The Old Swiss Confederacy
Old Swiss Confederacy Eidgenossenschaft (German) République des Suisses (French) Res publica Helvetiorum (Latin) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
c. 1300 – 1798 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
 Swiss cross (field sign c. 1470–1500) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
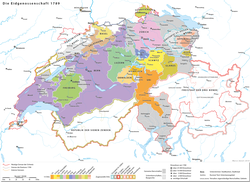 The Old Swiss Confederacy in the 18th century | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | see Vorort[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Middle French / French, Alemannic German, Lombard, Rhaeto-Romansh | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholic Reformed | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Legislature | Tagsatzung | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||
• Death of Rudolf I | 15 July 1291 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• Rütlischwur, Burgenbruch | 1307/1291 (traditional dates) 1291 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• Charles IV's Golden Bull | 1356 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• Battle of Marignano | 13–14 September 1515 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• Wars of Kappel | 1529 and 1531 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• Formal independence from the HRE | 15 May/24 October 1648 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• Swiss peasant war | January–June 1653 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• Collapse | 5 March 1798 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Switzerland |
 |
Early history |
|
Old Swiss Confederacy |
|
Transitional period |
|
Modern history |
|
Timeline |
Topical |
|
The Old Swiss Confederacy (Modern German: Alte Eidgenossenschaft; historically Eidgenossenschaft, after the Reformation also République des Suisses, Res publica Helvetiorum "Republic of the Swiss") was a loose confederation of independent small states (cantons, German Orte or Stände[2]) within the Holy Roman Empire. It is the precursor of the modern state of Switzerland.
It formed during the 14th century, from a nucleus in what is now Central Switzerland, expanding to include the cities of Zürich and Berne by the middle of the century. This formed a rare union of rural and urban communes, all of which enjoyed imperial immediacy in the Holy Roman Empire.
This confederation of eight cantons (Acht Orte) was politically and militarily successful for more than a century, culminating in the Burgundy Wars of the 1470s which established it as a power in the complicated political landscape dominated by France and the Habsburgs. Its success resulted in the addition of more confederates, increasing the number of cantons to thirteen (Dreizehn Orte) by 1513. The confederacy pledged neutrality in 1647 (under the threat of the Thirty Years' War), although many Swiss served privately as mercenaries in the Italian Wars and during the Early Modern period.
After the Swabian War of 1499 the confederacy was a de facto independent state throughout the early modern period, although still nominally part of the Holy Roman Empire until 1648 when the Treaty of Westphalia ended the Thirty Years' War. The Swiss Reformation divided the confederates into Reformed and Catholic parties, resulting in internal conflict from the 16th to the 18th centuries; as a result, the federal diet (Tagsatzung) was often paralysed by hostility between the factions. The Swiss Confederacy fell to invasion by the French Revolutionary Army in 1798, after which it became the short-lived Helvetic Republic.
Contents
1 Name
2 History
2.1 Foundation
2.2 Expansion
2.3 Reformation
2.4 Early modern period
2.5 Collapse
3 Structure
4 List of territories
4.1 Cantons
4.2 Associates
4.2.1 Closest associates
4.2.2 Eternal associates
4.2.3 Protestant associates
4.2.4 Other
4.3 Condominiums
4.3.1 German bailiwicks
4.3.2 Italian bailiwicks
4.3.3 Two-party condominiums
4.3.3.1 Bern and Fribourg
4.3.3.2 Glarus and Schwyz
4.3.3.3 Condominiums with third-parties
4.4 Protectorates
4.5 Separate subjects
4.5.1 Uri
4.5.2 Schwyz
4.5.3 Glarus
4.5.4 Valais
4.5.5 Three Leagues
5 Notes and references
6 Further reading
7 External links
Name

The "Swiss Bull" (Der Schweitzer Stier), horns decorated with a wreath showing the coats of arms of the Thirteen Cantons of the Confederacy (1584)
The adjective "old" was introduced after the Napoleonic era with Ancien Régime, retronyms distinguishing the pre-Napoleonic from the restored confederation. During its existence the confederacy was known as Eidgenossenschaft or Eydtgnoschafft ("oath fellowship"), in reference to treaties among cantons; this term was first used in the 1370 Pfaffenbrief. Territories of the confederacy came to be known collectively as Schweiz or Schweizerland (Schwytzerland in contemporary spelling), with the English Switzerland beginning during the mid-16th century. From that time the Confederacy was seen as a single state, also known as the Swiss Republic (Republic der Schweitzer, République des Suisses and Republica Helvetiorum by Josias Simmler in 1576) after the fashion of calling individual urban cantons republics (such as the Republics of Zürich, Berne and Basel).
