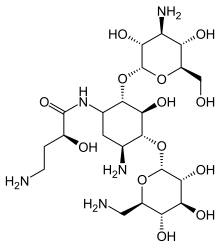
Amikacin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Amikin, Amiglyde-V, other |
AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682661 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | intramuscular, intravenous |
| Drug class | Aminoglycoside |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | >90%[1] |
| Protein binding | 0–11% |
| Metabolism | Mostly unmetabolized |
| Elimination half-life | 2–3 hours |
| Excretion | kidney |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII |
|
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.048.653 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H43N5O13 |
| Molar mass | 585.603 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
.mw-parser-output .nobold{font-weight:normal} (verify) | |
Amikacin is an antibiotic used for a number of bacterial infections.[2] This includes joint infections, intra-abdominal infections, meningitis, pneumonia, sepsis, and urinary tract infections.[2] It is also used for the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis.[3] It is used either by injection into a vein or muscle.[2]
Amikacin, like other aminoglycoside antibiotics, can cause hearing loss, balance problems, and kidney problems.[2] Other side effects include paralysis, resulting in the inability to breathe.[2] If used during pregnancy it may cause permanent deafness in the baby.[2] Amikacin works by blocking the function of the bacteria's 30S ribosomal subunit, making it unable to produce proteins.[2]
Amikacin was patented in 1971 and came into commercial use in 1976.[4][5] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system.[6] The wholesale cost in the developing world is 13.80 to US$130.50 for a month.[7] In the United States a typical course of treatment costs 25 to US$50.[8] It is made from kanamycin.[2]
.mw-parser-output .toclimit-2 .toclevel-1 ul,.mw-parser-output .toclimit-3 .toclevel-2 ul,.mw-parser-output .toclimit-4 .toclevel-3 ul,.mw-parser-output .toclimit-5 .toclevel-4 ul,.mw-parser-output .toclimit-6 .toclevel-5 ul,.mw-parser-output .toclimit-7 .toclevel-6 ul{display:none}
Contents
1 Medical uses
1.1 Available forms
1.2 Special populations
2 Adverse effects
3 Contraindications
4 Interactions
5 Pharmacology
5.1 Mechanism of action
5.1.1 Resistance
5.2 Pharmacokinetics
6 Chemistry
7 Veterinary use
8 References
Medical uses
Amikacin is most often used for treating severe infections with multidrug-resistant, aerobic Gram-negative bacteria, especially Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter, Enterobacter, E. coli, Proteus, Klebsiella, and Serratia.[9] The only Gram-positive bacteria that amikacin strongly affects are Staphylococcus[9] and Nocardia.[10] Amikacin can also be used to treat non-tubercular mycobacterial infections and tuberculosis (if caused by sensitive strains) when first-line drugs fail to control the infection.[2] It is rarely used alone.[11]
It is often used in the following situations:[2]
Bronchiectasis[12]
- Bone and joint infections
Granulocytopenia, when combined with ticarcillin, in people with cancer[13]
- Intra-abdominal infections (such as peritonitis) as an adjunct to other medicines, like clindamycin, metronidazole, piperacillin/tazobactam, or ampicillin/sulbactam
Meningitis:
- for meningitis by E. coli, as an adjunct to imipenem
- for meningitis caused by Pseudomonas, as an adjunct to meropenem
- for meningitis caused by Acetobacter, as an adjunct to imipenem or colistin
- for neonatal meningitis caused by Streptococcus agalactiae or Listeria monocytogenes, as an adjunct to ampicillin
- for neonatal meningitis caused by Gram negative bacteria such as E. coli, as adjunct to a 3rd-generation cephalosporin
- for meningitis by E. coli, as an adjunct to imipenem
- Mycobacterial infections, including as a second-line agent for active tuberculosis.[14] It is also used for infections by Mycobacterium avium, M. abcessus, M. chelonae, and M. fortuitum.
