Wuhan
Wuhan .mw-parser-output .nobold{font-weight:normal} 武汉市 | ||
|---|---|---|
Prefecture-level & Sub-provincial city | ||
 From left to right, from top to bottom: The City flower of Wuhan, The Seal of Wuhan, The City tree of Wuhan, Skyline of Wuhan and Wuhan Yangtze River Bridge with the city's official slogan "Wuhan, different every day (武汉,每天不一样)", Yingwuzhou Yangtze River Bridge, Yellow Crane Tower, Wuhan Customs House, Wuhan University, Changchun Taoist Temple, Gude Buddhist Temple, Revolution of 1911 Square, Professional tennis player Li Na, Optics Valley Tram, Bianzhong of Marquis Yi of Zeng and Wuhan ferry. | ||
| ||
| Nickname(s): 'China's Thoroughfare',[2] the Chicago of China,[3][4][5]'River City' | ||
| Motto(s): 'Wuhan, Different Everyday!', 大江大湖大武汉 | ||
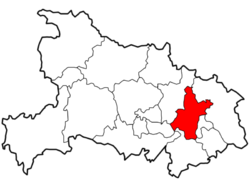 Location of Wuhan City jurisdiction in Hubei | ||
 Wuhan Location in Eastern China Show map of Eastern China  Wuhan Wuhan (China) Show map of China  Wuhan Wuhan (Asia) Show map of Asia | ||
| Coordinates: 30°35′N 114°17′E / 30.583°N 114.283°E / 30.583; 114.283Coordinates: 30°35′N 114°17′E / 30.583°N 114.283°E / 30.583; 114.283 | ||
| Country | People's Republic of China | |
| Province | Hubei | |
| Settled | 1500 BC | |
| First unified | January 1, 1927[1] | |
| Divisions[1][6] County-level Township-level | 13 districts 156 subdistricts, 1 towns, 3 townships | |
| Government | ||
| • Party Secretary | Ma Guoqiang | |
| • Mayor | Zhou Xianwang (周先旺,agent)[7] | |
| Area [8] | ||
| • Prefecture-level & Sub-provincial city | 8,494.41 km2 (3,279.71 sq mi) | |
| • Urban (2018)[9] | 1,528 km2 (590 sq mi) | |
| Elevation [citation needed] | 37 m (121 ft) | |
| Population (2015) | ||
| • Prefecture-level & Sub-provincial city | 10,607,700 | |
| • Density | 1,200/km2 (3,200/sq mi) | |
| • Urban (2018)[9] | 7,980,000 | |
| • Metro [10] | 19 million | |
| Demonym(s) | Wuhanese | |
| Languages | ||
| • Languages | Wuhan dialect, Standard Chinese | |
| Major ethnic groups | ||
| • Major ethnic groups | Han | |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) | |
| Postal code | 430000–430400 | |
| Area code(s) | 0027 | |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-HB-01 | |
| GDP[12] | 2016 | |
| - Total | CNY 1.19 trillion USD 180 billion (8th) | |
| - Per capita | CNY 119,000 USD 18,030 (nominal) - 33,000 (purchasing power parity) (11th) | |
| - Growth | ||
| License plate prefixes | 鄂A 鄂O (police and authorities) | |
| City tree | Metasequoia[11] | |
| City flower | Plum blossom[13] | |
| Website | 武汉政府门户网站 (Wuhan Government Web Portal) (in Chinese); English Wuhan (in English) | |
| Wuhan | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 "Wuhan" in Simplified (top) and Traditional (bottom) Chinese characters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 武汉 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 武漢 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | "[The combined cities of] Wǔ[chāng] and Hàn[kǒu]" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Wuhan ([ù.xân] (![]() listen); simplified Chinese: 武汉; traditional Chinese: 武漢) is the capital of Hubei province, People's Republic of China.[14] It's the most populous city in Central China,[15] and one of the nine National Central Cities of China.[16] It lies in the eastern Jianghan Plain on the middle reaches of the Yangtze River's intersection with the Han river. Arising out of the conglomeration of three cities, Wuchang, Hankou, and Hanyang, Wuhan is known as 'China's Thoroughfare';[2] it is a major transportation hub, with dozens of railways, roads and expressways passing through the city and connecting to other major cities. Because of its key role in domestic transportation, Wuhan is sometimes referred to as "the Chicago of China" by foreign sources.[3][4][5]
listen); simplified Chinese: 武汉; traditional Chinese: 武漢) is the capital of Hubei province, People's Republic of China.[14] It's the most populous city in Central China,[15] and one of the nine National Central Cities of China.[16] It lies in the eastern Jianghan Plain on the middle reaches of the Yangtze River's intersection with the Han river. Arising out of the conglomeration of three cities, Wuchang, Hankou, and Hanyang, Wuhan is known as 'China's Thoroughfare';[2] it is a major transportation hub, with dozens of railways, roads and expressways passing through the city and connecting to other major cities. Because of its key role in domestic transportation, Wuhan is sometimes referred to as "the Chicago of China" by foreign sources.[3][4][5]
Holding sub-provincial status,[17] Wuhan is recognized as the political, economic, financial, cultural, educational and transportation center of central China.[15] In 1927, Wuhan was briefly the capital of China under the left wing of the Kuomintang (KMT) government led by Wang Jingwei.[18] The city later served as the wartime capital of China in 1937 for 10 months.[19][20]
The Wuhan Gymnasium held the 2011 FIBA Asia Championship and will be one of the venues for the 2019 FIBA Basketball World Cup.[21]
The 7th Military World Games will be hosted from Oct. 18 to 27, 2019 in Wuhan.[22][23]
Contents
1 Etymology
2 History
2.1 Antiquity
2.2 Early Imperial China
2.3 Qing dynasty
2.3.1 Wuchang Uprising
2.4 Republic of China
2.5 People's Republic of China
3 Geography
3.1 Cityscape
3.2 Overview
3.3 Climate
4 Government and politics
4.1 Administrative divisions
4.2 Diplomatic missions
5 Economy
5.1 Industrial zones
6 Demographics
6.1 Religion
7 Transportation
7.1 Railways
7.2 Wuhan Metro
7.3 Trams
7.4 Maritime transport
7.5 Ferry
7.6 Airports
7.7 Highways and Expressways
7.8 Bicycle-sharing system
8 Destinations
9 Education
9.1 Schools and universities
9.2 Scientific research
10 Media
11 Culture
11.1 Language
11.2 Cuisine
11.3 Opera
11.4 Sports
12 Architecture
12.1 Bridges
12.2 Skyscrapers
13 Notable Wuhanese
13.1 Politics
13.2 Business
13.3 Science
13.4 Sports
13.5 Other fields
14 Sister cities
15 Nature and wildlife
16 See also
17 References
18 Further reading
19 External links
Etymology
'Wuhan' is derived from the pinyin romanization of the Standard Mandarin pronunciation of the name of the city '武汉' (Wǔhàn). The Chinese '武汉' (Wuhan) is a portmanteau: The 'Wu' (武) in 'Wuhan' is derived from the 'Wu' in 'Wuchang' (武昌) (literally prospering military, regarding its logistics role of the military bases established before the Battle of Red Cliffs). Wuchang was the name given to the area in AD 221 when warlord Sun Quan moved the capital of Eastern Wu to È county (in present-day Ezhou City), and renamed È to Wuchang. The 'han' (traditional Chinese: 漢; simplified Chinese: 汉) in 'Wuhan' comes from the 'Han' in 'Hankou' (漢口), which literally means "Mouth of the Han", from its position at the confluence of the Han with the Yangtze River. In 1926, the Northern Expedition reached the Wuhan area and it was decided to merge Hankou, Wuchang and Hanyang into one city in order to make a new capital for Nationalist China. On January 1, 1927,[24] the resulting city was proclaimed as '武汉' (Wuhan).[25][26][27]
History
Antiquity

Panlongcheng, located in the southernmost area of the Erligang culture
With a 3,500-year-long history, Wuhan is one of the most ancient and populated metropolitan cities in China. Panlongcheng, an archaeological site primarily associated with the Erligang culture (c. 1510 – c. 1460 BC) (being sparsely populated during the earlier Erlitou period), is located in modern-day Huangpi District. During the Western Zhou, the State of E controlled the present-day Wuchang area south of the Yangtze River. After the conquest of the E state in 863 BC, the present-day Wuhan area was controlled by the State of Chu for the rest of the Western Zhou and Eastern Zhou periods.
Early Imperial China
During the Han dynasty, Hanyang became a fairly busy port. The Battle of Xiakou in AD 203 and Battle of Jiangxia five years later were fought over control of Jiangxia Commandery (present-day Xinzhou District in northeast Wuhan). In the winter of 208/9, one of the most famous battles in Chinese history and a central event in the Romance of the Three Kingdoms—the Battle of Red Cliffs—took place in the vicinity of the cliffs near Wuhan.[28] Around that time, walls were built to protect Hanyang (AD 206) and Wuchang (AD 223). The latter event marks the foundation of Wuhan. In AD 223, the Yellow Crane Tower, one of the Four Great Towers of China, was constructed on the Wuchang side of the Yangtze River by order of Sun Quan, leader of the Eastern Wu. The tower become a sacred site of Taoism.[29]

Depiction of the Yellow Crane Tower (Yuan dynasty)
Due to tensions between the Eastern Wu and Cao Wei states, in the autumn of 228,[a]Cao Rui, grandson of Cao Cao and the second emperor of the state of Cao Wei, ordered the general Man Chong to lead troops to Xiakou (夏口; in present-day Wuhan).[31][32] In 279, Wang Jun and his army conquered strategic locations in Wu territory such as Xiling (in present-day Yichang, Hubei), Xiakou (夏口; present-day Hankou) and Wuchang (武昌; present-day Ezhou, Hubei).
In fall 550, Hou Jing sent Ren Yue to attack both Xiao Daxin and Xiao Fan's son Xiao Si (蕭嗣). Ren killed Xiao Si in battle, and Xiao Daxin, unable to resist, surrendered, allowing Hou to take his domain under control. Meanwhile, Xiao Guan, who had by now settled at Jiangxia (江夏, in modern Wuhan), was planning to attack Hou, but this drew Xiao Yi's ire—believing that Xiao Guan was intending to contend for the throne—and he sent Wang to attack Xiao Guan. In summer 567, Chen Xu commissioned Wu Mingche as the governor of Xiang Province and had him command a major part of the troops against Hua, along with Chunyu Liang (淳于量). The opposing sides met at Dunkou (沌口, in modern Wuhan).

