Magnetic domain

Microcrystalline grains within a piece of Nd2Fe14B (the alloy used in neodymium magnets) with magnetic domains made visible with a Kerr microscope. The domains are the light and dark stripes visible within each grain. The outlined grain has its magnetocrystalline axis almost vertical, so the domains are seen end-on.
A magnetic domain is a region within a magnetic material in which the magnetization is in a uniform direction. This means that the individual magnetic moments of the atoms are aligned with one another and they point in the same direction. When cooled below a temperature called the Curie temperature, the magnetization of a piece of ferromagnetic material spontaneously divides into many small regions called magnetic domains. The magnetization within each domain points in a uniform direction, but the magnetization of different domains may point in different directions. Magnetic domain structure is responsible for the magnetic behavior of ferromagnetic materials like iron, nickel, cobalt and their alloys, and ferrimagnetic materials like ferrite. This includes the formation of permanent magnets and the attraction of ferromagnetic materials to a magnetic field. The regions separating magnetic domains are called domain walls, where the magnetization rotates coherently from the direction in one domain to that in the next domain. The study of magnetic domains is called micromagnetics.
Magnetic domains form in materials which have magnetic ordering; that is, their dipoles spontaneously align due to the exchange interaction. These are the ferromagnetic, ferrimagnetic and antiferromagnetic materials. Paramagnetic and diamagnetic materials, in which the dipoles align in response to an external field but do not spontaneously align, do not have magnetic domains.
Contents
1 Development of domain theory
2 Domain structure
2.1 Why domains form
2.2 Size of domains
2.3 Magnetic anisotropy
2.4 Magnetostriction
2.5 Grain structure
2.6 "Magnetized" states
3 Landau-Lifshitz energy equation
4 Domain imaging techniques
4.1 Magneto-optic Kerr effect (MOKE)
4.2 Lorentz microscopy
4.3 Magnetic force microscopy (MFM)
4.4 Bitter method
5 See also
6 References
7 External links
Development of domain theory
Magnetic domain theory was developed by French physicist Pierre-Ernest Weiss[1] who, in 1906, suggested existence of magnetic domains in ferromagnets.[2] He suggested that large number of atomic magnetic moments (typically 1012-1018)[citation needed] were aligned parallel. The direction of alignment varies from domain to domain in a more or less random manner, although certain crystallographic axis may be preferred by the magnetic moments, called easy axes. Weiss still had to explain the reason for the spontaneous alignment of atomic moments within a ferromagnetic material, and he came up with the so-called Weiss mean field. He assumed that a given magnetic moment in a material experienced a very high effective magnetic field due to the magnetization of its neighbors. In the original Weiss theory the mean field was proportional to the bulk magnetization M, so that
He=α M{displaystyle H_{e}=alpha M}
where α {displaystyle alpha }
He=α Ms{displaystyle H_{e}=alpha M_{s}}
Where Ms{displaystyle M_{s}}
Later, the quantum theory made it possible to understand the microscopic origin of the Weiss field. The exchange interaction between localized spins favored a parallel (in ferromagnets) or an anti-parallel (in anti-ferromagnets) state of neighboring magnetic moments
Domain structure
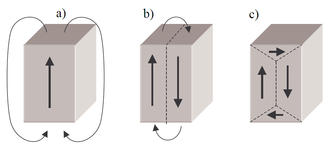
How dividing a ferromagnetic material into magnetic domains reduces the magnetostatic energy
Why domains form
The reason a piece of magnetic material such as iron spontaneously divides into separate domains, rather than exist in a state with magnetization in the same direction throughout the material, is to minimize its internal energy.[3] A large region of ferromagnetic material with a constant magnetization throughout will create a large magnetic field extending into the space outside itself (diagram a, right). This requires a lot of magnetostatic energy stored in the field. To reduce this energy, the sample can split into two domains, with the magnetization in opposite directions in each domain (diagram b right). The magnetic field lines pass in loops in opposite directions through each domain, reducing the field outside the material. To reduce the field energy further, each of these domains can split also, resulting in smaller parallel domains with magnetization in alternating directions, with smaller amounts of field outside the material.
The domain structure of actual magnetic materials does not usually form by the process of large domains splitting into smaller ones as described here. When a sample is cooled below the Curie temperature, for example, the equilibrium domain configuration simply appears. But domains can split, and the description of domains splitting is often used to reveal the energy tradeoffs in domain formation.