History

Territorial development of Old Swiss Confederacy, 1291–1797
Foundation
The nucleus of the Old Swiss Confederacy was an alliance among the valley communities of the central Alps to facilitate management of common interests (such as trade) and ensure peace along trade routes through the mountains. The foundation of the Confederacy is marked by the Rütlischwur (dated to 1307 by Aegidius Tschudi) or the 1315 Pact of Brunnen.
Since 1889, the Federal Charter of 1291 among the rural communes of Uri, Schwyz, and Unterwalden has been considered the founding document of the confederacy.[3]
Expansion
The initial pact was augmented by pacts with the cities of Lucerne, Zürich, and Berne. This union of rural and urban communes, which enjoyed the status of imperial immediacy within the Holy Roman Empire, was engendered by pressure from Habsburg dukes and kings who had ruled much of the land. In several battles with Habsburg armies, the Swiss were victorious; they conquered the rural areas of Glarus and Zug, which became members of the confederacy.[3]
From 1353 to 1481, the federation of eight cantons—known in German as the Acht Orte (Eight Cantons)—consolidated its position. The members (especially the cities) enlarged their territory at the expense of local counts—primarily by buying judicial rights, but sometimes by force. The Eidgenossenschaft, as a whole, expanded through military conquest: the Aargau was conquered in 1415 and the Thurgau in 1460. In both cases, the Swiss profited from weakness in the Habsburg dukes. In the south, Uri led a military territorial expansion that (after many setbacks) would by 1515 lead to the conquest of the Ticino.
None of these territories became members of the confederacy; they had the status of condominiums (regions administered by several cantons).
At this time, the eight cantons gradually increased their influence on neighbouring cities and regions through additional alliances. Individual cantons concluded pacts with Fribourg, Appenzell, Schaffhausen, the abbot and the city of St. Gallen, Biel, Rottweil, Mulhouse and others. These allies (known as the Zugewandte Orte) became closely associated with the confederacy, but were not accepted as full members.
The Burgundy Wars prompted a further enlargement of the confederacy; Fribourg and Solothurn were accepted in 1481. In the Swabian War against Holy Roman Emperor Maximilian I, the Swiss were victorious and exempted from imperial legislation. The associated cities of Basel and Schaffhausen joined the confederacy as a result of that conflict, and Appenzell followed suit in 1513 as the thirteenth member. The federation of thirteen cantons (Dreizehn Orte) constituted the Old Swiss Confederacy until its demise in 1798.
The expansion of the confederacy was stopped by the Swiss defeat in the 1515 Battle of Marignano. Only Berne and Fribourg were still able to conquer the Vaud in 1536; the latter primarily became part of the canton of Berne, with a small portion under the jurisdiction of Fribourg.
Reformation

The forces of Zürich are defeated in the Second War of Kappel.
The Reformation in Switzerland led to doctrinal division amongst the cantons.[3] Zürich, Berne, Basel, Schaffhausen and associates Biel, Mulhouse, Neuchâtel, Geneva and the city of St. Gallen became Protestant; other members of the confederation and the Valais remained Catholic. In Glarus, Appenzell, in the Grisons and in most condominiums both religions coexisted; Appenzell split in 1597 into a Catholic Appenzell Inner Rhodes and a Protestant Appenzell Outer Rhodes.
The division led to civil war (the Wars of Kappel) and separate alliances with foreign powers by the Catholic and Protestant factions, but the confederacy as a whole continued to exist. A common foreign policy was blocked, however, by the impasse. During the Thirty Years' War, religious disagreements among the cantons kept the confederacy neutral and spared it from belligerents. At the Peace of Westphalia, the Swiss delegation was granted formal recognition of the confederacy as a state independent of the Holy Roman Empire.