Wuying Pagoda, a Buddhist pagoda rebuilt in Wuchang during the Southern Song dynasty.
The city has long been renowned as a center for the arts (especially poetry) and for intellectual studies.Cui Hao, a celebrated poet of the Tang dynasty, visited the building in the early 8th century; his poem made it the most celebrated building in southern China.[33]
In spring 877, Wang Xianzhi captured E Prefecture (鄂州, in modern Wuhan). He then returned north, joining forces with Huang again, and they surrounded Song Wei at Song Prefecture (宋州, in modern Shangqiu, Henan). In winter 877, Huang Chao pillaged Qi and Huang (黃州, in modern Wuhan) Prefectures.
Before Kublai Khan arrived in 1259, word reached him that Möngke had died. Kublai decided to keep the death of his brother secret and continued the attack on the Wuhan area, near the Yangtze. While Kublai's force besieged Wuchang, Uryankhadai joined him.[citation needed] The present-day Wuying Pagoda was constructed at the end of the Song Dynasty between attacks by the Mongolian forces. Under the Mongol rulers (Yuan dynasty) (after 1301), the Wuchang prefecture, headquartered in the town, became the capital of Hubei province. Hankou, from the Ming to late Qing, was under the administration of the local government in Hanyang, although it was already one of the four major national markets (zh:四大名镇) in Ming dynasty.
Qing dynasty

Guiyuan Temple
Hanyang's Guiyuan Temple was built in the 15th year of Shunzhi (1658).[34] By the dawn of the 18th century, Hankou had become one of China's top four most important towns of trade. In the late 19th century, railroads were extended on a north-south axis through the city, making Wuhan an important transshipment point between rail and river traffic. Also during this period foreign powers extracted mercantile concessions, with the riverfront of Hankou being divided up into foreign-controlled merchant districts. These districts contained trading firm offices, warehouses, and docking facilities. The French had a concession in Hankou.[35]

Wuhan in 1864

The mid-19th century Yellow Crane Tower (1871)
During the Taiping Rebellion, the Wuhan area was controlled for many years by rebel forces and the Yellow Crane Tower, Xingfu Temple, Zhuodaoquan Temple and other buildings were destroyed. During the Second Opium War (known in the West as the Arrow War, 1856–1860), the government of the Qing dynasty was defeated by the western powers and signed the Treaties of Tianjin and the Convention of Peking, which stipulated eleven cities or regions (including Hankou) as trading ports. In December 1858, James Bruce, 8th Earl of Elgin, High Commissioner to China, led four warships up the Yangtze River in Wuhan to collect the information needed for opening the trading port in Wuhan. And in the spring of 1861, Counselor Harry Parkes and Admiral Herbert were sent to Wuhan to open a trading port. On the basis of the Convention of Peking, Harry Parkes concluded the Hankou Lend-Lease Treaty with Guan Wen, the governor-general of Hunan and Hubei. It brought an area of 30.53 square kilometres (11.79 sq mi) along the Yangtze River (from Jianghan Road to Hezuo Road today) to become a British Concession and permitted Britain to set up its consulate in the concession. Thus, Hankou became an open trading port.

Foreign concessions along the Hankow Bund c. 1900.
In 1889, Zhang Zhidong was transferred from Viceroy of Liangguang (Guangdong and Guangxi provinces) to Viceroy of Huguang (Hunan and Hubei provinces). He governed the province for 18 years, until 1907. During this period, he elucidated the theory of "Chinese learning as the basis, Western learning for application," known as the ti-yong ideal. He set up many heavy industries, founded Hanyang Steel Plant, Daye Iron Mine, Pingxiang Coal Mine and Hubei Arsenal and set up local textile industries, boosting the flourishing modern industry in Wuhan. Meanwhile, he initiated education reform, opened dozens of modern educational organizations successively, such as Lianghu (Hunan and Hubei) Academy of Classical Learning, Civil General Institute, Military General Institute, Foreign Languages Institute and Lianghu (Hunan and Hubei) General Normal School, and selected a great many students for study overseas, which well promoted the development of China’s modern education. Furthermore, he trained a modern military and organized a modern army including a zhen and a xie (both zhen and xie are military units in the Qing dynasty) in Hubei. All of these laid a solid foundation for the modernization of Wuhan.
Originally known as the Hubei Arsenal, the Hanyang Arsenal was founded in 1891 by Qing official Zhang Zhidong, who diverted funds from the Nanyang Fleet in Guangdong to build the arsenal. It cost about 250,000 pounds sterling and was built in 4 years.[36] On 23 April 1894, construction was completed and the arsenal, occupying some 40 acres (160,000 m2), could start production of small-calibre cannons. It built magazine-fed rifles, Gruson quick fire guns, and cartridges.[37]
Wuchang Uprising

Wuchang Uprising Memorial, the original site of revolutionary government in 1911

Present-day Wuhan area in 1915
On October 10, 1911, Sun Yat-sen's followers launched the Wuchang Uprising,[38] which led to the collapse of the Qing dynasty,[39] as well as the establishment of the Chinese Republic.[40] Wuhan was the capital of the left-wing Kuomintang government led by Wang Jingwei, in opposition to Chiang Kai-shek's right-wing government during the 1920s.
The Wuchang Uprising of October 1911, which overthrew the Qing dynasty, originated in Wuhan.[38] Before the uprising, anti-Qing secret societies were active in Wuhan. In September 1911, the outbreak of the protests in Sichuan forced the Qing authorities to send part of the New Army garrisoned in Wuhan to suppress the rebellion.[41] On September 14 the Literary Society (文學社) and the Progressive Association (共進會), two local revolutionary organizations in Hubei,[41] set up joint headquarters in Wuchang and planned for an uprising. On the morning of October 9, a bomb at the office of the political arrangement exploded prematurely and alerted local authorities.[42] The proclamation for the uprising, beadroll and the revolutionaries’ official seal fell into the hands of Rui Cheng, the governor-general of Hunan and Hubei, who demolished the uprising headquarters the same day and set out to arrest the revolutionaries listed in the beadroll.[42] This forced the revolutionaries to launch the uprising earlier than planned.[38]
On the night of October 10, the revolutionaries fired shots to signal the uprising at the engineering barracks of Hubei New Army.[38] They then led the New Army of all barracks to join the revolution.[43] Under the guidance of Wu Zhaolin, Cai Jimin and others, this revolutionary army seized the official residence of the governor and government offices.[41] Rui Cheng fled in panic into the Chu-Yu Ship. Zhang Biao, the commander of the Qing army, also fled the city. On the morning of the 11th, the revolutionary army took the whole city of Wuchang, but leaders such as Jiang Yiwu and Sun Wu disappeared.[38] Thus the leaderless revolutionary army recommended Li Yuanhong, the assistant governor of the Qing army, as the commander-in-chief.[44] Li founded the Hubei Military Government, proclaimed the abolition of the Qing rule in Hubei, the founding of the Republic of China and published an open telegram calling for other provinces to join the revolution.[38][41]
As the revolution spread to other parts of the country, the Qing government concentrated loyalist military forces to suppress the uprising in Wuhan. From October 17 to December 1, the revolutionary army and local volunteers defended the city in the Battle of Yangxia against better armed and more numerous Qing forces commanded by Yuan Shikai. Huang Xing (黃興) would arrive in Wuhan in early November to take command of the revolutionary army.[41] After fierce fighting and heavy casualties, Qing forces seized Hankou and Hanyang. But Yuan agreed to halt the advance on Wuchang and participated in peace talks, which would eventually lead to the return of Sun Yat-sen from exile, founding of the Republic of China on January 1, 1912.[40][45] Through the Wuchang Uprising, Wuhan is known as the birthplace of the Xinhai Revolution, named after the Xinhai year on the Chinese calendar.[46] The city has several museums and memorials to the revolution and the thousands of martyrs who died defending the revolution.
Republic of China
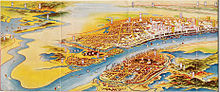
A map of Wuhan painted by Japanese in 1930, with Hankou being the most prosperous sector
With the northern extension of the Northern Expedition, the center of the Great Revolution shifted from the Pearl River basin to the Yangtze River basin. On November 26, the KMT Central Political Committee decided to move the capital from Guangzhou to Wuhan. In middle December, most of the KMT central executive commissioners and national government commissioners arrived in Wuhan, set up the temporary joint conference of central executive commissioners and National Government commissioners, performed the top functions of central party headquarters and National Government, declared they would work in Wuhan on January 1, 1927, and decided to combine the towns of Wuchang, Hankou, and Hanyang into Wuhan City, called "Capital District". The national government was in the Nanyang Building in Hankou, while the central party headquarters and other organizations chose their locations in Hankou or Wuchang.[18] In March 1927, Mao Zedong appeared at the Third Plenum of the KMT Central Executive Committee in Wuhan, which sought to strip General Chiang of his power by appointing Wang Jingwei leader. The first phase of the Northern Expedition was interrupted by the political split in the Kuomintang following the formation of the Nanjing faction in April 1927 against the existing faction in Wuhan.[47] Members of the Chinese Communist Party, who had survived the April 12 massacre, met at Wuhan and re-elected Chen Duxiu (Ch'en Tu-hsiu) as the Party's Secretary General.[48] The split was partially motivated by the purge of the Communists within the party, which marked the end of the First United Front, and Chiang Kai-shek briefly stepped down as the commander of the National Revolutionary Army.[49]
In June 1927, Stalin sent a telegram to the Communists in Wuhan, calling for mobilisation of an army of workers and peasants.[50] This alarmed Wang Jingwei, who decided to break with the Communists and come to terms with Chiang Kai-shek. The Wuhan coup was a political shift made on July 15, 1927 by Wang Jingwei towards Chiang Kai-shek, and his Shanghai-based rival in the Kuomintang (KMT). The Wuhan Nationalist Government was established in Wuhan on February 21, 1927 and ended by August 19, 1927.[51]
In the 1931 China floods, Wuhan was a refuge for flood victims from outlying areas, who had been arriving since the late spring. But when the city itself was inundated in the early summer, and after a catastrophic dike failure just before 6:00 AM on July 27,[52]:270 an estimated 782,189 urban citizens and rural refugees were left homeless. The flood covered an area of 32 square miles and the city was flooded under many feet of water for close to three months.[52]:269–270 Large numbers gathered on flood islands throughout the city, with 30,000 sheltering on a railway embankment in central Hankou. With little food and a complete breakdown in sanitation, thousands soon began to succumb to diseases.[53] Jin Shilong, Senior Engineer at the Hubei Flood Prevention Agency, described the flooding:
There was no warning, only a sudden great wall of water. Most of Wuhan's buildings in those days were only one story high, and for many people there was no escape- they died by the tens of thousands. ... I was just coming off duty at the company's main office, a fairly new three-story building near the center of town ... When I heard the terrible noise and saw the wall of water coming, I raced to the top story of the building. ... I was in one of the tallest and strongest buildings left standing. At that time no one knew whether the water would subside or rise even higher.[52]:270
The high-water mark was reached on 19 August at Hankou, with the water level exceeding 16 m (53 ft) above normal.[54][55] In 1936, when natural disaster struck Central China with widespread flooding affecting Hebei, Hunan, Jiangxi, Wuhan and Chongqing caused by the Yangtze and Huai Rivers bursting their banks, Ong Seok Kim, as Chairman of the Sitiawan Fundraising and Disaster Relief Committee, raised money and materials in support of the victims.[56][57][58][59]

The gunboat Zhongshan
During the Second Sino-Japanese War and following the fall of Nanking in December 1937, Wuhan had become the provisional capital of China's Kuomintang government, and became another focal point of pitched air battles beginning in early 1938 between modern monoplane bomber and fighter aircraft of the Imperial Japanese forces and the Chinese Air Force, which included support from the Soviet Volunteer Group in both planes and personnel, as U.S. support in war materials waned.[60] As the battle raged on through 1938, Wuhan and the surrounding region had become the site of the Battle of Wuhan. After being taken by the Japanese in late 1938, Wuhan became a major Japanese logistics center for operations in southern China.

