University Press, 2010
ISBN 1400831105 p416
^ ab Christoph Baumer, The History of Central Asia: The Age of the Steppe Warriors. I.B. Tauris, 2012
ISBN 1780760604 p90
^ ab Chris Fowler, Jan Harding, Daniela Hofmann, eds, The Oxford Handbook of Neolithic Europe. OUP Oxford, 2015
ISBN 0191666882 p113
^ Anthony, David A. (2007). The horse, the wheel, and language: how Bronze-Age riders from the Eurasian steppes shaped the modern world. Princeton, N.J: Princeton University Press. p. 67. ISBN 0-691-05887-3.
^ Gasser, Aleksander (March 2003). "World's Oldest Wheel Found in Slovenia". Government Communication Office of the Republic of Slovenia.
^ Gordon, J. E. (1978). Structures, or Why Things Don't Fall Down. London: Pelican. p. 146. ISBN 9780140219616.
^ Brewer, E. Cobham. Dictionary of Phrase & Fable. Char’iot. Bartleby.com: Great Books Online – Encyclopedia, Dictionary, Thesaurus and hundreds more. Retrieved March 5, 2008.
^ Karl, Raimund (2006). "Chariot and wagon". In Koch, John T. Celtic Culture: A Historical Encyclopedia. 2. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO. p. 401. ISBN 1-85109-440-7. Retrieved 29 August 2014.
^ Delamarre, Xavier (2003). Dictionnaire de la langue gauloise (in French). Paris: Éditions Errance. ISBN 2-87772-369-0.
^ The Project Gutenberg EBook of "De Bello Gallico" and Other Commentaries by Caius Julius Caesar, translated by W. A. MacDevitt (1915).
^ METmuseum.org
^ The Golden Chariot of Achilles Archived March 16, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
^ The Charioteer of Delphi: Circus Maximus. Archived March 16, 2008, at the Wayback Machine. The Roman Mysteries books by Caroline Lawrence.
^ Raulwing 2000
^ Joost Crouwel (2013). "Studying the Six Chariots from the Tomb of Tutankhamun – An Update". In Veldmeijer, Andre J.; Ikram, Salima. Chasing Chariots: Proceedings of the First International Chariot Conference (Cairo 2012). Sidestone Press. p. 74. ISBN 978-9088902093.
^ Rix, Helmut; Kümmel, Martin; Zehnder, Thomas; Lipp, Reiner; Schirmer, Brigitte (2001). Lexikon der indogermanischen Verben (in German) (2nd ed.). Wiesbaden: Ludwig Reichert. p. 507. ISBN 3-89500-219-4.
^ Elena Efimovna Kuzʹmina (2007). The Origin of the Indo-Iranians. p. 134.
^ ab Paolo Matthiae,Nicoló Marchetti (2013). Ebla and its Landscape: Early State Formation in the Ancient Near East. p. 436.
^ David W. Anthony (2010). The Horse, the Wheel, and Language: How Bronze-Age Riders from the Eurasian Steppes Shaped the Modern World. p. 403.
^ "History Alive! The Ancient World:Lesson 5- Ancient Sumer, Section 8- Technology". learntci.com. History Alive. Retrieved 13 January 2015.
^ The Jewish Study Bible (2014, Oxford University Press,
ISBN 978-0-19-997846-5)
^ TJSB commentary: "Criticism of the nation's sins: magic, amassing extraordinary amounts of wealth, pursuing military power, and idolatry. All these vices embody inappropriate confidence in humanity's own powers. This confidence is not only mistaken, but offensive to God."; TJSB 2014, p. 771
^ TJSB commentary: "A second passage on the enemy's approach, this time using weather images (clouds and whirlwind) and fauna (horses and eagles, see Hab. 1:8)"; TJSB 2014, p. 917
^ TJSB commentary: "Nebuchadrezzar conquered Tyre using cavalry and chariots surrounding the city and embankments placed against the city walls (...) the city was sacked and covered with water (...) In contrast, Ezekiel's description presupposes the tactics and weapons of land war, which were useless against an island state."; TJSB 2014, p. 1079
^ TJSB commentary: "The strength of divine Presence over military might is a central biblical theme."; TJSB 2014, p. 1289
^ TJSB commentary: "Throughout the Song, the lovers use comparison to praise one another's beauty and charm. Mare in Pharaoh's chariots, either an image of adorned majesty (...) or a reference to an ancient battle strategy in which a mare was let loose among cavalry to distract the stallions."; TJSB 2014, p. 1562.