Early modern period
Growing social differences and an increasing absolutism in the city cantons during the Ancien Régime led to local popular revolts. An uprising during the post-war depression after the Thirty Years' War escalated to the Swiss peasant war of 1653 in Lucerne, Berne, Basel, Solothurn and the Aargau. The revolt was put down swiftly by force and with the help of many cantons.
Religious differences were accentuated by a growing economic discrepancy. The Catholic, predominantly rural central-Swiss cantons were surrounded by Protestant cantons with increasingly commercial economies. The politically dominant cantons were Zürich and Berne (both Protestant), but the Catholic cantons were influential since the Second War of Kappel in 1531. A 1655 attempt (led by Zürich) to restructure the federation was blocked by Catholic opposition, which led to the first battle of Villmergen in 1656; the Catholic party won, cementing the status quo. The problems remained unsolved, erupting again in 1712 with the second battle of Villmergen. This time the Protestant cantons won, dominating the confederation. True reform, however, was impossible; the individual interests of the thirteen members were too diverse, and the absolutist cantonal governments resisted all attempts at confederation-wide administration. Foreign policy remained fragmented.
Collapse
Attempting to gain control of key Alpine passes and establish a buffer against hostile monarchies, France first invaded associates of the Swiss Confederation; part of the bishopric of Basel was absorbed by France in 1793. In 1797, Napoleon annexed the Valtellina (on the border with Graubünden) into the new Cisalpine Republic in northern Italy and invaded the southern remainder of the bishopric of Basel.[4][5]
In 1798 the confederacy was invaded by the French Revolutionary Army at the invitation of the Republican faction in Vaud, led by Frédéric-César de La Harpe. Vaud was under Bernese control, but chafed under a government with a different language and culture. The ideals of the French Revolution found a receptive audience in Vaud, and when Vaud declared itself a republic the French had a pretext to invade the confederation.
The invasion was largely peaceful (since the Swiss people failed to respond to political calls to take up arms), and the collapse of the confederacy was due more to internal strife than external pressure. Only Bern put up an effective resistance, but after its defeat in the March Battle of Grauholz it capitulated. The canton of Bern was divided into the canton of Oberland (with Thun as its capital) and the canton of Léman (with Lausanne as its capital).
The Helvetic Republic was proclaimed on 12 April 1798 as "one and indivisible", abolishing cantonal sovereignty and feudal rights and reducing the cantons to administrative districts. This system was unstable due to widespread opposition, and the Helvetic Republic collapsed as a result of the Stecklikrieg. A federalist compromise solution was attempted, but conflict between the federalist elite and republican subjects persisted until the formation of the federal state in 1848.
Structure

Federal Charter of 1291

Old Swiss Confederacy on 1637 map
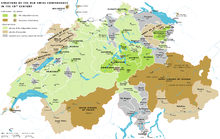
Old Swiss Confederacy in the 18th century
The (Alte) Eidgenossenschaft was initially united not by a single pact, but by overlapping pacts and bilateral treaties between members.[6] The parties generally agreed to preserve the peace, aid in military endeavours and arbitrate disputes. Slowly, the members began to see the confederation as a unifying entity. In the Pfaffenbrief, a treaty of 1370 among six of the eight members (Glarus and Berne did not participate) forbidding feuds and denying clerical courts jurisdiction over the confederacy, the cantons for the first time used the term Eidgenossenschaft. The first treaty uniting the eight members of the confederacy was the Sempacherbrief of 1393, concluded after victories over the Habsburgs at Sempach in 1386 and Näfels in 1388, which forbade a member from unilaterally beginning a war without the consent of the other cantons. A federal diet, the Tagsatzung, developed during the 15th century.
Pacts and renewals (or modernizations) of earlier alliances reinforced the confederacy. The individual interests of the cantons clashed in the Old Zürich War (1436–1450), caused by territorial conflict among Zürich and the central Swiss cantons over the succession of the Count of Toggenburg. Although Zürich entered an alliance with the Habsburg dukes, it then rejoined the confederacy. The confederation had become so close a political alliance that it no longer tolerated separatist tendencies in its members.