Size of domains
As explained above, a domain which is too big is unstable, and will divide into smaller domains. But a small enough domain will be stable and will not split, and this determines the size of the domains created in a material. This size depends on the balance of several energies within the material.[3] Each time a region of magnetization splits into two domains, it creates a domain wall between the domains, where magnetic dipoles (molecules) with magnetization pointing in different directions are adjacent. The exchange interaction which creates the magnetization is a force which tends to align nearby dipoles so they point in the same direction. Forcing adjacent dipoles to point in different directions requires energy. Therefore, a domain wall requires extra energy, called the domain wall energy, which is proportional to the area of the wall.
Thus the net amount that the energy is reduced when a domain splits is equal to the difference between the magnetic field energy saved, and the additional energy required to create the domain wall. The field energy is proportional to the cube of the domain size, while the domain wall energy is proportional to the square of the domain size. So as the domains get smaller, the net energy saved by splitting decreases. The domains keep dividing into smaller domains until the energy cost of creating an additional domain wall is just equal to the field energy saved. Then the domains of this size are stable. In most materials the domains are microscopic in size, around 10−4 - 10−6 m[citation needed].
Magnetic anisotropy
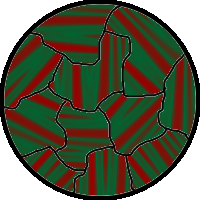
Micrograph of surface of ferromagnetic material, showing the crystal grains, each divided into several domains parallel to its "easy" axis of magnetization, with the magnetization in alternating directions (red and green areas).

Animation showing how magnetostriction works. A changing external magnetic field causes the magnetic dipoles to rotate, changing the dimensions of the crystal lattice.
An additional way for the material to further reduce its magnetostatic energy is to form domains with magnetization at right angles to the other domains (diagram c, right), instead of just in opposing parallel directions.[3] These domains, called flux closure domains, allow the field lines to turn 180° within the material, forming closed loops entirely within the material, reducing the magnetostatic energy to zero. However, forming these domains incurs two additional energy costs. First, the crystal lattice of most magnetic materials has magnetic anisotropy, which means it has an "easy" direction of magnetization, parallel to one of the crystal axes. Changing the magnetization of the material to any other direction takes additional energy, called the "magnetocrystalline anisotropy energy".
Magnetostriction
The other energy cost to creating domains with magnetization at an angle to the "easy" direction is caused by the phenomenon called magnetostriction.[3] When the magnetization of a piece of magnetic material is changed to a different direction, it causes a slight change in its shape. The change in magnetic field causes the magnetic dipole molecules to change shape slightly, making the crystal lattice longer in one dimension and shorter in other dimensions. However, since the magnetic domain is "squished in" with its boundaries held rigid by the surrounding material, it cannot actually change shape. So instead, changing the direction of the magnetization induces tiny mechanical stresses in the material, requiring more energy to create the domain. This is called "magnetoelastic anisotropy energy".
To form these closure domains with "sideways" magnetization requires additional energy due to the aforementioned two factors. So flux closure domains will only form where the magnetostatic energy saved is greater than the sum of the "exchange energy" to create the domain wall, the magnetocrystalline anisotropy energy, and the magnetoelastic anisotropy energy. Therefore, most of the volume of the material is occupied by domains with magnetization either "up" or "down" along the "easy" direction, and the flux closure domains only form in small areas at the edges of the other domains where they are needed to provide a path for magnetic field lines to change direction (diagram c, above).
Grain structure
The above describes magnetic domain structure in a perfect crystal lattice, such as would be found in a single crystal of iron. However most magnetic materials are polycrystalline, composed of microscopic crystalline grains. These grains are not the same as domains. Each grain is a little crystal, with the crystal lattices of separate grains oriented in random directions. In most materials, each grain is big enough to contain several domains. Each crystal has an "easy" axis of magnetization, and is divided into domains with the axis of magnetization parallel to this axis, in alternate directions.
"Magnetized" states
It can be seen that, although on a microscopic scale almost all the magnetic dipoles in a piece of ferromagnetic material are lined up parallel to their neighbors in domains, creating strong local magnetic fields, energy minimization results in a domain structure that minimizes the large-scale magnetic field. The magnetization of neighboring domains point in different directions, confining the field lines to microscopic loops between neighboring domains within the material, so the combined fields cancel at a distance. Therefore, a bulk piece of ferromagnetic material in its lowest energy state has little or no external magnetic field. The material is said to be "unmagnetized".