Rhodococcus equi, which causes an infection resembling tuberculosis- Respiratory tract infections, including as an adjunct to beta-lactams or carbapenem for hospital-acquired pneumonia
Septicemia, including that in neonates,[9] as an adjunct to beta-lactams or carbapenem- Skin and suture-site infections[9]
Urinary tract infections that are caused by bacteria resistant to less toxic drugs (often by Enterobacteriaceae or P. aeruginosa)
Amikacin may be combined with a beta-lactam antibiotic for empiric therapy for people with neutropenia and fever.[2]
Available forms
Amikacin may be administered once or twice a day and is usually given by the intravenous or intramuscular route, though it can be given via nebulization. There is no oral form available, as amikacin is not absorbed orally. In people with kidney failure, dosage must be adjusted according to the creatinine clearance, usually by reducing the dosing frequency.[9] In people with a CNS infection such as meningitis, amikacin can be given intrathecally (by direct injection into the spine) or intraventricularly (by injection into the ventricles of brain).[2]
An liposome inhalation suspension is also available and approved to treat Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC).[15]
Special populations
Amikacin should be used in smaller doses in the elderly, who often have age-related decreases in kidney function, and children, whose kidneys are not fully developed yet. It is considered pregnancy category D in both the United States and Australia, meaning they have a probability of harming the fetus.[2] Around 16% of amikacin crosses the placenta; while the half-life of amikacin in the mother is 2 hours, it is 3.7 hours in the fetus.[9] A pregnant woman taking amikacin with another aminoglycoside has a possibility of causing congenital deafness in her child. While it is known to cross the placenta, amikacin is only partially secreted in breast milk.[2]
In general, amikacin should be avoided in infants.[16] Infants also tend to have a larger volume of distribution due to their higher concentration of extracellular fluid, where aminoglycosides reside.[1]
The elderly tend to have amikacin stay longer in their system; while the average clearance of amikacin in a 20-year-old is 6 L/hr, it is 3 L/hr in an 80-year-old.[17]
Clearance is even higher in people with cystic fibrosis.[18]
In people with muscular disorders such as myasthenia gravis or Parkinson's disease, amikacin's paralytic effect on neuromuscular junctions can worsen muscle weakness.[2]
Adverse effects
Side-effects of amikacin are similar to those of other aminoglycosides. Kidney damage and ototoxicity (which can lead to hearing loss) are the most important effects, occurring in 1–10% of users.[12] The nephro- and ototoxicity are thought to be due to aminoglycosides' tendency to accumulate in the kidneys and inner ear.[1]
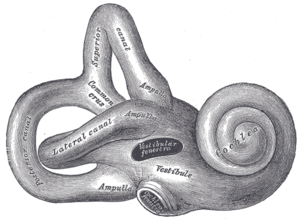
Diagram of the inner ear. Amikacin causes damage to the cochlea and vestibules.
Amikacin can cause neurotoxicity if used at a higher dose or for longer than recommended. The resulting effects of neurotoxicity include vertigo, numbness, tingling of the skin (paresthesia), muscle twitching, and seizures.[2] Its toxic effect on the 8th cranial nerve causes ototoxicity, resulting in loss of balance and, more commonly, hearing loss.[1] Damage to the cochlea, caused by the forced apoptosis of the hair cells, leads to the loss of high-frequency hearing and happens before any clinical hearing loss can be detected.[9][19] Damage to the ear vestibules, most likely by creating excessive oxidative free radicals. It does so in a time-dependent rather than dose-dependent manner, meaning that risk can be minimized by reducing the duration of use.[20]