Tagsatzung of 1531 in Baden (1790s drawing)
The Tagsatzung was the confederation council, typically meeting several times a year. Each canton delegated two representatives (including the associate states, which had no vote). The canton where the delegates met initially chaired the gathering, but during the 16th century Zürich permanently assumed the chair (Vorort) and Baden became the seat. The Tagsatzung dealt with inter-cantonal affairs and was the court of last resort in disputes between member states, imposing sanctions on dissenting members. It also administered the condominiums; the reeves were delegated for two years, each time by a different canton.[7]
A unifying treaty of the Old Swiss Confederacy was the Stanser Verkommnis of 1481. Conflicts between rural and urban cantons and disagreements over the bounty of the Burgundian Wars had led to skirmishes. The city-states of Fribourg and Solothurn wanted to join the confederacy, but were distrusted by the central Swiss rural cantons. The compromise by the Tagsatzung in the Stanser Verkommnis restored order and assuaged the rural cantons' complaints, with Fribourg and Solothurn accepted into the confederation. While the treaty restricted freedom of assembly (many skirmishes arose from unauthorised expeditions by soldiers from the Burgundian Wars), it reinforced agreements amongst the cantons in the earlier Sempacherbrief and Pfaffenbrief.
The civil war during the Reformation ended in a stalemate. The Catholic cantons could block council decisions but, due to geographic and economic factors, could not prevail over the Protestant cantons. Both factions began to hold separate councils, still meeting at a common Tagsatzung (although the common council was deadlocked by disagreements between both factions until 1712, when the Protestant cantons gained power after their victory in the second war of Villmergen). The Catholic cantons were excluded from administering the condominiums in the Aargau, the Thurgau and the Rhine valley; in their place, Berne became co-sovereign of these regions.
List of territories
Cantons

The 13 cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy

Structure of the Confederacy during the 18th century
The confederation expanded in several stages: first to the Eight Cantons (Acht Orte), then in 1481 to ten, in 1501 to twelve, and finally to thirteen cantons (Dreizehn Orte).[8]
- Founding cantons (Urkantone):
 Uri, founding canton named in the Federal Charter of 1291
Uri, founding canton named in the Federal Charter of 1291
 Schwyz, founding canton named in the Federal Charter of 1291
Schwyz, founding canton named in the Federal Charter of 1291
 Unterwalden, founding canton named in the Federal Charter of 1291
Unterwalden, founding canton named in the Federal Charter of 1291
- 14th century: expansion to the Achtörtige Eidgenossenschaft following the battles of Morgarten and Laupen:
 Lucerne, city canton, since 1332
Lucerne, city canton, since 1332
 Zürich, city canton, since 1351
Zürich, city canton, since 1351
 Glarus, rural canton, since 1352
Glarus, rural canton, since 1352
 Zug, city canton, since 1352
Zug, city canton, since 1352
 Berne, city canton, since 1353; associate since 1323
Berne, city canton, since 1353; associate since 1323
- 15th century: expansion to the Zehnörtige Eidgenossenschaft following the Burgundian Wars:
 Fribourg, city canton, since 1481; associate since 1454
Fribourg, city canton, since 1481; associate since 1454
 Solothurn, city canton, since 1481; associate since 1353
Solothurn, city canton, since 1481; associate since 1353
- 16th century: expansion to the Dreizehnörtige Eidgenossenschaft following the Swabian War:
 Basel, city canton, since 1501
Basel, city canton, since 1501
 Schaffhausen, city canton, since 1501; associate since 1454
Schaffhausen, city canton, since 1501; associate since 1454
 Appenzell, rural canton, since 1513; associate since 1411
Appenzell, rural canton, since 1513; associate since 1411
Associates

Zugewante Orte of the Old Swiss Confederacy
Associates (Zugewandte Orte) were close allies of the Old Swiss Confederacy, connected to the union by alliance treaties with all or some of the individual members of the confederacy.