^ TJSB commentary: "Only in the case of Judah is there a justification for non-dispossessing."; TJSB 2014, p. 499
^ David Ussishkin, "Jezreel—Where Jezebel Was Thrown to the Dogs", Biblical Archaeology Review, July / August 2010.
^ "Archaeological mystery solved" Archived 2010-07-05 at the Wayback Machine., University of Haifa press release, July 1, 2010.
^ Dr. Aaron Ralby (2013). "Battle of Kadesh, c. 1274 BCE: Clash of Empires". Atlas of Military History. Parragon. pp. 54–55. ISBN 978-1-4723-0963-1.
^ Shaughnessy, Edward L. (1988). "Historical Perspectives on The Introduction of The Chariot Into China". Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies. Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies, Vol. 48, No. 1. 48 (1): 189–237. doi:10.2307/2719276. JSTOR 2719276.
^ Gernet, Jacques. A History of Chinese Civilization, Cambridge University Press, 2nd edition 1996,
ISBN 0-521-49781-7, p. 51.
^ [Mencius · Liang Hui Huang (King the Hui of Liang, Hui is a posthumous name) Volume One] 'The kingslayer of a country of ten thousands chariots, must be the house of thousand chariots. The kingslayer of a country of thousand chariots, must be the house of hundred chariots.' [Zhao Qi's note] Zhao Qi's note: ' Ten thousands chariots, is the son of heaven (King of Zhou).'
^ [Zhan Guo Ce·Zhao Ce] 'Nowadays, Kingdom of Qin is a country of ten thousands chariots, Kingdom of Liang (Kingdom of Wei, 'Da Liang' is the capital of Wei) is also a country of ten thousands chariots.'
^ Sparreboom 1985:87
^ "STANDARD RAILWAY GAUGE". Townsville Daily Bulletin. Queensland: National Library of Australia. 5 October 1937. p. 12. Retrieved 3 June 2011.
Further reading
- Anthony, David W. The Horse, The Wheel and Language: How Bronze-Age Riders from the Eurasian Steppes Shaped the Modern World Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2007 (
ISBN 9780691058870). - Chamberlin, J. Edward. Horse: How the horse has shaped civilizations. N.Y.: United Tribes Media Inc., 2006 (
ISBN 0-9742405-9-1). - Cotterell, Arthur. Chariot: From chariot to tank, the astounding rise and fall of the world's first war machine. Woodstock & New York: The Overlook Press, 2005 (
ISBN 1-58567-667-5). - Crouwel, Joost H. Chariots and other means of land transport in Bronze Age Greece (Allard Pierson Series, 3). Amsterdam: Allard Pierson Museum, 1981 (
ISBN 90-71211-03-7). - Crouwel, Joost H. Chariots and other wheeled vehicles in Iron Age Greece (Allard Pierson Series, 9). Amsterdam: Allard Pierson Museum:, 1993 (
ISBN 90-71211-21-5).
Drews, Robert. The coming of the Greeks: Indo-European conquests in the Aegean and the Near East. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1988 (hardcover,
ISBN 0-691-03592-X); 1989 (paperback,
ISBN 0-691-02951-2).- Drews, Robert. The end of the Bronze Age: Changes in warfare and the catastrophe ca. 1200 B.C. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1993 (hardcover,
ISBN 0-691-04811-8); 1995 (paperback,
ISBN 0-691-02591-6). - Drews, Robert. Early riders: The beginnings of mounted warfare in Asia and Europe. N.Y.: Routledge, 2004 (
ISBN 0-415-32624-9). - Fields, Nic; Brian Delf (illustrator). Bronze Age War Chariots (New Vanguard). Oxford; New York: Osprey Publishing, 2006 (
ISBN 978-1841769448). - Greenhalg, P A L. Early Greek warfare; horsemen and chariots in the Homeric and Archaic Ages. Cambridge University Press, 1973. (
ISBN 9780521200561). - Kulkarni, Raghunatha Purushottama. Visvakarmiya Rathalaksanam: Study of Ancient Indian Chariots: with a historical note, references, Sanskrit text, and translation in English. Delhi: Kanishka Publishing House, 1994 (
ISBN 978-8173-91004-3)
Lee-Stecum, Parshia (October 2006). "Dangerous Reputations: Charioteers and Magic in Fourth-Century Rome". Greece & Rome. 53 (2): 224–234. doi:10.1017/S0017383506000295. ISSN 0017-3835.