However, the domains can also exist in other configurations in which their magnetization mostly points in the same direction, creating an external magnetic field. Although these are not minimum energy configurations, due to a phenomenon where the domain walls become "pinned" to defects in the crystal lattice they can be local minimums of the energy, and therefore can be very stable. Applying an external magnetic field to the material can make the domain walls move, causing the domains aligned with the field to grow, and the opposing domains to shrink. When the external field is removed, the domain walls remain pinned in their new orientation and the aligned domains produce a magnetic field. This is what happens when a piece of ferromagnetic material is "magnetized" and becomes a permanent magnet.
Heating a magnet, subjecting it to vibration by hammering it, or applying a rapidly oscillating magnetic field from a degaussing coil, tends to pull the domain walls free from their pinned states, and they will return to a lower energy configuration with less external magnetic field, thus "demagnetizing" the material.
Landau-Lifshitz energy equation
Electromagnetic dynamic magnetic domain motion of grain oriented electrical silicon steel

Moving domain walls in a grain of silicon steel caused by an increasing external magnetic field in the "downward" direction, observed in a Kerr microscope. White areas are domains with magnetization directed up, dark areas are domains with magnetization directed down.
The contributions of the different internal energy factors described above is expressed by the free energy equation proposed by Lev Landau and Evgeny Lifshitz in 1935,[4] which forms the basis of the modern theory of magnetic domains. The domain structure of a material is the one which minimizes the Gibbs free energy of the material. For a crystal of magnetic material, this is the Landau-Lifshitz free energy, E, which is the sum of these energy terms:[5]
E=Eex+ED+Eλ+Ek+EH{displaystyle E=E_{ex}+E_{D}+E_{lambda }+E_{k}+E_{H},}
where
Eex is exchange energy: This is the energy due to the exchange interaction between magnetic dipole molecules in ferromagnetic, ferrimagnetic and antiferromagnetic materials. It is lowest when the dipoles are all pointed in the same direction, so it is responsible for magnetization of magnetic materials. When two domains with different directions of magnetization are next to each other, at the domain wall between them magnetic dipoles pointed in different directions lie next to each other, increasing this energy. This additional exchange energy is proportional to the total area of the domain walls.
ED is magnetostatic energy: This is a self-energy, due to the interaction of the magnetic field created by the magnetization in some part of the sample on other parts of the same sample. It is dependent on the volume occupied by the magnetic field extending outside the domain. This energy is reduced by minimizing the length of the loops of magnetic field lines outside the domain. For example, this tends to encourage the magnetization to be parallel to the surfaces of the sample, so the field lines won't pass outside the sample. Reducing this energy is the main reason for the creation of magnetic domains.
Eλ is magnetoelastic anisotropy energy: This energy is due to the effect of magnetostriction, a slight change in the dimensions of the crystal when magnetized. This causes elastic strains in the lattice, and the direction of magnetization that minimizes these strain energies will be favored. This energy tends to be minimized when the axis of magnetization of the domains in a crystal are all parallel.
Ek is magnetocrystalline anisotropy energy: Due to its magnetic anisotropy, the crystal lattice is "easy" to magnetize in one direction, and "hard" to magnetize in others. This energy is minimized when the magnetization is along the "easy" crystal axis, so the magnetization of most of the domains in a crystal grain tend to be in either direction along the "easy" axis. Since the crystal lattice in separate grains of the material is usually oriented in different random directions, this causes the dominant domain magnetization in different grains to be pointed in different directions.
EH is Zeeman energy: This is energy which is added to or subtracted from the magnetostatic energy, due to the interaction between the magnetic material and an externally applied magnetic field. It is proportional to the negative of the cosine of the angle between the field and magnetization vectors. Domains with their magnetic field oriented parallel to the applied field reduce this energy, while domains with their magnetic field oriented opposite to the applied field increase this energy. So applying a magnetic field to a ferromagnetic material generally causes the domain walls to move so as to increase the size of domains lying mostly parallel to the field, at the cost of decreasing the size of domains opposing the field. This is what happens when ferromagnetic materials are "magnetized". With a strong enough external field, the domains opposing the field will be swallowed up and disappear; this is called saturation.
Some sources define a wall energy EW equal to the sum of the exchange energy and the magnetocrystalline anisotropy energy, which replaces Eex and Ek in the above equation.