Closest associates
Three of the associates were known as Engere Zugewandte:
 Biel – 1344–82 treaties with Fribourg, Berne and Solothurn. Nominally, Biel was subject to the Bishopric of Basel.
Biel – 1344–82 treaties with Fribourg, Berne and Solothurn. Nominally, Biel was subject to the Bishopric of Basel.
 Imperial Abbey of St. Gallen – 1451 treaty with Schwyz, Lucerne, Zürich and Glarus, renewed in 1479 and 1490. The abbey was simultaneously a protectorate.
Imperial Abbey of St. Gallen – 1451 treaty with Schwyz, Lucerne, Zürich and Glarus, renewed in 1479 and 1490. The abbey was simultaneously a protectorate.
 Imperial City of St. Gallen – 1454 treaty with Schwyz, Lucerne, Zürich, Glarus, Zug and Berne.
Imperial City of St. Gallen – 1454 treaty with Schwyz, Lucerne, Zürich, Glarus, Zug and Berne.
Eternal associates
Two federations were known as Ewige Mitverbündete:
 Sieben Zenden, an independent federation in the Valais – Became a Zugewandter Ort in 1416 through an alliance with Uri, Unterwalden and Lucerne, followed by a treaty with Berne in 1446.
Sieben Zenden, an independent federation in the Valais – Became a Zugewandter Ort in 1416 through an alliance with Uri, Unterwalden and Lucerne, followed by a treaty with Berne in 1446.
Three Leagues were independent federations on the territory of the Grisons and became an associates of the Old Swiss Confederacy in 1497/98 through the events of the Swabian War. The Three Leagues together concluded an alliance pact with Berne in 1602.
 Grey League, who had been allied with Glarus, Uri and Obwalden through pacts from 1400, 1407 and 1419, entered an alliance with seven of the old eight cantons (the Acht Orte without Berne) in 1497
Grey League, who had been allied with Glarus, Uri and Obwalden through pacts from 1400, 1407 and 1419, entered an alliance with seven of the old eight cantons (the Acht Orte without Berne) in 1497
 League of God's House (Gotteshausbund) followed suit a year later.
League of God's House (Gotteshausbund) followed suit a year later.
 League of the Ten Jurisdictions, the third of the leagues, entered an alliance with Zürich and Glarus in 1590.
League of the Ten Jurisdictions, the third of the leagues, entered an alliance with Zürich and Glarus in 1590.
Protestant associates
There were two Evangelische Zugewandte:
 Imperial City of Mulhouse – Concluded a first treaty with some cantons in 1466 and became an associate in 1515 through a treaty with all 13 members of the Confederacy, remaining so until events of the French Revolutionary Wars in 1797.
Imperial City of Mulhouse – Concluded a first treaty with some cantons in 1466 and became an associate in 1515 through a treaty with all 13 members of the Confederacy, remaining so until events of the French Revolutionary Wars in 1797.
 Imperial City of Geneva – 1536 treaty with Berne and a 1584 treaty with Zürich and Berne.
Imperial City of Geneva – 1536 treaty with Berne and a 1584 treaty with Zürich and Berne.
Other
 County of Neuchâtel – 1406 and 1526 treaties with Berne and Solothurn, 1495 treaty with Fribourg and 1501 treaty with Lucerne.
County of Neuchâtel – 1406 and 1526 treaties with Berne and Solothurn, 1495 treaty with Fribourg and 1501 treaty with Lucerne.
 Imperial Valley of Urseren – 1317 treaty with Uri; annexed by Uri in 1410.
Imperial Valley of Urseren – 1317 treaty with Uri; annexed by Uri in 1410.
 Weggis – 1332–1380 by treaties with Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden and Lucerne; annexed by Lucerne in 1480.
Weggis – 1332–1380 by treaties with Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden and Lucerne; annexed by Lucerne in 1480.
 Murten – from 1353 by treaty with Berne; became a confederal condominium in 1475.
Murten – from 1353 by treaty with Berne; became a confederal condominium in 1475.
 Payerne – from 1353 by treaty with Berne; annexed by Berne in 1536.
Payerne – from 1353 by treaty with Berne; annexed by Berne in 1536.
