Transverse wave
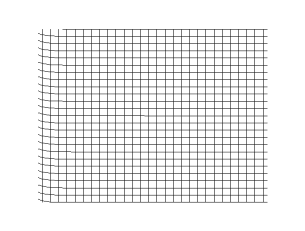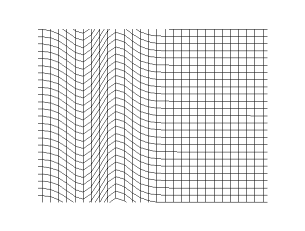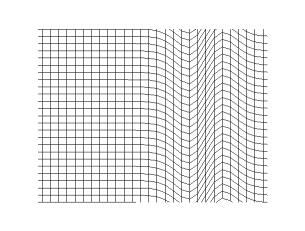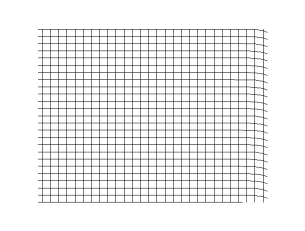
Transverse plane wave in linear polarization, i.e. oscillating only in the y-direction.
The wave shown could occur on a water surface.
(Although strictly speaking water waves have a small longitudinal component as well.)

A light wave is an example of a transverse electromagnetic wave; the shape of the wave is one of the sinusoidal plane-wave solutions of the electromagnetic wave equation.
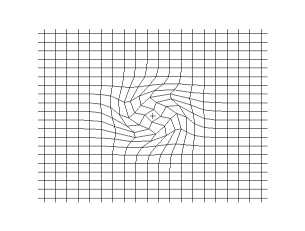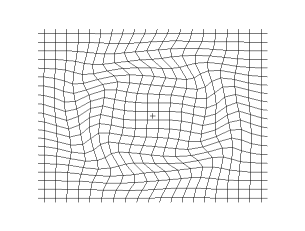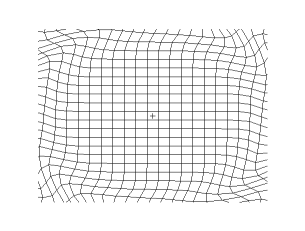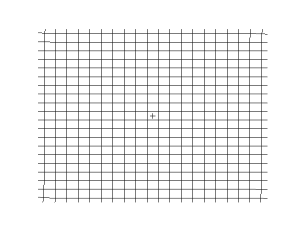
Propagation of a transverse spherical wave in a 2d grid (empirical model)
A transverse wave is a moving wave that consists of oscillations occurring perpendicular (right angled) to the direction of energy transfer (or the propagation of the wave).
If a transverse wave is moving in the positive x-direction, its oscillations are in up and down directions that lie in the y–z plane.
Light is an example of a transverse wave, while sound is a longitudinal wave. A ripple in a pond and a wave on a string are easily visualized as transverse waves.
Contents
1 Explanation
1.1 "Polarized" waves
1.2 Electromagnetic waves
2 See also
3 References
4 External links
Explanation
Transverse waves are waves that are oscillating perpendicularly (at a right angle) to the direction of propagation. If you anchor one end of a ribbon or string and hold the other end in your hand, you can create transverse waves by moving your hand up and down. Notice though, that you can also launch waves by moving your hand side-to-side. This is an important point. There are two independent directions in which wave motion can occur. In this case, these motions are the Y and Z directions mentioned above, while the wave propagates away in the X direction. The other type of waves is the longitudinal wave, which oscillates in the direction of its propagation.
"Polarized" waves
Continuing with the string example, if you move your hand in a clockwise circle, you will launch waves in the form of a left-handed helix as they propagate away. Similarly, if you move your hand in a counter-clockwise circle, a right-handed helix will form. These phenomena of simultaneous motion in two directions go beyond the kinds of waves we observe on the surface of water - in that a wave on a string can be two-dimensional.
Two-dimensional transverse waves exhibit a phenomenon called polarization. A wave produced by moving your hand in a straight line, up and down for instance, is a linearly polarized wave, a special case. A wave produced by moving your hand in a circle or an ellipse is a circularly or elliptically polarized wave, two other special cases.
Electromagnetic waves
Electromagnetic waves behave in this same way. Electromagnetic waves are also two-dimensional transverse waves.
Transverse waves are waves that travel perpendicular to the direction of the vibration.
Ray theory does not describe phenomena such as interference and diffraction, which require wave theory (involving the phase of the wave).
You can think of a ray of light, in optics, as an idealized narrow beam of electromagnetic radiation. Rays are used to model the propagation of light through an optical system, by dividing the real light field up into discrete rays that can be computationally propagated through the system by the techniques of ray tracing. [1]
A light ray is a line or curve that is perpendicular to the light's wavefronts (and is therefore collinear with the wave vector). Light rays bend at the interface between two dissimilar media and may be curved in a medium in which the refractive index changes. Geometric optics describes how rays propagate through an optical system.[1]
This two-dimensional nature should not be confused with the two components of an electromagnetic wave, the electric and magnetic field components, which are shown in the light wave diagram here. Each of these fields, the electric and the magnetic, exhibits two-dimensional transverse wave behavior, just like the waves on a string.
See also
- Longitudinal wave
Luminiferous aether – the postulated medium for light waves; accepting that light was a transverse wave prompted a search for evidence of this physical medium- Shear wave splitting
- Sinusoidal plane-wave solutions of the electromagnetic wave equation
- Transverse mode
References
^ ab Moore, Ken (2005-07-25). "What is a ray?". ZEMAX Users' Knowledge Base. Archived from the original on 2013-06-24. Retrieved 2008-05-30..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
External links
- Interactive simulation of transverse wave
- Wave types explained with high speed film and animations
Weisstein, Eric Wolfgang (ed.). "Transverse Wave". ScienceWorld.
Transverse and Longitudinal Waves Introductory module on these waves at Connexions