Amikacin causes nephrotoxicity (damage to the kidneys), by acting on the proximal renal tubules. It easily ionizes to a cation and binds to the anionic sites of the epithelial cells of the proximal tubule as part of receptor-mediated pinocytosis. The concentration of amikacin in the renal cortex becomes ten times that of amikacin in the plasma;[16] it then most likely interferes with the metabolism of phospholipids in the lysosomes, which causes lytic enzymes to leak into the cytoplasm.[1] Nephrotoxicity results in increased serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, red blood cells, and white blood cells, as well as albuminuria (increased output of albumin in the urine), glycosuria (excretion of glucose into the urine), decreased urine specific gravity, and oliguria (decrease in overall urine output).[9][19] It can also cause urinary casts to appear.[1] The changes in renal tubular function also change the electrolyte levels and acid-base balance in the body, which can lead to hypokalemia and acidosis or alkalosis.[20] Nephrotoxicity is more common in those with pre-existing hypokalema, hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, acidosis, low glomerular filtration rate, diabetes mellitus, dehydration, fever, and sepsis, as well as those taking antiprostaglandins.[2][16][1][20] The toxicity usually reverts once the antibiotic course has been completed,[1] and can be avoided altogether by less frequent dosing (such as once every 24 hours rather than once every 8 hours).[16]
Amikacin can cause neuromuscular blockade (including acute muscular paralysis) and respiratory paralysis (including apnea).[2]
Rare side effects (occurring in fewer than 1% of users) include allergic reactions, skin rash, fever, headaches, tremor, nausea and vomiting, eosinophilia, arthralgia, anemia, hypotension, and hypomagnesemia. In intravitreous injections (where amikacin is injected into the eye), macular infarction can cause permanent vision loss.[9][12]
Contraindications
Amikacin should be avoided in those who are sensitive to any aminoglycoside, as they are cross-allergenic (that is, an allergy to one aminoglycoside also confers hypersensitivity to other aminoglycosides). It should also be avoided in those sensitive to sulfite (seen more among people with asthma),[9] since most amikacin usually comes with sodium metabisulfite, which can cause an allergic reaction.[2]
In general, amikacin should not be used with or just before/after another drug that can cause neurotoxicity, ototoxicity, or nephrotoxicity. Such drugs include other aminoglycosides; the antiviral acyclovir; the antifungal amphotericin B; the antibiotics bacitracin, capreomycin, colistin, polymyxin B, and vancomycin; and cisplatin, which is used in chemotherapy.[2]
Amikacin should not be used with neuromuscular blocking agents, as they can increase muscle weakness and paralysis.[2]
Interactions
Amikacin can be inactivated by other beta-lactams, though not to the extent as other aminoglycosides, and is still often used with penicillins (a type of beta-lactam) to create an additive effect against certain bacteria, and carbapenems, which can have a synergistic against some Gram-positive bacteria. Another group of beta-lactams, the cephalosporins, can increase the nephrotoxicity of aminoglycoside as well as randomly elevating creatinine levels. The antibiotics chloramphenicol, clindamycin, and tetracycline have been known to inactivate aminoglycosides in general by pharmacological antagonism.[2]
The effect of amikacin is increased when used with drugs derived from the botulinum toxin,[12]anesthetics, neuromuscular blocking agents, or large doses of blood that contains citrate as an anticoagulant.[2]
Potent diuretics not only cause ototoxicity themselves, but they can also increase the concentration of amikacin in the serum and tissue, making the ototoxicity even more likely.[2]Quinidine also increases levels of amikacin in the body.[12] The NSAID indomethacin can increase serum aminoglycoside levels in premature infants.[2] Contrast mediums such as ioversol increases the nephrotoxicity and otoxicity caused by amikacin.[12]
Amikacin can decrease the effect certain vaccines, such as the live BCG vaccine (used for tuberculosis), the cholera vaccine, and the live typhoid vaccine by acting as a pharmacological antagonist.[12]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action

The 30S subunit of the prokaryotic ribosome. The orange represents the 16S rRNA, and the blue represents the various proteins attached.