 Vogtei of Bellinzona – from 1407 by treaty with Uri and Obwalden; became a confederal condominium from 1419–22.
Vogtei of Bellinzona – from 1407 by treaty with Uri and Obwalden; became a confederal condominium from 1419–22.
 County of Sargans – from 1437 by treaty with Glarus and Schwyz; became a confederal condominium in 1483.
County of Sargans – from 1437 by treaty with Glarus and Schwyz; became a confederal condominium in 1483.
 Barony of Sax-Forstegg – from 1458 by treaty with Zürich; annexed by Zürich in 1615
Barony of Sax-Forstegg – from 1458 by treaty with Zürich; annexed by Zürich in 1615
 Stein am Rhein – from 1459 by treaty with Zürich and Schaffhausen; annexed by Zürich in 1484.
Stein am Rhein – from 1459 by treaty with Zürich and Schaffhausen; annexed by Zürich in 1484.
 County of Gruyère – had been allied with Fribourg and Berne since the early 14th century, becoming a full associate of the Confederation in 1548. When the counts fell bankrupt in 1555, the country was partitioned in twain:[9]
County of Gruyère – had been allied with Fribourg and Berne since the early 14th century, becoming a full associate of the Confederation in 1548. When the counts fell bankrupt in 1555, the country was partitioned in twain:[9]- Lower Gruyère – from 1475 by treaty with Fribourg
- Upper Gruyère – from 1403 by treaty with Berne; annexed by Berne in 1555:
 Imperial Valley of Saanen
Imperial Valley of Saanen
 Imperial Valley of Château-d'Œx
Imperial Valley of Château-d'Œx
 County of Werdenberg – from 1493 by treaty with Lucerne; annexed by Glarus in 1517.
County of Werdenberg – from 1493 by treaty with Lucerne; annexed by Glarus in 1517.
 Imperial City of Rottweil – from 1519–1632 through a treaty with all 13 members; a first treaty on military cooperation had already been concluded in 1463. In 1632, the treaty was renewed with Lucerne, Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden, Zug, Solothurn and Fribourg.
Imperial City of Rottweil – from 1519–1632 through a treaty with all 13 members; a first treaty on military cooperation had already been concluded in 1463. In 1632, the treaty was renewed with Lucerne, Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden, Zug, Solothurn and Fribourg.
 Bishopric of Basel – 1579–1735 by treaty with Lucerne, Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden, Zug, Solothurn and Fribourg.
Bishopric of Basel – 1579–1735 by treaty with Lucerne, Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden, Zug, Solothurn and Fribourg.
Condominiums
Condominiums (German: Gemeine Herrschaften) were common subject territories under the administration of several cantons. They were governed by reeves (Vögte) delegated for two years, each time from another of the responsible cantons. Berne initially did not participate in the administration of some of the eastern condominiums, as it had no part in their conquest and its interests were focused more on the western border. In 1712, Berne replaced the Catholic cantons in the administration of the Freie Ämter ("Free Districts"), the Thurgau, the Rhine valley, and Sargans, and furthermore the Catholic cantons were excluded from the administration of the County of Baden.[6]
German bailiwicks
The "German bailiwicks" (German: Deutsche Gemeine Vogteien, Gemeine Herrschaften) were generally governed by the Acht Orte apart from Berne until 1712, when Bern joined the sovereign powers:
 Freie Ämter – conquered 1415 and partitioned in 1712:
Freie Ämter – conquered 1415 and partitioned in 1712:
- Upper Freiamt was governed by the Acht Orte;
- Lower Freiamt was governed by Zürich, Bern and Glarus alone.
 County of Baden – conquered 1415; from 1712 governed by Zürich, Bern and Glarus.
County of Baden – conquered 1415; from 1712 governed by Zürich, Bern and Glarus.
 County of Sargans – from 1460/83
County of Sargans – from 1460/83
 Landgraviate of Thurgau – from 1460
Landgraviate of Thurgau – from 1460
 Vogtei of Rheintal – from 1490, Acht Orte minus Bern, plus the Imperial Abbey of St Gall. Appenzell added in 1500; Berne added in 1712.