- Littauer, Mary A.; Crouwel, Joost H. Chariots and related equipment from the tomb of Tutankhamun (Tutankhamun's Tomb Series, 8). Oxford: The Griffith Institute, 1985 (
ISBN 0-900416-39-4). - Littauer, Mary A.; Crouwel, Joost H.; Raulwing, Peter (Editor). Selected writings on chariots and other early vehicles, riding and harness (Culture and history of the ancient Near East, 6). Leiden: Brill Academic Publishers, 2002 (
ISBN 90-04-11799-7). - Moorey, P.R.S. "The Emergence of the Light, Horse-Drawn Chariot in the Near-East c. 2000–1500 B.C.", World Archaeology, Vol. 18, No. 2. (1986), pp. 196–215.
- Piggot, Stuart. The earliest wheeled transport from the Atlantic Coast to the Caspian Sea. Ithaca, New York: Cornell University Press, 1983 (
ISBN 0-8014-1604-3). - Piggot, Stuart. Wagon, chariot and carriage: Symbol and status in the history of transport. London: Thames & Hudson, 1992 (
ISBN 0-500-25114-2). - Pogrebova M. The emergence of chariots and riding in the South Caucasus in Oxford Journal of Archaeology, Volume 22, Number 4, November 2003, pp. 397–409.
- Raulwing, Peter. Horses, Chariots and Indo-Europeans: Foundations and Methods of Chariotry Research from the Viewpoint of Comparative Indo-European Linguistics. Budapest: Archaeolingua, 2000 (
ISBN 9638046260). - Sandor, Bela I. The rise and decline of the Tutankhamun-class chariot in Oxford Journal of Archaeology, Volume 23, Number 2, May 2004, pp. 153–175.
- Sandor, Bela I. Tutankhamun's chariots: Secret treasures of engineering mechanics in Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures, Volume 27, Number 7, July 2004, pp. 637–646.
- Sparreboom M. Chariots in the Veda (Memoirs of the Kern Institute, Leiden, 3). Leiden: Brill Academic Publishers, 1985 (
ISBN 90-04-07590-9).
Wilford, John Noble (1994-02-22). "Remaking the Wheel: Evolution of the Chariot". The New York Times. The New York Times Company. Retrieved 2015-07-29.
External links
 "Chariot". Encyclopædia Britannica. 5 (11th ed.). 1911.
"Chariot". Encyclopædia Britannica. 5 (11th ed.). 1911.
- Sumerian war chariots reconstructed. Photographic restoration of three of the chariots on the Standard of Ur.
- Sumerian war chariots deconstructed. What did a Sumerian war chariot really look like?
- "The Horse, the Wheel and Language, How Bronze-Age Riders from the Eurasian Steppes shaped the Modern World", David W Anthony, 2007
Ancient Egyptian chariots: history, design, use. Ancient Egypt: an introduction to its history and culture.
Chariot Usage in Greek Dark Age Warfare, by Carolyn Nicole Conter: Title page for Electronic Theses and Dissertations ETD etd-11152003-164515. Florida State University ETD Collection.
Chariots in Greece. Hellenica – Michael Lahanas.
Kamat Research Database – Prehistoric Carts. Varieties of Carts and Chariots in prehistoric cave shelter paintings found in Central India. Kamat's Potpourri – The History, Mystery, and Diversity of India.
Ludi circenses (longer version). SocietasViaRomana.net.