Chiang Kai-Shek was having a parade before the Japanese Army invaded Wuhan
In early October 1938, Japanese troops moved east and north in the outskirts of Wuhan. As a result, numerous companies and enterprises and large numbers of people had to withdraw from Wuhan to the west of Hubei and Sichuan. The KMT navy undertook the responsibility of defending the Yangtze River on patrol and covering the withdrawal. On October 24, while overseeing the waters of the Yangtze River near the town of Jinkou (Jiangxia District in Wuhan) in Wuchang, the KMT gunboat Zhongshan came up against six Japanese aircraft. Though two were eventually shot down, the Zhongshan sank with 25 casualties. Raised from the bottom of the Yangtze River in 1997, and restored at a local shipyard, the Zhongshan has been moved to a purpose-built museum in Wuhan's suburban Jiangxia District, which opened on September 26, 2011.[61]
As a key center on the Yangtze, Wuhan was an important base for Japanese operations in China.[62] On 18 December 1944, Wuhan was bombed by 77 American bombers that set off a firestorm that destroyed much of the city.[63] For the next three days, Wuhan was bombed by the Americans, destroying all of the docks and warehouses of Wuhan, as well as the Japanese air bases in the city. The air raids killed thousands of Chinese civilians.[63] "According to casualty statistics compiled by Hankou city in 1946, more than 20,000 were killed or injured in the December bombings of 1944."[64]

People's Liberation Army troops at Zhongshan Avenue, Hankou on May 16, 1949
People's Liberation Army troops entered Wuhan on May 16, 1949.[65]
People's Republic of China

In his poem "Swimming" (1956), engraved on the 1954 Flood Memorial in Wuhan, Mao Zedong envisions "walls of stone" to be erected upstream.[66]
The Changjiang Water Resources Commission was re-established in February 1950 with its headquarters seated in Wuhan. From June to September 1954, the Yangtze River Floods were a series of catastrophic floodings that occurred mostly in Hubei Province. Due to an unusually high volume of precipitation as well as an extraordinarily long rainy season in the middle stretch of the Yangtze River late in the spring of 1954, the river started to rise above its usual level in around late June. In 1969, a large stone monument was erected in the riverside park in Hankou honoring the heroic deeds in fighting the 1954 Yangtze River floods.
Before construction of the Wuhan Yangtze River Bridge, Hunslet Engine Company built two extra heavy 0-8-0 locomotives for loading the train ferries for crossing the Yangtze River in Wuhan.

The First Yangtze River Bridge under construction
The project of building the Wuhan Yangtze River Bridge, also known as the First Yangtze River Bridge, was regarded as one of the key projects during the first five-year plan. On October 25, 1955, construction began on the bridge proper. The same day in 1957, the whole project was completed and an opening-to-traffic ceremony was held on October 15. The First Yangtze River Bridge united the Beijing–Hankou Railway with the Guangdong–Hankou Railway into the Beijing–Guangzhou Railway, making Wuhan a 'thoroughfare to nine provinces' (九省通衢) in name and in fact.
After Chengdu Conference, Mao went to Chongqing and Wuhan in April to inspect the countryside and factories. In Wuhan, he called all the leaders of provinces and municipalities who had not attended Chengdu Conference to report their work. Tian Jiaying, the secretary of Mao, said that Wuhan Conference was a supplement to Chengdu Conference.[67]
In July 1967, civil strife struck the city in the Wuhan Incident ("July 20th Incident"), an armed conflict between two hostile groups who were fighting for control over the city at the height of the Cultural Revolution.[68]
In 1981, the Wuhan City Government commenced reconstruction of the tower at a new location, about 1 km (0.62 mi) from the original site, and it was completed in 1985. In 1957, the Wuhan Yangtze River Bridge was built with one trestle of the bridge on the Yellow Crane Tower's site.[69]

The present-day Yellow Crane Tower
On June 22, 2000, a Wuhan Airlines flight from Enshi to Wuhan was forced to circle for 30 minutes due to thunderstorms. The aircraft eventually crashed on the banks of Han River in Hanyang District,[70] all on-board perished (there were varying accounts of number of crews and passengers). In addition, the crash also killed 7 people on the ground.[71][72][73]
Chinese protesters organized boycotts of the French-owned retail chain Carrefour in major Chinese cities including Kunming, Hefei and Wuhan, accusing the French nation of pro-secessionist conspiracy and anti-Chinese racism.[74] The BBC reported that hundreds of people demonstrated in Beijing, Wuhan, Hefei, Kunming and Qingdao.[75][76] On May 19, 2011, Fang Binxing, the Principal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications (also known as "Father of China's Great Fire Wall"[77][78]) was hit on the chest by a shoe thrown at him by a Huazhong University of Science and Technology student who calls herself "hanunyi" (寒君依, or 小湖北) while Fang was giving a lecture at Wuhan University.[79][80][81][82][83][84]

A morning view of Wuhan from the East Lake Greenway, an ecologic preserve near the Wuhan University for all the people in Wuhan
The city has been subject to devastating floods, which are now supposed to be controlled by the ambitious Three Gorges Dam, a project which was completed in 2008.[85][86] The 2008 Chinese winter storms damaged water supply equipment in Wuhan: up to 100,000 people were out of running water when several water pipes burst, cutting the supply to local households.[87] The 2010 Northern Hemisphere summer heat wave hit Wuhan on July 3.[88]
In the 2010 China floods, the Han River at Wuhan experienced its worst flooding in twenty years, as officials continued sandbagging efforts along the Han and Yangtze Rivers in the city and checked reservoirs.[89] In the 2011 China floods, Wuhan was flooded, with parts of the city losing power.[90] In the 2016 China floods, Wuhan saw 570 mm (22 in) of rainfall during the first week of July, surpassing the record that fell on the city in 1991. A red alert for heavy rainfall was issued on 2 July, the same day that eight people died after a 15-metre (49 ft) section of a 2 m (6.6 ft) tall wall collapsed on top of them.[91] The city's subway system, the Wuhan Metro was partially submerged as was the main railway station.[92] At least 14 city residents were killed, one was missing, and more than 80,000 were relocated.[93]
On January 31, 2018, Theresa May, Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, visited Wuhan and visited the Yellow Crane Tower and the First Yangtze River Bridge.[94]
On April 26, 2018, The prime minister of India Narendra Modi visited Wuhan for two days of informal meetings with Chinese President Xi Jinping. During this summit, they visited the East Lake and Hubei Provincial Museum.
Geography
Cityscape

Left to right: Yangtze River, Wuchang, Wuhan Yangtze River Bridge, Hanyang Tortoise Mountain TV Tower, mouth of the Han River and Hankou.


Left to right: Tortoise Mountain TV Tower and Hanyang, Wuhan Center and Hankou, Wuhan Yangtze River Bridge, Yangtze River, Wuchang, Wuhan Greenland Center and Yellow Crane Tower.
Overview

Satellite image of Wuhan

Looking west from the Yellow Crane Tower in Wuchang. The First Bridge over the Yangtze, and the Tortoise Hill in Hanyang, with its TV tower, are in the background.
Wuhan is in east-central Hubei, at latitude 29° 58'–31° 22' N and longitude 113° 41'–115° 05' E. Wuhan sits at the confluence of the Han River flowing into the Yangtze River at the East of the Jianghan Plain along the Yangtze's middle reaches.
The metropolitan area comprises three parts—Wuchang, Hankou, and Hanyang—commonly called the "Three Towns of Wuhan" (hence the name "Wuhan", combining "Wu" from the first city and "Han" from the other two). The consolidation of these cities occurred in 1927 and Wuhan was thereby established. The three former cities face each other across the rivers and are linked by bridges, including one of the first modern bridges in China, known as the "First Bridge".
- Wuchang lies South East of the Yangtze River that separates it from both Hankou and Hanyang.
- Hankou sits North of the Yangtze River separating it from Wuchang. Hankou is North of the Han River separating it from Hanyang.
- Hanyang lies West of the Yangtze separating it from Wuchang. Hanyang is south of the Han river separating it from Hankou.
It is simple in terrain—low and flat in the middle and hilly in the south, with the Yangtze and Han rivers winding through the city. The She River enters the Yangtze in Huangpi District. Wuhan occupies a land area of 8,494.41 square kilometres (3,279.71 sq mi), most of which is plain and decorated with hills and a great number of lakes and ponds, including East Lake and Tangxun Lake, which are the largest lakes entirely within a city in China.[95][better source needed] Other well-known lakes include South Lake and Sand Lake. Liangzi Lake, the largest lake by surface area in Hubei province, is located in the southeast of Jiangxia District. At 709 m (2,326 ft) above sea level, the highest point in Wuhan is the main peak of Yunwu Mountain (云雾山) in northwestern Huangpi District.[96] There are also several mountains within the city limits of Wuhan including Mount Luojia (珞珈山) in Wuchang District[94] as well as Mount Hong (洪山) and Mount Yujia (喻家山/瑜珈山) in Hongshan District.[97]
Climate

After a rare snow in Wuhan, the front door of a middle school was covered by thin ice surfaces
Wuhan's climate is humid subtropical (Köppen Cfa) with abundant rainfall and four distinctive seasons. Wuhan is known for its very humid summers, when dewpoints can often reach 26 °C (79 °F) or more.[98] Historically, along with Chongqing and Nanjing, Wuhan is referred to as one of the "Three Furnacelike Cities" along the Yangtze River for the high temperatures in the summertime.[99] However, the climate data of recent years suggests that Wuhan is no longer among the top tier of "The hottest cities in summer" list, the New Four Furnacelike Cities are Chongqing, Fuzhou, Hangzhou, and Nanchang.[100][101] The Spring and autumn are generally mild, while winter is cool with occasional snow. The monthly 24-hour average temperature ranges from 4.0 °C (39.2 °F) in January to 29.1 °C (84.4 °F) in July.[102] Annual precipitation totals 1,320 mm (52 in),[102] the majority of which falls from April to July; the annual mean temperature is 17.13 °C (62.8 °F),[102] the frost-free period lasts 211 to 272 days.[103] With monthly possible sunshine percentage ranging from 31 percent in March to 59 percent in August, the city proper receives 1,865 hours of bright sunshine annually.[102] Extreme low and high temperatures recorded are −18.1 °C (−1 °F) on 31 January 1977 and 39.7 °C (103 °F) on 27 July 2017 (unofficial record of 41.3 °C (106 °F).[when?][104][105]
| Climate data for Wuhan (1981–2010, extremes 1951–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 25.4 (77.7) | 29.1 (84.4) | 32.4 (90.3) | 35.1 (95.2) | 36.1 (97.0) | 37.8 (100.0) | 39.7 (103.5) | 39.6 (103.3) | 37.6 (99.7) | 34.4 (93.9) | 30.4 (86.7) | 23.3 (73.9) | 39.7 (103.5) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 8.1 (46.6) | 10.7 (51.3) | 15.2 (59.4) | 22.1 (71.8) | 27.1 (80.8) | 30.2 (86.4) | 32.9 (91.2) | 32.5 (90.5) | 28.5 (83.3) | 23.0 (73.4) | 16.8 (62.2) | 10.8 (51.4) | 21.5 (70.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.0 (39.2) | 6.6 (43.9) | 10.9 (51.6) | 17.4 (63.3) | 22.6 (72.7) | 26.2 (79.2) | 29.1 (84.4) | 28.4 (83.1) | 24.1 (75.4) | 18.2 (64.8) | 11.9 (53.4) | 6.2 (43.2) | 17.1 (62.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 1.0 (33.8) | 3.5 (38.3) | 7.4 (45.3) | 13.6 (56.5) | 18.9 (66.0) | 22.9 (73.2) | 26.0 (78.8) | 25.3 (77.5) | 20.7 (69.3) | 14.7 (58.5) | 8.4 (47.1) | 2.9 (37.2) | 13.8 (56.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −18.1 (−0.6) | −14.8 (5.4) | −5.0 (23.0) | −0.3 (31.5) | 7.2 (45.0) | 13.0 (55.4) | 17.3 (63.1) | 16.4 (61.5) | 10.1 (50.2) | 1.3 (34.3) | −7.1 (19.2) | −10.1 (13.8) | −18.1 (−0.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 48.7 (1.92) | 65.5 (2.58) | 91.0 (3.58) | 135.7 (5.34) | 166.8 (6.57) | 218.2 (8.59) | 228.1 (8.98) | 117.5 (4.63) | 74.0 (2.91) | 80.9 (3.19) | 60.0 (2.36) | 29.6 (1.17) | 1,316 (51.82) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 9.5 | 9.8 | 13.1 | 12.5 | 12.2 | 11.8 | 11.6 | 9.6 | 7.5 | 9.0 | 8.0 | 6.9 | 121.5 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 76 | 75 | 76 | 75 | 74 | 77 | 77 | 77 | 75 | 76 | 75 | 73 | 76 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 101.9 | 97.0 | 121.8 | 152.8 | 181.0 | 170.9 | 220.2 | 226.4 | 175.8 | 151.9 | 139.3 | 126.5 | 1,865.5 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 33 | 33 | 31 | 39 | 43 | 43 | 54 | 59 | 48 | 46 | 45 | 43 | 43 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration[106][102] | |||||||||||||
Government and politics