Vogtei of Rheintal – from 1490, Acht Orte minus Bern, plus the Imperial Abbey of St Gall. Appenzell added in 1500; Berne added in 1712.
Italian bailiwicks
Several bailiwicks (Vogteien) were generally referred to as "transmontane bailiwicks" (German: Ennetbergische Vogteien, Italian: Baliaggi Ultramontani).
In 1440, Uri conquered the Leventina Valley from the Visconti, dukes of Milan. Some of this territory had previously been annexed between 1403 and 1422. Further territories were acquired in 1500; see History of Ticino for further details.
Three bailiwicks, all now in the Ticino, were condominiums of the Forest cantons of Uri, Schwyz and Nidwalden:
Vogtei of Blenio – 1477–80 and from 1495
Vogtei of Rivera – 1403–22 and from 1495
Vogtei of Bellinzona – from 1500
Four other Ticinese bailiwicks were condominiums of the Zwölf Orte (the original 13 cantons, minus Appenzell) from 1512:
- Landvogtei of Valmaggia
- Landvogtei of Lugano
- Landvogtei of Locarno
- Landvogtei of Mendrisio
Another three bailiwicks were condominiums of the Zwölf Orte from 1512, but were lost from the Confederacy three years later and are all now comuni of Lombardy:
- Travaglia
- Cuvio
Eschental (now Ossola)
Two-party condominiums
Bern and Fribourg
 County of Grasburg / Schwarzenburg – from 1423
County of Grasburg / Schwarzenburg – from 1423
 Murten – from 1475
Murten – from 1475
 Grandson – from 1475
Grandson – from 1475
 Orbe and Echallens – from 1475
Orbe and Echallens – from 1475
Glarus and Schwyz
 Uznach – from 1437
Uznach – from 1437
 , Windegg / Gaster – from 1438
, Windegg / Gaster – from 1438
 Hohensax / Gams – from 1497
Hohensax / Gams – from 1497
Condominiums with third-parties
- Lordship of Tessenberg – from 1388, condominium between Berne and Bishopric of Basel
Protectorates
 Bellelay Abbey – protectorate of Bern, Biel and Solothurn from 1414; nominally under the jurisdiction of the Bishopric of Basel
Bellelay Abbey – protectorate of Bern, Biel and Solothurn from 1414; nominally under the jurisdiction of the Bishopric of Basel
 Einsiedeln Abbey – protectorate of Schwyz from 1357
Einsiedeln Abbey – protectorate of Schwyz from 1357
 Engelberg Abbey – protectorate of Lucerne, Uri, Schwyz and Unterwalden from 1425
Engelberg Abbey – protectorate of Lucerne, Uri, Schwyz and Unterwalden from 1425
 Erguel – protectorate of Biel/Bienne under military jurisdiction from 1335; also subject to the Bishopric of Basel
Erguel – protectorate of Biel/Bienne under military jurisdiction from 1335; also subject to the Bishopric of Basel
 Imperial Abbey of St. Gallen – protectorate of Schwyz, Lucerne, Zürich and Glarus from 1451; the abbey was simultaneously a Zugewandter Ort.
Imperial Abbey of St. Gallen – protectorate of Schwyz, Lucerne, Zürich and Glarus from 1451; the abbey was simultaneously a Zugewandter Ort.
 Republic of Gersau, an independent village – allied with Schwyz since 1332; Lucerne, Uri and Unterwalden were also protecting powers.
Republic of Gersau, an independent village – allied with Schwyz since 1332; Lucerne, Uri and Unterwalden were also protecting powers.
 Moutier-Grandval Abbey – protectorate of Berne from 1486; the abbey was also subject to the Bishopric of Basel and, until 1797, the Holy Roman Empire
Moutier-Grandval Abbey – protectorate of Berne from 1486; the abbey was also subject to the Bishopric of Basel and, until 1797, the Holy Roman Empire
 La Neuveville – protectorate of Berne from 1388; also subject to the Bishopric of Basel.
La Neuveville – protectorate of Berne from 1388; also subject to the Bishopric of Basel.