Amikacin irreversibly binds to 16S rRNA and the RNA-binding S12 protein of the 30S subunit of prokaryotic ribosome and inhibits protein synthesis by changing the ribosome's shape so that it cannot read the mRNA codons correctly.[9][21] It also interferes with the region that interacts with the wobble base of the tRNA anticodon.[22] It works in a concentration-dependent manner, and has better action in an alkaline environment.[1]
At normal doses, amikacin-sensitive bacteria respond within 24–48 hours.[9]
Resistance
Amikacin evades attacks by all antibiotic-inactivating enzymes that are responsible for antibiotic resistance in bacteria, except for aminoacetyltransferase and nucleotidyltransferase.[23] This is accomplished by the L-hydroxyaminobuteroyl amide (L-HABA) moiety attached to N-1 (compare to kanamycin, which simply has a hydrogen), which blocks the access and decreases the affinity of aminoglycoside-inactivating enzymes.[23][24][25] Amikacin ends up with only one site where these enzymes can attack, while gentamicin and tobramycin have six.[11]
Bacteria that are resistant to streptomycin and capreomycin are still susceptible to amikacin; bacteria that are resistant to kanamycin have varying susceptibility to amikacin. Resistance to amikacin also confers resistance to kanamycin and capreomycin.[26]
Resistance to amikacin and kanamycin in Mycobacterium, the causative agent of tuberculosis, is due to a mutation in the rrs gene, which codes for the 16S rRNA. Mutations such as these reduce the binding affinity of amikacin to the bacteria's ribosome.[27] Variations of aminoglycoside acetyltransferase (AAC) and aminoglycoside adenylyltransferase (AAD) also confer resistance: resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa is caused by AAC(6')-IV, which also confers resistance to kanamycin, gentamicin, and tobramycin, and resistance in Staphylococcus aureus and S. epidermidis is caused by AAD(4',4), which also confers resistance to kanamycin, tobramycin, and apramycin.[24] Some strains of S. aureus can also inactivate amikacin by phosphorylating it.[13]
Pharmacokinetics
Amikacin is not absorbed orally and thus must be administered parenterally. It reaches peak serum concentrations in 0.5–2 hours when administered intramuscularly. Less than 11% of the amikacin actually binds to plasma proteins. It is distributed into the heart, gallbladder, lungs, and bones, as well as in bile, sputum, interstitial fluid, pleural fluid, and synovial fluids. It is usually found at low concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid, except when administered intraventricularly.[2] In infants, amikacin is normally found at 10–20% of plasma levels in the spinal fluid, but the amount reaches 50% in cases of meningitis.[9] It does not easily cross the blood-brain barrier or enter ocular tissue.[1]
While the half-life of amikacin is normally two hours, it is 50 hours in those with end-stage renal disease.[11]
The vast majority (95%) of amikacin from an IM or IV dose is secreted unchanged via glomerular filtration and into the urine within 24 hours.[2][11] Factors that cause amikacin to be excreted via urine include its relatively low molecular weight, high water solubility, and unmetabolized state.[16]
Chemistry
Amikacin is derived from kanamycin A:[28][29]

Veterinary use
While amikacin is only FDA-approved for use in dogs and for intrauterine infection in horses, it is one of the most common aminoglycosides used in veterinary medicine,[30] and has been used in dogs, cats, guinea pigs, chinchillas, hamsters, rats, mice, prairie dogs, cattle, birds, snakes, turtles and tortoises, crocodilians, bullfrogs, and fish.[1][31][32] It is often used for respiratory infections in snakes, bacterial shell disease in turtles, and sinusitis in macaws. It is generally contraindicated in rabbits and hares (though it has still been used) because it harms the balance of intestinal microflora.[1]
In dogs and cats, amikacin is commonly used as a topical antibiotic for ear infections and for corneal ulcers, especially those that are caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The ears are often cleaned before administering the medication, since pus and cellular debris lessen the activity of amikacin.[30] Amikacin is administered to the eye when prepared as an ophthalmic ointment or solution, or when injected subconjunctivally.[33] Amikacin in the eye can be accompanied by cephazolin. Despite its use there amikacin (and all aminoglycosides) are toxic to intraocular structures.[34]
In horses, amikacin is FDA-approved for uterine infections (such as endometriosis and pyometra) when caused by susceptible bacteria.[35] It is also used in topical medication for the eyes and arthroscopic lavage; when combined with a cephalosporin, is used to treat subcutaneous infections that are caused by Staphylococcus. For infections in the limbs or joints, it is often administered with a cephalosporin via limb perfusion directly into the limb or injected into the joint.[30][36] Amikacin is also injected into the joints with the anti-arthritic medication Adequan in order to prevent infection.[37]
Side effects in animals include nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, and allergic reactions at IM injection sites. Cats tend to be more sensitive to the vestibular damage caused by ototoxicity. Less frequent side effects include neuromuscular blockade, facial edema, and peripheral neuropathy.[1][30]
The half-life in most animals is one to two hours.[38]
Treating overdoses of amikacin requires kidney dialysis or peritoneal dialysis, which reduce serum concentrations of amikacin, and/or penicillins, some of which can form complexes with amikacin that deactivate it.[1]
References
^ abcdefghijklmn Plumb, Donald C. (2011). "Amikacin Sulfate". Plumb's Veterinary Drug Handbook (7th ed.). Stockholm, Wisconsin; Ames, Iowa: Wiley. pp. 39–43. ISBN 978-0-470-95964-0..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzaa "Amikacin Sulfate". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
^ WHO Model Formulary 2008 (PDF). World Health Organization. 2009. p. 137. ISBN 9789241547659. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
^ Fischer, Janos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 507. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016.