The main gate of Wuhan Municipal Party Committee

The Main Gate of Wuhan Municipal People's Government
Wuhan is a sub-provincial city. Municipal government is regulated by the local Communist Party of China (CPC), led by the Wuhan CPC Secretary (Chinese: 武汉市委书记), Ma Guoqiang(马国强). The local CPC issues administrative orders, collects taxes, manages the economy, and directs a standing committee of the Municipal People's Congress in making policy decisions and overseeing the local government.
Government officials include the mayor (Chinese: 市长), Zhou Xianwang(周先旺), and vice-mayors. Numerous bureaus focus on law, public security, and other affairs.
Administrative divisions
The sub-provincial city of Wuhan currently comprises 13 districts.[107] As of the Sixth Census of China in 2010, the 13 districts comprised 160 township-level divisions including 156 subdistricts, 3 towns, 1 townships.[1][6]
| Map | District | Chinese (S) | Pinyin | Population (2010 census)[108][1][6] | Area (km²)[8] | Density (/km²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 1 2 3 Hanyang Wuchang Qingshan Hongshan Dongxihu Hannan Caidian Jiangxia Huangpi Xinzhou Hankou districts 1. Jiang'an 2. Jianghan 3. Qiaokou | ||||||
Central Districts | 6,434,373 | 888.42 | 7,242 | |||
Jiang'an | 江岸区 | Jiāng'àn Qū | 895,635 | 64.24 | 13,942 | |
Jianghan | 江汉区 | Jiānghàn Qū | 683,492 | 33.43 | 20,445 | |
Qiaokou | 硚口区 | Qiáokǒu Qū | 828,644 | 46.39 | 17,863 | |
Hanyang | 汉阳区 | Hànyáng Qū | 792,183[109] | 108.34 | 7,312 | |
Wuchang | 武昌区 | Wǔchāng Qū | 1,199,127 | 87.42 | 13,717 | |
Qingshan | 青山区 | Qīngshān Qū | 485,375 | 68.40 | 7,096 | |
Hongshan | 洪山区 | Hóngshān Qū | 1,549,917[110] | 480.20 | 3,228 | |
Suburban and Rural Districts | 3,346,271 | 7,605.99 | 440 | |||
Dongxihu | 东西湖区 | Dōngxīhú Qū | 451,880 | 439.19 | 1,029 | |
Hannan | 汉南区 | Hànnán Qū | 114,970 | 287.70 | 400 | |
Caidian | 蔡甸区 | Càidiàn Qū | 410,888 | 1,108.10 | 371 | |
Jiangxia | 江夏区 | Jiāngxià Qū | 644,835 | 2,010.00 | 321 | |
Huangpi | 黄陂区 | Huángpí Qū | 874,938 | 2,261.00 | 387 | |
Xinzhou | 新洲区 | Xīnzhōu Qū | 848,760 | 1,500.00 | 566 | |
Water Region (水上地区) | 4,748 | - | - | |||
Total | 9,785,392 | 8,494.41 | 1,152 | |||
Diplomatic missions
There are four countries that have consulates in Wuhan (Russia is planning on opening a new consulate in Wuhan):
| Consulate | year | Consular District |
|---|---|---|
| October 10, 1998 | Hubei/Hunan/Jiangxi | |
| November 20, 2008 | Hubei/Hunan/Henan/Jiangxi | |
| October 25, 2010 | Hubei/Hunan/Henan/Jiangxi | |
| January 8, 2015 | Hubei/Henan |
The current U.S. Consul General, the Honorable Mrs. Jamie Fouss, was stationed in Wuhan in August 2017. The office of the U.S. Consulate General, Central China (located in Wuhan) celebrated its official opening on November 20, 2008 and is the first new American consulate in China in over 20 years.[115][116] The consulate is currently scheduled to offer visa and citizen services in the Fall of 2018.
Japan[117]
and Russia[118] will be establishing consular offices in Wuhan.
Economy

A night sight near a modern shopping mall in Honshan District
Wuhan and France are linked by strong economics partnerships. For example, some French companies (Renault, PSA Group, ...) are established in Wuhan. It is the city in China which receives the most French investment.[119]
Wuhan has attracted foreign investment from over 80 countries, with 5,973 foreign-invested enterprises established in the city with a total capital injection of $22.45 billion USD.[120] Among these, about 50 French companies have operations in the city, representing over one third of French investment in China, and the highest level of French investment in any Chinese city.[121] The municipal government offers various preferential policies to encourage foreign investment, including tax incentives, discounted loan interest rates and government subsidies.
Wuhan is an important center for economy, trade, finance, transportation, information technology, and education in China. Its major industries include optic-electronic, automobile manufacturing, iron and steel manufacturing, new pharmaceutical sector, biology engineering, new materials industry and environmental protection. Wuhan Iron and Steel Corporation and Dongfeng-Citroen Automobile Co., Ltd headquartered in the city. Environmental sustainability is highlighted in Wuhan's list of emerging industries, which include energy efficiency technology and renewable energy.[120]
Wuhan is one of the most competitive forces for domestic trade in China, rivaling the first-tier cities of Shanghai, Beijing, and Guangzhou in its volume of retail. It is also among the top list of China's metropolises. Wuhan Department Store, Zhongshang Company, Hanyang Department Store, and Central Department Store enjoy the highest reputation and are Wuhan's four major commercial enterprises and listed companies. Hanzhengjie Small Commodities Market has been prosperous for hundreds of years and enjoys a worldwide reputation.
Industrial zones

Headquarters of Wu Chuan (Wuhan Shipbuilding Company)
Major industrial zones in Wuhan include:
- Wuhan Donghu New Technology Development Zone
Wuhan Donghu New Technology Development Zone is a national level high-tech development zone. Optical-electronics, telecommunications, and equipment manufacturing are the core industries of Wuhan East Lake High-Tech Development Zone (ELHTZ) while software outsourcing and electronics are also encouraged. ELHTZ is China's largest production centre for optical-electronic products with key players like Yangtze Optical Fiber and Cable,[122] (the largest fiber-optical cable maker in China), and Fiberhome Telecommunications.[123] Wuhan Donghu New Technology Development Zone also represents the development centre for China's laser industry with key players such as HG Tech[124] and Chutian Laser being based in the zone.[125]
- Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone
Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone is a national level industrial zone incorporated in 1993.[126] Its current zone size is about 10–25 square km and it plans to expand to 25–50 square km. Industries encouraged in Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone include Auto-mobile Production/Assembly, Biotechnology/Pharmaceuticals, Chemicals Production and Processing, Food/Beverage Processing, Heavy Industry, and Telecommunications Equipment.
- Wuhan Export Processing Zone
Wuhan Export Processing Zone was established in 2000. It is located in Wuhan Economic and Technology Development Zone, planned to cover 2.7 square kilometres (1.0 square mile) of land. The first 0.7-square-kilometre (0.3-square-mile) area has been launched.[127]
- Wuhan Optical Valley (Guanggu) Software Park
Wuhan Optical Valley (Guanggu) Software Park is located in Wuhan Donghu New Technology Development Zone. Wuhan Optics Valley Software Park is jointly developed by East Lake High-Tech Development Zone and Dalian Software Park Co., Ltd.[128] The planned area is 0.67 square kilometres (0.26 square miles) with total floor area of 6,000,000 square metres (65,000,000 square feet). The zone is 8.5 km (5.28 mi) away from the 316 National Highway and is 46.7 km (29.02 mi) away from the Wuhan Tianhe Airport.
- Wuhan Biolake
Biolake is an industry base established in 2008 in the Optics Valley of China. Located in East Lake New Technology Development Zone of Wuhan, Biolake covers 15 km2 (5.8 sq mi), and has six parks including Bio-innovation Park, Bio-pharma Park, Bio-agriculture Park, Bio-manufacturing Park, Medical Device Park and Medical Health Park, to accommodate both research activities and living.[129][130][131][132][133]
Demographics
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
| 1953 | 1,427,300 | — |
| 1982 | 4,101,000 | +3.71% |
| 1990 | 6,901,911 | +6.72% |
| 2000 | 8,312,700 | +1.88% |
| 2007 | 7,243,000 | −1.95% |
| 2010 | 9,785,388 | +10.55% |
| 2014 | 10,338,000 | +1.38% |
| 2015 | 10,607,700 | +2.61% |
| Population size may be affected by changes on administrative divisions. 1953,[134][135] 1982,[136] 1990,[137] 2000 [108] 2007[138] 2015[139] | ||
Wuhan is the most populous city in Central China and among the most populous in China. In the Sixth Census of China in 2010, Wuhan's built-up area made of 8 out of 10 urban districts (all but Xinzhou and Hannan not yet conurbated) was home to 8,821,658 inhabitants.[140] As of 2015[update], the city of Wuhan had an estimated population of 10,607,700 people.[139]
The encompassing metropolitan area was estimated by the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) to have, as of 2010[update], a population of 19 million.[141][10]
Religion
Religion in Wuhan (2017)[142]
Chinese religion or not religious (including Taoists (0.93%)) (79.2%)
Buddhism (14.69%)
Protestantism (2.86%)
Islam (1.64%)
Catholicism (0.34%)
Other (1.61%)
According to a survey published in 2017, 79.2% of the population of Wuhan are not religious or practise worship of gods and ancestors; among these, 0.93% are Taoists, a title traditionally denoting just the Taoist clergy. Among other religious doctrines, 14.69% of the population adheres to Buddhism, 2.86% to Protestantism, 0.34% to Catholicism and 1.64% to Islam, and 1.61% of the population adheres to unspecified other religions.[142]
- Religious sites in Wuhan

Baotong Buddhist Temple

Gude Buddhist Temple
Thanksgiving Protestant Church

Holy Family Catholic Church
Transportation
Railways

The old Dazhimen railway Station (大智门火车站), the original Hankou terminus of the Beijing-Hankou Railway. Constructed in 1900–1903, it was closed in 1991, after the opening of the present Hankou Railway Station.
China Railway Wuhan Group manages the Wuhan Railway Hub. Wuhan Railway Hub is considered one of the four key railway hubs of China.[143] The city of Wuhan is served by three major railway stations: the Hankou Railway Station in Hankou, the Wuchang Railway Station in Wuchang, and the Wuhan Railway Station, located in a newly developed area east of the East Lake (Hongshan District). As the stations are many miles apart, it is important for passengers to be aware of the particular station(s) used by a particular train.
The (original) Hankou Station was the terminus for the Jinghan Railway from Beijing, while the Wuchang Station was the terminus for the Yuehan Railway to Guangzhou. Since the construction of the First Yangtze Bridge and the linking of the two lines into the Jingguang Railway, both Hankou and Wuchang stations have been served by trains going to all directions, which contrasts with the situation in such cities as New York or Moscow, where different stations serve different directions.
With the opening of the Hefei-Wuhan high-speed railway on April 1, 2009,[144] Wuhan became served by high-speed trains with Hefei, Nanjing, and Shanghai; several trains a day now connect the city with Shanghai, getting there in under 6 hours. As of early 2010, most of these express trains leave from the Hankou Railway Station.

Wuhan Railway Station, completed in 2009
In 2006, construction began on the new Wuhan Railway Station with 11 platforms, located on the northeastern outskirts of the city. In December 2009, the station was opened, as China unveiled its second high-speed train with scheduled runs from Guangzhou to Wuhan. Billed as the fastest train in the world, it can reach a speed of 394 km/h (244.82 mph). The travel time between the two cities has been reduced from ten and a half hours to just three. The rail service has been extended north to Beijing.[145]
As of 2011[update], the new Wuhan Railway Station is primarily used by the Wuhan-Guangzhou high-speed trains, while most regular trains to other destinations continue to use the Hankou and Wuchang stations.
Construction work is carried out on several lines of the new Wuhan Metropolitan Area Intercity Railway, which will eventually connect Wuhan's three main rail terminals with several stations throughout the city's outer areas and farther suburbs, as well as with the nearby cities of Xianning, Huangshi, Huanggang, and Xiaogan. The first line of the system, the one to Xianning, opened for passenger operations at the end of 2013.
The main freight railway station and marshalling yard of the Wuhan metropolitan area is the gigantic Wuhan North railway station, with 112 tracks and over 650 switches. It is located in Hengdiang Subdistrict (横店街道) of Huangpi District, located 20 km (12 mi) north of the Wuhan Station and 23 km (14 mi) from Hankou Station.
Wuhan Metro

Map of Wuhan Metro (2018)
When Wuhan Metro opened in September 2010, Wuhan became the fifth Chinese city with a metro system (after Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, and Guangzhou).[146] The first 10.2 kilometres (6.3 mi)-long line (10 stations) is an elevated rail (and therefore called 'light rail' in Chinese terminology). It runs from Huangpu Road Station to Zongguan Station in the downtown area of the Hankou District, and it is the first one in the country to use a communication-based train control system (a Moving Block signalling system, provided by Alcatel). The designed minimum interval is only 90 seconds between two trains and it features driverless operation.[146] Phase 2 of this line will extend the length to 28.8 km (17.90 mi) with 26 stations in total. It plans to start revenue service on July 28, 2010.[147]
Metro Line 2 opened on December 28, 2012, extending total system length to 56.85 km (35.32 mi). This is the first Metro line crossing the Yangtze River (Chang Jiang).
Line 4 opened on December 28, 2013, connecting Wuhan Railway Station and Wuchang Railway Station. Since that date, all three main railway stations of the city are connected by the metro lines. In December 2016, the extension of Metro's Line 2 extending to Wuhan Tianhe Airport opened as well.
By the end of 2018, Wuhan Metro includes Line 1, Line 2, Line 3, Line 4, Line 6, Line 7, Line 8, Line 11 and Yangluo Line/Line 21.[148]
Trams

A tram in University Science Park Station
Trams were brought to the streets of Wuhan on July 28, 2017 with the first line (Auto-city T1 Line) opened that day.[149] The trams under construction or planning in Wuhan are:
- Auto-city trams, with Lines T1, T2, T6, and T8 in the Wuhan Economic Development Area, in the far western reaches on Hanyang. T1 Line is operational as of 2017.
- Optics Valley trams, two lines (T1 and T2) south and east of Guanggu Circle (Guanggu Guangchang) in southeastern Wuchang. The system opened on January 18, 2018.[150]
- The Old Hankou Streetcar, a loop line around Hankou city.
Maritime transport
Wuhan is a major hub for maritime transport in central China. The Port of Wuhan provide services for the local population and shipping services.
Ferry

View from ferry (2015)
As a city located at bank of Yangtze River, Wuhan has long history of ferry services. Modern ferry services were established in 1900 by steam boat. In 1937, train ferry was established to transport train cart from Hankou to Wuchang.[151] There are numbered stops that allow people get on and off the ferry around Wuhan and there is a tourist ferry in the night.
Currently, ferry services rea provided by Wuhan Ferry Company. In 2010, the company bought 10 new ships to replace the ones that had been in service for 29 years.[152]
Airports
Opened in April 1995 to substitute for the old Hankou Wangjiadun Airport and Nanhu Airport as the major airport of Wuhan,[153][154]Wuhan Tianhe International Airport is one of the busiest airports in central China. It is located in Wuhan's suburban Huangpi District 26 kilometres (16 mi) north of Wuhan city proper. The extension of Line 2 of Wuhan Metro to Tianhe Airport opened on 28 December 2016.[155] It has also been selected as China's fourth international hub airport after Beijing Capital International Airport, Shanghai-Pudong and Guangzhou Baiyun. A second terminal was completed in March 2008, having been started in February 2005 with an investment of CNY 3.372 billion. International flights to neighboring Asian countries have also been enhanced, including direct flights to Tokyo and Nagoya, Japan. Terminal 3 has been available for service since early 2017.
Hannan Municipal Airport is an municipal airport that serves Hannan District. It is the biggest airport in China that only handles general aviation.[156] And it is the biggest municipal airport in Hubei Province. Caidian Municipal Airport is an under-construction airport which will serve Caidian District. The airport began construction on 1 December 2017.[157]
Highways and Expressways
Numerous major highways and expressways pass through Wuhan including:
- China National Highway 107
- China National Highway 316
- China National Highway 318
- G42 Shanghai–Chengdu Expressway
- G0422 Wuhan–Shenzhen Expressway
Bicycle-sharing system
As of May 2011[update], the Wuhan and Hangzhou Public Bicycle bike-share systems in China were the largest in the world, with around 90,000 and 60,000 bicycles respectively.[158] In 2012 the Wuhan and Hangzhou Public Bicycle programs in China are the largest in the world, with around 90,000 and 60,000 bicycles respectively. China has seen a rise in private "dockless" bike shares with fleets that dwarf systems in size outside China.[159] Initially, a number of traditional (third generation) docked public bike systems operated by local municipal governments opened across China, with the largest ones being in Wuhan and Hangzhou. The first was introduced in Beijing in 2007. However, third generation bike sharing is not considered successful for the majority cities in China. Bike sharing in Beijing virtually stopped and it also has encountered difficulties in Shanghai and Wuhan.[160]
Destinations

A replica set of bronze concert bells is in the background and a set of stone chimes is to the right.

The pagoda on Moshan Hill at East Lake

Happy Valley Wuhan amusement park
- The Yellow Crane Tower (Huanghelou) is presumed to have been first built in approximately 220 AD. The tower has been destroyed and reconstructed numerous times, and was burned last according to some sources in 1884. The tower underwent complete reconstruction in 1981. The reconstruction utilized modern materials and added an elevator while maintaining the traditional design in the tower's outward appearance.
Wuchang has the largest and second largest lakes within a city in China, the East Lake and Tangxun Lake, as well as the South Lake. East Lake in Wuhan is six times the size of the West Lake in Hangzhou, Zhejiang province. The total area is more than 80 km2 (31 sq mi) of which the lake is covering an area of 33 km2 (13 sq mi). In the springtime, the shores of East Lake become a garden of flowers with the Mei blossoms as the king and the Cherry Blossom as the queen among the species at East Lake Cherry Blossom Park. Another famous flower is the lotus. The lake has a long history and especially the Chu Kingdom is well represented around East Lake. At East Lake you find fascinating gardens like the Mei Blossom Garden, Forest of the Birds, Cherry Blossom Garden and monuments from ancient times, beautiful hills and green nature. Moreover, in the Moshan Botanic Garden there are many types of plum blossoms, as well as lotus flowers.

Bianzhong of Marquis Yi of Zeng, made in 433 B.C., now on display at the Hubei Provincial Museum in Wuhan
- The Hubei Provincial Museum: With over 200,000 valued artifacts, this is one of the leading museums in China. Especially the artefacts from the tomb of Marquis Yi of Zeng (Zeng Hou Yi), who lived in the 5th century B.C., is a world unique treasure. The bell chime of Marquis Yi of Zeng is a bronze instrument performed 2430 years ago in ancient China (Warring States Period), and was discovered in the Tomb of Marquis Yi of Zeng in Suizhou, Hubei in 1978. The whole chime weighs 5 tons, can perfectly play sound which was heard 2430 years ago, and was considered "The Eighth Wonder of the World".
- The Wuhan Museum has a collection of more than 100,000 artifacts, including ceramic, bronze ware, paintings and calligraphy, jade, wood carving, enamel ware, seals and so on. As a modern comprehensive museum, Wuhan Museum has the function in cultural relic collection, academic reach, publicity and education, cultural exchange, and recreation and entertainment.[161]
Happy Valley Wuhan is a theme park in Hongshan District. Opened on 29 April 2012, it is the fifth installation of the Happy Valley theme park chain.[162]
- The Rock and Bonsai Museum includes a mounted platybelodon skeleton, many unique stones, a quartz crystal the size of an automobile, and an outdoor garden with miniature trees in the penjing ("Chinese Bonsai") style.
Jiqing Street (吉庆街) holds many roadside restaurants and street performers during the evening and is the site of a Live Show with stories of events on this street by contemporary writer Chi Li.- The Lute Platform in Hanyang was where the legendary musician Yu Boya is said to have played. This is the birthplace of the renowned legend of seeking a soul mate through "high mountains and flowing water". According to the story of 知音 (zhīyīn; "understanding music"), Yu Boya played for the last time over the grave of his friend Zhong Ziqi, then smashed his lute because the only person able to appreciate his music was dead.[163]
Mao's Villa (毛泽东别墅), Mao Zedong's villa between 1960 and 1974; includes garden, living quarters, conference room, bomb shelter and swimming pool.[164][165]
- Some luxury riverboat tours begin here after a flight from Beijing or Shanghai, with several days of flatland cruising and then climbing through the Three Gorges with passage upstream past the Gezhouba and Three Gorges dams to the city of Chongqing. With the completion of the dam, a number of cruises now start from the upstream side and continue west, with tourists travelling by motor coach from Wuhan.
Wuying Pagoda or the "Shadowless Pagoda" is the oldest standing architectural feature in Wuhan, dating from the closing days of the Southern Song Dynasty.
Chu River and Han Street, a popular shopping district located in Wuchang with many tourist attractions, including Han Show theater, Madame Tussauds wax museum, and Movie Culture Park, etc. This project was initiated as a water connecting channel between East Lake and Shahu Lake.
Wuhan Zoo in Hanyang[166]
- Wuhan, capital city of the Hubei Province, is a popular shopping and culinary tourist destination for both Chinese nationals and overseas visitors.
Education
Schools and universities