 Pfäfers Abbey – protectorate of the Acht Orte minus Berne from 1460; annexed to the County of Sargans in 1483
Pfäfers Abbey – protectorate of the Acht Orte minus Berne from 1460; annexed to the County of Sargans in 1483
 Rapperswil – protectorate of Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden and Glarus from 1464; of Zürich, Berne and Glarus from 1712
Rapperswil – protectorate of Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden and Glarus from 1464; of Zürich, Berne and Glarus from 1712
 County of Toggenburg – protectorate of Schwyz and Glarus from 1436; of Zürich and Berne from 1718. The county was simultaneously subject to St Gallen Abbey.
County of Toggenburg – protectorate of Schwyz and Glarus from 1436; of Zürich and Berne from 1718. The county was simultaneously subject to St Gallen Abbey.
Separate subjects
Some territories were separate subjects of cantons or associates, Einzelörtische Untertanen von Länderorten und Zugewandten:
Uri
 Valley of Leventina (1403, 1439)
Valley of Leventina (1403, 1439)
 Valley of Urseren (1440)
Valley of Urseren (1440)
Schwyz
 Küssnacht (1402)
Küssnacht (1402)
 Einsiedeln Abbey (1397 / 1424)
Einsiedeln Abbey (1397 / 1424)
 March (1405 / 36)
March (1405 / 36)
 Höfe (1440)
Höfe (1440)
Glarus
 County of Werdenberg (1485 / 1517); annexed to Lucerne in 1485; to Glarus in 1517
County of Werdenberg (1485 / 1517); annexed to Lucerne in 1485; to Glarus in 1517
Valais
 St-Maurice (1475 / 77)
St-Maurice (1475 / 77)
 Monthey (1536)
Monthey (1536)
 Nendaz-Hérémence (1475 / 77)
Nendaz-Hérémence (1475 / 77)
 Port Valais/Vionnaz
Port Valais/Vionnaz
Lötschental (15th century); the five upper Zenden
Three Leagues
 Bormio (1512)
Bormio (1512)
Chiavenna (1512)
Valtellina (1512)
Drei Pleven (1512–26)
 Maienfeld (Bündner Herrschaft) (1509–1790); simultaneously a member of the League of the Ten Jurisdictions.
Maienfeld (Bündner Herrschaft) (1509–1790); simultaneously a member of the League of the Ten Jurisdictions.
Notes and references
^ the Swiss diet was presided de facto by Zürich during most of the 15th century. After the Reformation in Switzerland, the system of administration became more multipolar, with Lucerne and Berne playing an important role besides Zürich.Vorort in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
^ In the charters of the 14th century described as "communities" (communitas hominum, Lantlüte), the German term Orte becomes common in the early 15th century, used alongside Stand "estate" after the Reformation. The French term canton is used in Fribourg in 1475, and after 1490 is increasingly used in French and Italian documents. It only enters occasional German usage after 1648, and only gains official status as synonym of Stand with the Act of Mediation of 1803. Kantone in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland, 2016.
^ abc Schwabe & Co.: Geschichte der Schweiz und der Schweizer, Schwabe & Co 1986/2004. .mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
ISBN 3-7965-2067-7 (in German)
^ Swissworld.org accessed 1 February 2013
^ French Invasion in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
^ ab Würgler, A.: Eidgenossenschaft in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland, 8 September 2004.
^ Im Hof, U.. Geschichte der Schweiz, 7th ed., Stuttgart: W. Kohlhammer, 1974/2001.
ISBN 3-17-017051-1. (in German)
^ Boschetti-Maradi, A.: County of Gruyère in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland, 2004-06-28.
Further reading
- Aubert, J.-F.: Petite histoire constitutionnelle de la Suisse, 2nd ed.; Francke Editions, Bern, 1974. (in French)
- Peyer, H. C.: Verfassungsgeschichte der alten Schweiz, Schulthess Polygraphischer Verlag, Zürich, 1978.
ISBN 3-7255-1880-7. (in German)
External links
 Media related to Alte Eidgenossenschaft (Old Swiss Confederacy) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Alte Eidgenossenschaft (Old Swiss Confederacy) at Wikimedia Commons