^ Oxford Handbook of Infectious Diseases and Microbiology. OUP Oxford. 2009. p. 56. ISBN 9780191039621. Archived from the original on 24 November 2015.
^ "WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (19th List)" (PDF). World Health Organization. April 2015. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
^ "Amikacin Sulfate". International Drug Price Indicator Guide. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
^ Hamilton, Richart (2015). Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 35. ISBN 9781284057560.
^ abcdefghijklm US National Library of Medicine (17 August 2016). "AMIKACIN SULFATE- amikacin sulfate injection". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 16 August 2017. Retrieved 8 August 2017.
^ Scholar, Eric M.; Pratt, William B. (22 May 2000). The Antimicrobial Drugs (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press, USA. pp. 15–19. ISBN 978-0-19-975971-2. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.
^ abcd Cunha, Burke A. (1 November 2006). "New Uses for Older Antibiotics: Nitrofurantoin, Amikacin, Colistin, Polymyxin B, Doxycycline, and Minocycline Revisited". Medical Clinics of North America. Antimicrobial Therapy. 90 (6): 1089–1107. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2006.07.006. ISSN 0025-7125.
^ abcdefg "amikacin (Rx)". Medscape. WebMD. Archived from the original on 9 August 2017. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
^ ab Aronson J. K., eds. (2016). "Amikacin". Meyler's Side Effects of Drugs (16th ed.). Oxford: Elsevier. pp. 207–209. ISBN 978-0-444-53716-4.CS1 maint: Uses editors parameter (link)
^ Vardanyan, Ruben; Hruby, Victor (2016). "Chapter 32: Antimicobacterial Drugs". Synthesis of Best-Seller Drugs. Boston: Academic Press. pp. 669–675. ISBN 978-0-12-411492-0.
^ "Press Announcements - FDA approves a new antibacterial drug to treat a serious lung disease using a novel pathway to spur innovation". www.fda.gov. Retrieved 12 November 2018.
^ abcde Ettinger, Stephen J.; Feldman, Edward C. (24 December 2009). Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 1976, 523. ISBN 978-1-4377-0282-8. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.
^ Maire, P.; Bourguignon, L.; Goutelle, S.; Ducher, M.; Jelliffe, R. (2017). "Chapter 20 - Individualizing Drug Therapy in the Elderly". Individualized Drug Therapy for Patients. Boston: Academic Press. pp. 373–382. ISBN 978-0-12-803348-7.
^ Eghianruwa, Kingsley (2014). Essential Drug Data for Rational Therapy in Veterinary Practice. Author House. p. 16. ISBN 978-1-4918-0000-3. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.
^ ab Morris, Daniel O.; Kennis, Robert A. (11 October 2012). Clinical Dermatology, An Issue of Veterinary Clinics: Small Animal Practice, E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 29. ISBN 978-1-4557-7377-0. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.
^ abc Corti, Natascia; Taegtmeyer, Anne; Imhof, Alexander (1 January 2011). "Miscellaneous antibacterial drugs". Side Effects of Drugs Annual. A worldwide yearly survey of new data in adverse drug reactions. 33: 509–540. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-53741-6.00026-X. ISBN 9780444537416. ISSN 0378-6080.
^ Bauman, Robert W. (2015). Microbiology: with diseases by body system (4th ed.). Boston: Pearson. ISBN 978-0-321-91855-0.