Old Russia-style library in Huazhong University of Science and Technology

Overlook of the library in Huazhong University of Science and Technology with 72% campus green rate

Wuhan National Laboratories for Opto-electronics (WNLO), Huazhong University of Science and Technology

The old library of Wuhan University
There are 35 higher educational institutions in Wuhan, making it a leading educational hub for China. Prominent institutions include Huazhong University of Science and Technology and Wuhan University. Three state-level development zones and many enterprise incubators are also significant in Wuhan's education and business development. Wuhan ranks third in China in overall strength of science and technology.[167]
As of the end of 2013, in Wuhan there were 1,024 kindergartens with 224,300 children, 590 primary schools with 424,000 students, 369 general high schools with 314,000 students, 105 secondary vocational and technical schools with 98,600 students, and 80 colleges and universities with 966,400 undergraduates and junior college students and 107,400 postgraduate students.[168] There are several international schools in Wuhan.
Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST), located in the Optics Valley of China near East Lake, is a Project 985 and Class A Double First Class University.[169] HUST manages Wuhan National Laboratories for Opto-electronics (WNLO), which is one of the five national laboratories in China. HUST is also one of four Chinese universities eligible to run the national laboratory and the national major science and technology infrastructure. Founded in 1953 as Huazhong Institute of Technology, it combined with three other universities (including former Tongji Medical University founded in 1907) in 2000 to form the new HUST, and has 42 schools and departments covering 12 comprehensive disciplines.[170][171] HUST has 12 Fellows of Chinese Academy of Sciences and 17 Fellows of Chinese Academy of Engineering.[172]U.S. News' 2019 U.S. News and World Report ranked HUST as 260th in the world, and 9th in China.[173] More than 2,000 international students from 120 countries pursue degrees at HUST.[174]
Wuhan University is another Project 985 university; the original Wuhan University combined with three other universities in 2000 to form a single university with 36 schools in 6 faculties. Since the 1950s it has received international students from more than 109 countries.[175]
Scientific research

The Water Resources and Hydro Power Lab, Wuhan University (2005)
Wuhan contains three national development zones and four scientific and technological development parks, as well as numerous enterprise incubators, over 350 research institutes, 1470 high-tech enterprises, and over 400,000 experts and technicians.
Founded in 1958, the Wuhan Branch of Chinese Academy of Sciences is one of the twelve national branches of CAS. It is composed of 9 independent organizations, including the headquarters at Xiaohongshan, Wuchang. It has had a staff of 3,900, among which 8 are CAS fellows, and one is a Chinese Academy of Engineering fellow. As of 2013, the achievements gained by WHB had won 23 National Awards and 778 Provincial Awards.[176] Wuhan Research Institute of Post and Telecommunications (now known as FiberHome Technologies Group) is the national center for optical communication research in China, and is where the first optical fiber in the country was produced.[177]
Wuhan University of Technology is another major national university in the area. Founded in the year 2000, it was merged from three major universities, Wuhan University of Technology (established in 1948), Wuhan Transportation University (established in 1946) and Wuhan Automotive Polytechnic University (established in 1958). Wuhan University of Technology is one of the leading Chinese universities accredited by the Ministry of Education and one of the universities constructed with priority by "State Project 211" for Chinese higher education institutions. The University has three main campuses located in the Wuchang District.
Media

Tortoise Mountain TV Tower
The headquarters of Hubei Television is located in Wuchang District. Tortoise Mountain TV Tower is China's first self-developed TV tower, opened in 1986. The modern newspapers in Wuhan can be dated back to 1866, when Hankow Times, a newspaper in English, was founded. Before 1949, more than 50 newspapers and magazines were published by foreigners in Wuhan. Chao-wen Hsin-pao, founded by Ai Xiaomei in 1873, was the first Chinese newspaper to appear in Hankou (one of the cities that was merged into Wuhan). During the Northern Expedition era (1926–1928), journalism in Wuhan came to a climax; more than 120 newspapers and periodicals, including national newspapers such as Central Daily News and Republican Daily News, were founded or published during this time.[178]Chutian Metropolis Daily and Wuhan Evening News are two major local commercial tabloid newspapers. Both of them have entered the list of 100 most widely circulated newspapers of the world.
Culture
Wuhan is one of the birthplaces of the powerful ancient state of Chu, and inherits the culture of that state.[further explanation needed]
The plum blossom is the city's emblem, chosen partly because of the long history of local plum cultivation and use, and partly to recognize the plum's current economic significance in terms of cultivation and research. Local wild plums were used medicinally during the Qin and Han dynasties. Cultivation of the fruit began during the Song dynasty. Some traditional new year customs revolve around the planting of plums.[13]
Language
Wuhan natives speak a variety of Southwestern Mandarin Chinese referred to as Wuhan dialect which differs slightly between the districts of Wuhan, including Wuchang dialect in Wuchang District, Hankou dialect in the Hankou districts, Hanyang dialect in Hanyang District, and Qingshan dialect in Qingshan District.
Cuisine

Fried hongshan caitai (洪山菜薹)
Hubei cuisine is one of China’s ten major styles of cooking. With a history of more than 2,000 years, Hubei cuisine, originating in ancient Chu cuisine, has developed a number of distinctive dishes, such as steamed blunt-snout bream in clear soup, preserved ham with flowering Chinese cabbage, and others. On the third day of the third month of the lunar calendar, many in Wuhan eat dìcài zhǔ jīdàn (地菜煮鸡蛋), an egg dish which is supposed to prevent illness in the coming year.[179]
"No need to be particular about the recipes; all foods have their own uses. Rice wine and tangyuan are excellent midnight snacks, while fat bream and flowering Chinese cabbages are great delicacies."[180] This attitude expressed in Hankou Zhuzhici reflects indirectly the eating habits and a wide variety of distinctive snacks with a long history in Wuhan, such as Qingshuizong (a pyramid-shaped dumpling made of glutinous rice wrapped in bamboo or reed leaves) in the Period of the Warring States, Chunbinbian in Northern and Southern dynasties, mung bean jelly in the Sui dynasty, youguo (a deep-fried twisted dough stick) in the Song and Yuan dynasties, rice wine and mianwo in the Ming and Qing dynasties, as well as three-delicacy stuffed skin of bean milk,[clarification needed] tangbao (steamed dumpling filled with minced meat and gravy) and hot braised noodles (reganmian) in modern times.
Guozao (過早) is a popular way to say 'having breakfast' in Wuhan,[181] and a part of the city's culture. As a hub for land transport in China, Wuhan has gathered and mixed together various habits and customs from neighboring cities and provinces in all directions, which gives rise to a concentration of diverse cuisines from different places. The most famous place to guozao (have breakfast) is Hubu Street (户部巷), a 150-meter-long street in the popular neighborhood of Simenkou (司门口). Along its short length one can find nearly all the traditional foods of Wuhan, such as:

Doupi on the left and Re-gan mian on the right
Hot and dry noodles, re-gan mian (热干面), consists of long freshly boiled noodles mixed with sesame paste. It is considered to be the most typical local food for breakfast.
Duck's neck or Ya Bozi (鸭脖子) is a local version of this popular Chinese dish, made of duck necks and spices.- Bean skin or doupi (豆皮) is a popular local dish with a filling of egg, rice, beef, mushrooms and beans cooked between two large round soybean skins and cut into pieces, structurally like a stuffed pizza without enclosing edges.
Soup dumpling or xiaolongtangbao (小笼汤包) is a kind of dumpling with thin skin made of flour, steamed with very juicy meat inside, hence the name: tang (soup) bao (bun) – every time one takes a bite from it the "soup" inside is liable to spill out.- A salty doughnut or mianwo (面窝) is a kind of doughnut with a salty taste. It is much thinner than a common doughnut and is a typical Wuhan local food.
Opera
Han opera, which is the local opera of Wuhan area, was one of China's oldest and most popular operas. During the late Qing dynasty, Han opera, blended with Hui opera, gave birth to Peking opera, the most popular opera in modern China. Thus Han opera has been called the "mother of Peking opera."[182][183]
Sports

Wuhan Zall Football Club
Wuhan has a professional football team, Wuhan Zall F.C., that plays in China League One. Xinhua Road Sport Center, the team's home stadium, with a capacity of 32,137, is located in the heart of the city next to Zhongshan Park. For the 2013 season, Wuhan Zall was promoted to the top tier league of Chinese football, Chinese Super League, and relocated its home to Wuhan Sports Center Stadium, a modern stadium with 54,357 seats located in the suburbs of the city. However, the team did not play well in the ensuing season and was demoted back to China League One as the 2013 season ended. For financial and transportation reasons, the team moved back to Xinhua Road Sport Center in 2014.
The Wuhan Gators are a professional arena football team based in Wuhan. They are members of the China Arena Football League (CAFL).[184]
Wuhan Sports Center hosted the FIFA Women's World Cup in 2007, including both group stage games and elimination phases. Wuhan is nicknamed the "fortune place" of Chinese football. Before the women's team lost the game to Brazil in 2007 Women's World Cup, Chinese national football teams, both men and women, had never lost any games in Wuhan.
The 13,000-seat Wuhan Gymnasium held the 2011 FIBA Asia Championship and will be one of the venues for the 2019 FIBA Basketball World Cup.[21]
The city has been the venue for the women's tennis tournament Wuhan Open, one of the WTA Premier 5 tournaments, since 2014.
Architecture
Bridges

The First Bridge at Wuhan. This view is upstream, toward the distant Three Gorges and Chongqing.
Wuhan has seven bridges and one tunnel across the Yangtze River. The Wuhan Yangtze River Bridge, also called the First Bridge, was built over the Yangtze in 1957, carrying a railroad directly across the river between hills known as Snake Hill and Turtle Hill. Before this bridge was built it could take up to an entire day to barge railcars across. Including its approaches, it is 5,511 feet (1,680 m) long, and it accommodates both a double-track railway on a lower deck and a four-lane roadway above. It was built with the assistance of advisers from the Soviet Union.
The Second Bridge, a cable-stayed bridge, built of pre-stressed concrete, has a central span of 400 metres (1,300 feet); it is 4,678 metres (15,348 feet) in length (including 1,877 metres (6,158 feet) of the main bridge) and 26.5 to 33.5 metres (86.9 to 109.9 feet) in width. Its main bridgeheads are 90 metres (300 feet) high each, pulling 392 thick slanting cables together in the shape of double fans, so that the central span of the bridge is well poised on the piers and the bridge's stability and vibration resistance are ensured. With six lanes on the deck, the bridge is designed to handle 50,000 motor vehicles passing every day. The bridge was completed in 1995.

