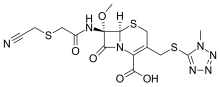
Cefmetazole
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| MedlinePlus | a601206 |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII |
|
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.054.877 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H17N7O5S3 |
| Molar mass | 471.538 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
.mw-parser-output .nobold{font-weight:normal} (verify) | |
Cefmetazole is a cephamycin antibiotic, usually grouped with the second-generation cephalosporins.
Adverse effects
The chemical structure of cefmetazole, like that of several other cephalosporins, contains an N-methylthiotetrazole (NMTT or 1-MTT) side chain. As the antibiotic is broken down in the body, it releases free NMTT, which can cause hypoprothrombinemia (likely due to inhibition of the enzyme vitamin K epoxide reductase) and a reaction with ethanol similar to that produced by disulfiram, due to inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase.[1]
Spectrum of bacterial susceptibility
Cefmetazole is a broad-spectrum cephalosporin antimicrobial and has been effective in treating bacteria responsible for causing urinary tract and skin infections. The following represents MIC susceptibility data for a few medically significant microorganisms.
Bacteroides fragilis: 0.06 - >256 µg/ml
Clostridium difficile: 8 - >128 µg/ml
Staphylococcus aureus: 0.5 - 256 µg/ml (includes MRSA)
[2]
References
^ Stork CM (2006). "Antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals". In Nelson LH, Flomenbaum N, Goldfrank LR, Hoffman RL, Howland MD, Lewin NA. Goldfrank's toxicologic emergencies. New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 847. ISBN 0-07-143763-0. Retrieved 2009-07-03..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ http://www.toku-e.com/Assets/MIC/Cefmetazole%20free%20acid.pdf
This systemic antibiotic-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |