1912 United States presidential election in Maine
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elections in Maine | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
Ballot measures
| ||||||||
City of Portland
| ||||||||
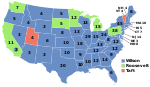
The 1912 United States presidential election in Maine took place on November 5, 1912, as part of the 1912 United States Presidential Election which was held throughout all contemporary 48 states. Voters chose six representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
Maine was won by the Democratic nominees, New Jersey Governor Woodrow Wilson and Indiana Governor Thomas R. Marshall. Wilson and Marshall defeated incumbent President William Howard Taft, and his running mate Vice President James S. Sherman and Progressive Party candidates, former President Theodore Roosevelt and his running mate California Governor Hiram Johnson.
Wilson won Maine by a narrow margin of 2.02 percent, becoming the first Democratic presidential candidate since Franklin Pierce in 1852 to win the state. It would be the final time until 1964 where a Democratic presidential candidate would carry Maine.
With 37.41% of the popular vote, Maine would prove to be Roosevelt's fifth strongest state in terms of popular vote percentage in the 1912 election after South Dakota, California, Michigan and Minnesota.[1]
Results
| United States presidential election in Maine, 1912[2] | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Running mate | Popular vote | Electoral vote | ||||
| Count | % | Count | % | |||||
Democratic | Woodrow Wilson of New Jersey | Thomas Riley Marshall of Indiana | 51,113 | 39.43% | 6 | 100.00% | ||
Progressive | Theodore Roosevelt of New York | Hiram Warren Johnson of California | 48,495 | 37.41% | 0 | 0.00% | ||
Republican | William Howard Taft of Ohio | Nicholas Murray Butler of New York | 26,545 | 20.48% | 0 | 0.00% | ||
Socialist | Eugene Victor Debs of Indiana | Emil Seidel of Wisconsin | 2,541 | 1.96% | 0 | 0.00% | ||
Prohibition | Eugene Wilder Chafin of Illinois | Aaron Sherman Watkins of Ohio | 946 | 0.73% | 0 | 0.00% | ||
Total | 129,640 | 100.00% | 6 | 100.00% | ||||
Results by county
| County | Wilson# | Wilson% | Taft# | Taft% | Roosevelt#[3] | Roosevelt% | Others# | Others% | Total votes cast[4] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Androscoggin | 4,516 | 44.38% | 859 | 8.44% | 4,424 | 43.47% | 377 | 3.70% | 10,176 |
Aroostook | 1,924 | 24.63% | 898 | 11.49% | 4,799 | 61.42% | 192 | 2.46% | 7,813 |
Cumberland | 8,480 | 41.04% | 5,154 | 24.95% | 6,537 | 31.64% | 490 | 2.37% | 20,661 |
Franklin | 1,421 | 37.36% | 668 | 17.56% | 1,633 | 42.93% | 82 | 2.16% | 3,804 |
Hancock | 2,655 | 43.09% | 1,399 | 22.70% | 1,932 | 31.35% | 176 | 2.86% | 6,162 |
Kennebec | 4,397 | 37.82% | 1,782 | 15.33% | 5,196 | 44.69% | 251 | 2.16% | 11,626 |
Knox | 2,751 | 50.03% | 1,097 | 19.95% | 1,392 | 25.31% | 259 | 4.71% | 5,499 |
Lincoln | 1,633 | 43.89% | 457 | 12.28% | 1,527 | 41.04% | 104 | 2.79% | 3,721 |
Oxford | 2,941 | 39.79% | 1,234 | 16.69% | 3,068 | 41.50% | 149 | 2.02% | 7,392 |
Penobscot | 5,093 | 36.17% | 3,367 | 23.91% | 5,294 | 37.59% | 328 | 2.33% | 14,082 |
Piscataquis | 1,210 | 32.10% | 807 | 21.41% | 1,705 | 45.23% | 48 | 1.27% | 3,770 |
Sagadahoc | 1,331 | 38.06% | 885 | 25.31% | 1,129 | 32.28% | 152 | 4.35% | 3,497 |
Somerset | 2,317 | 36.45% | 1,235 | 19.43% | 2,479 | 39.00% | 325 | 5.11% | 6,356 |
Waldo | 2,145 | 44.31% | 881 | 18.20% | 1,636 | 33.79% | 179 | 3.70% | 4,841 |
Washington | 3,178 | 44.44% | 1,862 | 26.03% | 1,993 | 27.87% | 119 | 1.66% | 7,152 |
York | 5,121 | 39.12% | 3,960 | 30.25% | 3,751 | 28.66% | 257 | 1.96% | 13,089 |
| Totals | 51,113 | 39.43% | 26,545 | 20.48% | 48,495 | 37.41% | 3,488 | 2.69% | 129,641 |
References
^ "1912 Presidential Election Statistics". Dave Leip’s Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. Retrieved 2018-03-05..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "1912 Presidential General Election Results – Maine". U.S. Election Atlas. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
^ Géoelections; 1912 Presidential Election Popular Vote (xlsx file for €15)
^ Robinson, Edgar Eugene; The Presidential Vote 1896-1932, pp. 223-224
ISBN 9780804716963