Second bridge
The Third Wuhan Yangtze River Bridge, also called Baishazhou Bridge, was completed in September 2000. Located 8.6 kilometres (5.3 miles) southwest of the First Bridge, construction of Baishazhou Bridge started in 1997. With an investment of over 1.4 billion yuan (about US$170,000,000), the bridge, which is 3,586 metres (11,765 feet) long and 26.5 metres (86.9 feet) wide, has six lanes and has a capacity of 50,000 vehicles a day. The bridge is expected to serve as a major passage for the future Wuhan Ring Road, greatly easing the city's traffic and aiding local economic development.
The Yangluo Bridge carries Wuhan's Ring Road across the Yangtze in the city's eastern suburbs (connecting the Hongshan District with the Xinzhou District). It was opened on December 26, 2007.
The Wuhan Tianxingzhou Yangtze River Bridge crosses the Yangtze in the northeastern part of the city, downstream of the Second bridge. It is named after Tianxing Island (Tianxingzhou), above which it crosses the river. Built at a cost of 11 billion yuan, the 4,657-meter cable suspension bridge was opened on December 26, 2009,[185] in time for the opening of the Wuhan Railway Station. It is a combined road and rail bridge, and carries the Wuhan–Guangzhou High-Speed Railway across the river.
Skyscrapers

Wuhan Center, tallest building in Wuhan since 2014

The Yellow Crane Tower on the southern bank of the Yangtze River (1874)
The Yellow Crane Tower, historically one of the tallest buildings in Wuhan, is considered one of the Four Great Towers of China and was destroyed twelve times, both by warfare and by fire. The tower is classified as an AAAAA scenic area by the China National Tourism Administration.[186] At 438-metre (1,437 ft) in height,[187] the Wuhan Center skyscraper, the tallest structure in Wuhan and in Central China, is the eighth tallest structure in China. The Minsheng Bank Building, the second tallest structure in Wuhan, was the tallest building in Wuhan when it was completed in 2007. It retained the title until Wuhan Center surpassed it in 2014.[188][189]Wuhan World Trade Tower is a 273-meter (896 foot) tall skyscraper located in Wuhan. It became the tallest building in Wuhan after its completion in 1998. However, it was surpassed by the Minsheng Bank Building in 2007. The Wuhan Greenland Center[190] is a planned 636-metre (2,087 ft), 126-floor mixed-use skyscraper currently under construction and scheduled for completion in 2019. If completed as planned, it will be among the world's tallest structures, and one of the world's tallest buildings by occupiable floor height. The Phoenix Towers are proposed supertall skyscrapers planned for construction in Wuhan. At 1 kilometre (3,300 ft) high, the towers would also be among the tallest structures in the world when completed.[191]
Notable Wuhanese

Li Na, a professional tennis player, serving at Wimbledon 2008, 1st round against Anastasia Rodionova

President Li Yuanhong
Politics
Li Yuanhong – former President of the Republic of China.
Wu Yi – former Vice-Premier and Minister of Health of the People's Republic of China[192]
Business
Wei Brian - Chinese entrepreneur
Science
Chang-Lin Tien – seventh Chancellor of the University of California, Berkeley (1990–1997) and a major founder of the U.S. National Academy of Engineering (NAE). Professor Tien is the first Asian to head a top university in the United States.
Sports
Deng Zhuoxiang – professional football player, scored many impressive goals for Chinese national team in important games including 3:0 South Korea and 1:0 France in 2010.
Fu Mingxia – female diver, four-time Olympic Gold Medalist (one in Barcelona 1992, two in Atlanta 1996, one in Sydney 2000), the only diver that has won gold medals at three Olympics as well as one of the very few divers in the world who is able to win world championships in both platform diving and springboard diving.
Gao Ling – professional badminton player, two-time Olympic gold medalist (Sydney 2000, Athens 2004).
Hao Junmin – professional football player, played for Schalke 04 in the German League.
Hu Jia – Chinese diver who won the gold medal at the 2004 Summer Olympics in the men's 10 metre platform.
Mei Fang – Chinese footballer who currently plays for Guangzhou Evergrande in the Chinese Super League.
Li Na – female tennis player, champion of the French Open 2011 and Australian Open 2014.
Li Ting – female tennis player, Olympic gold medalist (in women's doubles, Athens 2004).
Qiao Hong – female table tennis player, two-time Olympic gold medalist (in women's doubles, Barcelona 1992, Atlanta 1996).
Rong Hao – professional football player, with six Chinese Super League titles and two AFC Champions League champion titles.
Tang Jieli – AIBA Women's Boxing World Champion.[193]
Xiao Hailiang – Chinese diver, Olympic gold medalist (in 3-metre (9.8-foot) springboard synchronized diving, Sydney 2000).
Zeng Cheng – professional football player, with six Chinese Super League titles and two AFC Champions League champion titles.
Zhou Jihong – female diver, Olympic gold medalist (Los Angeles 1984), the first Chinese athlete to win an Olympic gold medal in diving.
Other fields
Chi Li – modern writer[194]
Hua Mulan – Ancient Chinese heroine whose story has been passed through ages in China and has been presented in a great number of books and motion pictures, including the popular Disney animated feature Mulan (1998)
Ying Chang Compestine, a Chinese American author, speaker, television host and chef
Samuel David Hawkins - American soldier in the Korean War who was captured by the North, subsequently defected to China at the time of the Korean Armistice Agreement. He worked as a mechanic in Wuhan before returning to the US in 1957.
Liu Yifei – actress and singer. Childhood friend with Yao Beina.
Peng Xiuwen – composer and conductor
Tian Yuan – singer and actress
Newsweek, vol. 115, no. 9, 26 Feb. 1990, p. 71. https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ulh&AN=9002261096&site=eds-live.</ref>
Paula Tsui – a singer who spent most of her singing career in Hong Kong
Wang Kai – actor
Wu Shuqing – female revolutionary and militia leader during the Xinhai Revolution
Xiong Bingkun (熊秉坤) – the soldier who started and led the Wuhan Uprising in the Chinese Revolution of 1911 which gave birth to the Republic of China, Asia's first republic country.
Xu Fan – actress
Yan Wenjing – writer whose work is included as one of the literary selections on the Putonghua Proficiency Test.
Yao Beina - Top female singer (during 2005-2015), known as the "Voice of China", spiritual leader of organ donation and charity (1981-2015).
Zhong Ziqi – The best friend of Yu Boya, an ancient Chinese musician whose musical composition "Flowing Water" was included on the Voyager Golden Record
Zhou Mi – musician, member of the band Super Junior M
Zhu Yilong – actor
Sister cities
Wuhan is twinned with:[195]