^ "Amikacin". DrugBank. 2 August 2017. Archived from the original on 16 August 2017. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
^ ab Mudd, Efrain (7 August 2017). "O Aminoglycosides". Pharmacological Sciences. Archived from the original on 16 August 2017. Retrieved 14 August 2017.
^ ab Kondo, Shinichi; Hotta, Kunimoto (1 January 1999). "Semisynthetic aminoglycoside antibiotics: Development and enzymatic modifications". Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy. 5 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1007/s101560050001. ISSN 1341-321X. PMID 11810483.
^ Park, Je Won; Ban, Yeon Hee; Nam, Sang-Jip; Cha, Sun-Shin; Yoon, Yeo Joon (1 December 2017). "Biosynthetic pathways of aminoglycosides and their engineering". Current Opinion in Biotechnology. Chemical biotechnology: Pharmaceutical biotechnology. 48: 33–41. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2017.03.019. ISSN 0958-1669. PMID 28365471.
^ Caminero, José A; Sotgiu, Giovanni; Zumla, Alimuddin; Migliori, Giovanni Battista (1 September 2010). "Best drug treatment for multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis" (PDF). The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 10 (9): 621–629. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(10)70139-0. ISSN 1473-3099.
^ Ahmad, Suhail; Mokaddas, Eiman (1 March 2014). "Current status and future trends in the diagnosis and treatment of drug-susceptible and multidrug-resistant tuberculosis". Journal of Infection and Public Health. 7 (2): 75–91. doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2013.09.001. ISSN 1876-0341. PMID 24216518.
^ Kawaguchi, H.; Naito, T.; Nakagawa, S.; Fujisawa, K. I. (December 1972). "BB-K 8, a new semisynthetic aminoglycoside antibiotic". The Journal of Antibiotics. 25 (12): 695–708. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.25.695. ISSN 0021-8820. PMID 4568692. Archived from the original on 16 August 2017.
^ Monteleone, Peter M.; Muhammad, Naseem; Brown, Robert D.; McGrory, John P.; Hanna, Samir A. (1 January 1983). "Amikacin Sulfate". Analytical Profiles of Drug Substances. Analytical Profiles of Drug Substances. 12: 37–71. doi:10.1016/S0099-5428(08)60163-X. ISBN 9780122608124. ISSN 0099-5428.
^ abcd Forney, Barbara. "Amikacin for Veterinary Use". Wedgewood Pharmacy. Archived from the original on 16 August 2017. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
^ Riviere, Jim E.; Papich, Mark G. (13 May 2013). Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. John Wiley & Sons. p. 931. ISBN 978-1-118-68590-7. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.
^ Mader, Douglas R.; Divers, Stephen J. (12 December 2013). Current Therapy in Reptile Medicine and Surgery - E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 382. ISBN 978-0-323-24293-6. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.
^ Maggs, David; Miller, Paul; Ofri, Ron (7 August 2013). Slatter's Fundamentals of Veterinary Ophthalmology - E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 37. ISBN 978-0-323-24196-0. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.
^ Hsu, Walter H. (25 April 2013). Handbook of Veterinary Pharmacology. John Wiley & Sons. p. 486. ISBN 978-1-118-71416-4.
^ US National Library of Medicine (9 March 2017). "AMIGLYDE-V- amikacin sulfate injection". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 16 August 2017. Retrieved 8 August 2017.
^ Orsini, James A. (1 August 2017). "Update on Managing Serious Wound Infections in Horses: Wounds Involving Joints and Other Synovial Structures". Journal of Equine Veterinary Science. 55: 115–122. doi:10.1016/j.jevs.2017.01.016. ISSN 0737-0806.
^ Wanamaker, Boyce P.; Massey, Kathy (25 March 2014). Applied Pharmacology for Veterinary Technicians - E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 392. ISBN 978-0-323-29170-5.
^ Papich, Mark G. (October 2015). "Amikacin". Saunders Handbook of Veterinary Drugs: Small and Large Animal (4th ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 25–27. ISBN 978-0-323-24485-5. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.