A stable domain structure is a magnetization function M(x), considered as a continuous vector field, which minimizes the total energy E throughout the material. To find the minimums a variational method is used, resulting in a set of nonlinear differential equations, called Brown's equations after William Fuller Brown Jr. Although in principle these equations can be solved for the stable domain configurations M(x), in practice only the simplest examples can be solved. Analytic solutions do not exist, and numerical solutions calculated by the finite element method are computationally intractable because of the large difference in scale between the domain size and the wall size. Therefore, micromagnetics has evolved approximate methods which assume that the magnetization of dipoles in the bulk of the domain, away from the wall, all point in the same direction, and numerical solutions are only used near the domain wall, where the magnetization is changing rapidly.

Rotation of orientation and increase in size of magnetic domains in response to an externally applied field.
Domain imaging techniques
There are a number of microscopy methods that can be used to visualize the magnetization at the surface of a magnetic material, revealing the magnetic domains. Each method has a different application because not all domains are the same. In magnetic materials, domains can be circular, square, irregular, elongated, and striped, all of which have varied sizes and dimensions.
Magneto-optic Kerr effect (MOKE)
Large domains, within the range of 25-100 micrometers can be easily seen by Kerr microscopy, which uses the magneto-optic Kerr effect, which is the rotation of the polarization of light reflected from a magnetized surface.
Lorentz microscopy
Lorentz microscopy is a transmission electron microscopy technique used to study magnetic domain structures at very high resolution. Off-axis electron holography is a related technique used to observe magnetic structures by detecting nanoscale magnetic fields.
Magnetic force microscopy (MFM)
Another technique for viewing sub-microscopic domain structures down to a scale of a few nanometers is magnetic force microscopy. MFM is a form of atomic force microscopy that uses a magnetically coated probe tip to scan the sample surface.
Bitter method
Bitter patterns are a technique for imaging magnetic domains that were first observed by Francis Bitter.[6] The technique involves placing a small quantity of ferrofluid on the surface of a ferromagnetic material. The ferrofluid arranges itself along magnetic domain walls, which have higher magnetic flux than the regions of the material located within domains.
A modified Bitter technique has been incorporated into a widely used device, the Large Area Domain Viewer, which is particularly useful in the examination of grain-oriented silicon steels.[7]
.mw-parser-output .tmulti .thumbinner{display:flex;flex-direction:column}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .trow{display:flex;flex-direction:row;clear:left;flex-wrap:wrap;width:100%;box-sizing:border-box}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsingle{margin:1px;float:left}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .theader{clear:both;font-weight:bold;text-align:center;align-self:center;background-color:transparent;width:100%}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .thumbcaption{text-align:left;background-color:transparent}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .text-align-left{text-align:left}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .text-align-right{text-align:right}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .text-align-center{text-align:center}@media all and (max-width:720px){.mw-parser-output .tmulti .thumbinner{width:100%!important;box-sizing:border-box;max-width:none!important;align-items:center}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .trow{justify-content:center}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsingle{float:none!important;max-width:100%!important;box-sizing:border-box;text-align:center}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .thumbcaption{text-align:center}}



See also
- Barkhausen effect
- Bloch wall
- Coercivity
- Topological defect
References
^ P. Weiss (1906) La variation du ferromagnetisme du temperature, Comptes Rendus, 143, p.1136-1149, cited in
Cullity, 2008, p.116
^ Cullity; C. D. Graham (2008). Introduction to Magnetic Materials, 2nd ed. New York: Wiley–IEEE. p. 116. ISBN 0-471-47741-9..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}.
^ abcd Feynman, Richard P.; Robert B. Leighton; Matthew Sands (1963). The Feynman Lectures on Physics, Vol. II. US: California Inst. of Technology. pp. 37.5–37.6. ISBN 0-201-02117-X.
^ Dan Wei (28 April 2012). Micromagnetics and Recording Materials. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-3-642-28577-6.
^ Carey R., Isaac E.D., Magnetic domains and techniques for their observation, The English University Press Ltd, London, (1966).
^ A Dictionary of Physics. Oxford University Press, 2009.
^ R. J. Taylor, A Large area domain viewer, Proceedings of SMM9, 1989
Jiles, David (1998). Introduction to magnetism and magnetic materials. London: Chapman & Hall. ISBN 0-412-79860-3.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Magnetic domains. |
Magnetismus und Magnetooptik a German text about magnetism and magneto-optics