1.Manchester 2.Swansea 3.Essonne 4.Bordeaux 5.Arnhem 6.Duisburg 7.Sankt Pölten 8.Győr
| Country | City | Since |
|---|---|---|
| September 7, 1979 | ||
| September 8, 1982 | ||
| October 8, 1982 | ||
| September 16, 1986[196] | ||
| August 12, 1987 | ||
| October 19, 1990 | ||
Khartoum | September 27, 1995 | |
| October 19, 1995 | ||
| June 18, 1998 | ||
| September 6, 1999 | ||
| October 29, 2000 | ||
| December 20, 2005 | ||
| April 4, 2006 | ||
Markham | September 12, 2006 | |
| September 28, 2007 | ||
| April 25, 2008 | ||
| November 8, 2011 | ||
| December 21, 2012 | ||
İzmir | June 6, 2013 | |
| July 12, 2013[202] | ||
| August 7, 2015 | ||
| April 7, 2016 | ||
| November 15, 2016 | ||
| May 11, 2017 | ||
| June 16, 2017 | ||
Swansea[205] | January 31, 2018 | |
Entebbe | April 13, 2018 | |
| November 16, 2018 |
And Wuhan has friendly exchange relationship with:[207]
| City | Country | Since |
|---|---|---|
| February 16, 1998 | ||
| October 17, 2003 | ||
St. Louis | September 27, 2004 | |
| September 9, 2006 | ||
Daejeon | November 1, 2006 | |
Gwangju | September 6, 2007 | |
Kolkata | July 24, 2008 | |
Suwon | December 5, 2008 | |
Taebaek | December 5, 2008 | |
| October 30, 2009 | ||
| November 6, 2009 | ||
| November 10, 2009 | ||
Cebu City | August 19, 2011 | |
| November 12,2011 | ||
| September 10, 2012 | ||
| September 20, 2012 | ||
Košice | November 6,2012 | |
| September 18,2012 | ||
| July 16, 2013 | ||
| November 21, 2013 | ||
Siem Reap Province | November 21, 2013 | |
Biratnagar | November 21, 2013 | |
| November 21, 2013 | ||
| March1 4,2014 | ||
| April 11, 2014 | ||
| May 30,2014 | ||
| June 2014 | ||
| June 23, 2014 | ||
| June 23, 2014 | ||
| June 23, 2014 | ||
| June 23, 2014 | ||
Hayward | June 23, 2014 | |
| June 23,2014 | ||
Moraga | June 23, 2014 | |
| June 23, 2014 | ||
Mountain View | June 23, 2014 | |
| June 23, 2014 | ||
Union City | June 23, 2014 | |
| June 25, 2014 | ||
| August 25, 2014 | ||
| August 27, 2014 | ||
Patan | October 20, 2014 | |
| October 24, 2014 | ||
| October 24, 2014 | ||
| October 24, 2014 | ||
| October 29, 2014 | ||
| November 3, 2014 | ||
| November 24, 2014 | ||
Heraklion | December 11, 2014 | |
Cape Town | December 9, 2014 | |
| April 29, 2015 | ||
| May 7, 2015 | ||
| May 20, 2015 | ||
| July 4, 2015 | ||
Gold Coast | September 29, 2015 | |
| November 1, 2015 | ||
| December 3, 2015 | ||
Galle | December 5, 2015 | |
Mungyeong | December 22, 2015 | |
Daegu | March 25, 2016 | |
Tacoma | April 5, 2016 | |
| April 8, 2016 | ||
Tabriz | May 28, 2016 | |
Marrakesh | June 3, 2016 | |
| July 11, 2016 | ||
| September 5, 2016 | ||
| September 10, 2016 | ||
Jinja | September 20, 2016 | |
| September 20, 2016 | ||
Maribor | September 23, 2016 | |
Montego Bay | September 28, 2016 | |
Victoria | October 17, 2016 | |
| November 25,2016 | ||
| December 16, 2016 | ||
| March 9, 2017 | ||
| March 20, 2017 | ||
| May 10, 2017 | ||
| August 29, 2017 | ||
| November 14, 2017 | ||
| November 20, 2017 | ||
| May 21, 2018 | ||
Fergana | October 14, 2018 |
Nature and wildlife
In Chinese mythology, the Baiji has many origin stories. In one legend, the Baiji was the daughter of a general who was deported from the city of Wuhan during a war. During his duty, the daughter ran away. Later, the general met a woman who told him how her father was a general, and when he realized that she was his daughter, he threw himself into the river out of shame. The daughter ran after him and also fell into the river. Before they were drowned, the daughter was transformed into a dolphin, and the general a porpoise.[208]
See also
- Historical capitals of China
- List of cities in the People's Republic of China by population
- List of current and former capitals of subnational entities of China
References
^ abcd 武汉市历史沿革 (in Chinese). www.xzqh.org (行政区划网站). 6 August 2014. Retrieved 10 February 2018..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ ab 图文:"黄金十字架"写就第一笔. Sina. 30 March 2009. Retrieved 21 February 2018.武汉历史上就是“九省通衢”,在中央促进中部崛起战略中被定位为“全国性综合交通运输枢纽”。
^ ab "Foreign News: On To Chicago". Time. June 13, 1938. Retrieved November 20, 2011.
^ ab Jacob, Mark (May 13, 2012). "Chicago is all over the place". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved May 22, 2012.
^ ab 水野幸吉 (Mizuno Kokichi) (2014). 中国中部事情:汉口 [Central China: Hankou]. Wuhan Press. p. 3. ISBN 9787543084612.
^ abc 行政建置 (in Chinese). Wuhan Municipal People's Government (武汉市人民政府门户网站). 8 January 2018. Retrieved 17 October 2018.
^ 武汉市信息公开. Retrieved 5 April 2018.2017年2月19日,在武汉市第十四届人民代表大会第一次会议上当选为武汉市政府市长。
^ ab "Wuhan Statistical Yearbook 2010" (PDF). Wuhan Statistics Bureau. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 5, 2011. Retrieved July 31, 2011.p. 15
^ ab Cox, W (2018). Demographia World Urban Areas. 14th Annual Edition (PDF). St. Louis: Demographia. p. 22.
^ ab OECD Urban Policy Reviews: China 2015, OECD READ edition. OECD iLibrary. OECD. 18 April 2015. p. 37. doi:10.1787/9789264230040-en. ISBN 9789264230033. ISSN 2306-9341.Linked from the OECD here
^ "THE CHRONOLOGY OF THE "LIVING FOSSIL" METASEQUOIA GLYPTOSTROBOIDES (TAXODIACEAE): A REVIEW (1943–2003)" (PDF). Harvard College. 2003. p. 15. Retrieved January 25, 2018.1984 In the spring, Metasequoia was chosen as the “City Tree” of Wuhan, the capital of Hubei.
^ "Archived copy" 武汉市2010年国民经济和社会发展统计公报. Wuhan Statistics Bureau. May 10, 2011. Archived from the original on October 23, 2012. Retrieved July 31, 2011.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ ab 北京奥运会火炬境内传递城市 (Beijing Olympic torch relay city within the city). blog.sina.com.cn. 26 March 2008.
^ "Illuminating China's Provinces, Municipalities and Autonomous Regions". PRC Central Government Official Website. Retrieved 2018-02-19.
^ ab "Focus on Wuhan, China". The Canadian Trade Commissioner Service. Archived from the original on December 12, 2013. Retrieved February 10, 2013.
^ Zhao Manfeng (赵满丰). 国家中心城市 [National central cities]. usa.chinadaily.com.cn. Retrieved 2018-05-20.
^ 中央机构编制委员会印发《关于副省级市若干问题的意见》的通知. 中编发[1995]5号 (in Chinese). Douding (豆丁网). February 19, 1995. Archived from the original on May 29, 2014. Retrieved May 28, 2014.
^ ab Stephen R. MacKinnon (2002). Remaking the Chinese City: Modernity and National Identity, 1900-1950. University of Hawaii Press. p. 161. ISBN 978-0824825188.
^ "AN AMERICAN IN CHINA: 1936-39 A Memoir". Archived from the original on May 12, 2013. Retrieved February 10, 2013.
^ Stephen R. MacKinnon. Wuhan, 1938: War, Refugees, and the Making of Modern China. University of California Press. p. 12. ISBN 978-0520254459.
^ ab The Official website of the 2019 FIBA Basketball World Cup, FIBA.com, Retrieved 9 March 2016.
^ "7th Military World Games to be held in Wuhan in 2019 - Xinhua | English.news.cn". www.xinhuanet.com. Retrieved 2018-05-20.
^ http://www.wuhan2019mwg.com official site
^ 武汉市历史沿革. 行政区划网站xzqh.org (in Chinese). 行政区划网站xzqh.org. 6 August 2014. Retrieved 6 April 2018.1927年1月1日,中央临时联席会议宣布,国民政府在汉口开始办公。国民政府命令将武昌、汉口、汉阳三镇合为京兆区,定名“武汉”,作为临时首都。4月16日,武汉市政委员会成立,武昌市政厅撤销;三镇首次统一行政建制。
^ 历史沿革. Archived from the original on June 25, 2012. Retrieved March 21, 2012.
^ 江汉综述. Retrieved March 21, 2012.
^ "武汉"的由来. Retrieved March 31, 2012.
^ "The engagement at the Red Cliffs took place in the winter of the 13th year of Jian'an, probably about the end of 208."(de Crespigny 1990:264)
^ Images of the Immortal: The Cult of Lü Dongbin at the Palace of Eternal Joy by Paul R. Katz, University of Hawaii Press, 1999, page 80
^ Zizhi Tongjian vol. 71.
^ http://www.ibiblio.org/chinesehistory/contents/06dat/geo.html#wuhan Hanyang was founded during the Sui dynasty (581-618); and Hankou, then known as Hsia-k'ou, during the Song (Sung) dynasty (960-1279).
^ (秋,使曹休從廬江南入合肥,令寵向夏口。) Sanguozhi vol. 26.
^ Wan: Page 42.
^ http://www.guiyuanchansi.com.cn/list.php?fid=82 归元禅寺位于武汉市汉阳区,东眺晴川阁、南滨鹦鹉洲、北邻古琴台,占地153亩,是湖北省重点文物保护单位。由浙江僧人白光、主峰于清顺治十五年(1658年)依王氏葵园而创建。
^ Greater France: A History of French Overseas Expansion, Google Print, p. 83, Robert Aldrich, Palgrave Macmillan, 1996,
ISBN 0-312-16000-3
^ Kathleen L Lodwick (2009). The Chinese Recorder. BiblioBazaar, LLC. p. 414. ISBN 1-115-48856-2. Retrieved 2010-06-28.
^ Anon (2009). Northern China, the Valley of the Blue River, Korea. 43 Maps and Plans. READ BOOKS. p. 386. ISBN 1-4446-7840-X. Retrieved 2010-06-28.
^ abcdef 戴逸, 龔書鐸. [2002] (2003) 中國通史. 清. Intelligence press.
ISBN 962-8792-89-X. pp 86-89.
^ Fenby, Jonathan. [2008] (2008). The History of Modern China: The Fall and Rise of a Great Power.
ISBN 978-0-7139-9832-0. pg 107, pg 116, pg 119.
^ ab Welland, Sasah Su-ling. [2007] (2007). A Thousand Miles of Dreams: The Journeys of Two Chinese Sisters. Rowman Littlefield Publishing.
ISBN 0-7425-5314-0,
ISBN 978-0-7425-5314-9. pg 87.
^ abcde Wang, Ke-wen. [1998] (1998). Modern China: An Encyclopedia of History, Culture and Nationalism. Taylor & Francis Publishing.
ISBN 0-8153-0720-9,
ISBN 978-0-8153-0720-4. pp 390-391.
^ ab 王恆偉. (2005) (2006) 中國歷史講堂 #6 民國. 中華書局.
ISBN 962-8885-29-4. pp 3-7.
^ Spence, Jonathan D. [1990] (1990). The Search for Modern China. W. W. Norton & Company.
ISBN 0-393-30780-8,
ISBN 978-0-393-30780-1. pp 250-256.
^ Harrison Henrietta. [2000] (2000). The Making of the Republican Citizen: Political Ceremonies and Symbols in China, 1911-1929. Oxford University Press.
ISBN 0-19-829519-7,
ISBN 978-0-19-829519-8. pp 16-17.
^ Bergere, Marie-Claire. Lloyd Janet. [2000] (2000). Sun Yat-sen. Stanford University Press.
ISBN 0-8047-4011-9,
ISBN 978-0-8047-4011-1. p 207.
^ 雙十節是? 陸民眾:「國民黨」國慶. Tvbs.com.tw. Retrieved on 2011-10-08.
^ Taylor 2009, p. 68.
^ Robert Jackson Alexander, International Trotskyism, 1929-1985: A Documented Analysis of the Movement (Duke University Press, 1991) p206
^ Taylor 2009, p. 72.
^ Harrison, The Long March to Power, p. 111
^ Clark, Anne Biller. Clark, Anne Bolling. Klein, Donald. Klein, Donald Walker. [1971] (1971). Harvard Univ. Biographic Dictionary of Chinese communism. Original from the University of Michigan v.1. Digitized Dec 21, 2006. p 134.
^ abc William Graves (1982). The Torrent of Life (Journey into China) (5th ed.). National Geographic Society. ISBN 0-87044-437-9.
^ Chris Courtney (2018). The Nature of Disaster in China: The 1931 Yangzi River Flood. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-108-41777-8.
^ Pietz, David (2002). Engineering the State: The Huai River and Reconstruction in Nationalist China 1927–1937. Routledge.
ISBN 0-415-93388-9. pp. xvii, 61–70.
^ Winchester, Simon (2004). The River at the Center of the World: A Journey Up the Yangtze, and Back in Chinese Time. Macmillan.
ISBN 0-312-42337-3.
^ 'http://eresources.nlb.gov.sg/newspapers/Digitised/Searchresults.aspx?q=%E7%8E%8B%E5%8F%94%E9%87%91&ct=article&ct=advertisement&ct=illustration&ct=letter&df=01%2F01%2F1923&dt=31%2F12%2F1970&t=nysp&mode=advanced&lang
^ Nanyang Siang Pau. Kuala Lumpur, 20 April 1940, p.13
^ Nanyang Siang Pau. Kuala Lumpur, 2 September 1935, p.8
^ Nanyang Siang Pau. Kuala Lumpur, 21 May 1938, p.14
^ http://surfcity.kund.dalnet.se/sino-japanese-1938.htm
^ "HOME-CCTVPLUS". newscontent.cctv.com.
^ http://www.chinaww2.com/2015/09/12/the-us-firebombing-of-wuhan-part-1/
^ ab Fenby, Jonathan Chiang Kai-Shek China's Generalissimo and the Nation He Lost, New York: Carroll & Graf, 2004 page 447.
^ http://www.chinaww2.com/2015/09/16/the-us-firebombing-of-wuhan-part-2/
^ 三联生活周刊. 1949年5月的武汉_三联生活周刊. www.lifeweek.com.cn.
^ ""Swimming" by Mao Zedong". Marxists.org. Retrieved August 1, 2009.
^ 1917-, Li, Rui,; 1917-, 李锐, (2007). Li Rui wen ji. [Xianggang]: Xianggang she hui ke xue jiao yu chu ban you xian gong si. ISBN 9789889958114. OCLC 688480117.
^ Thomas W. Robinson (1971). "The Wuhan Incident: Local Strife and Provincial Rebellion During the Cultural Revolution". The China Quarterly (47): 413–18. JSTOR 652320.
^ Fang Wang (14 April 2016). Geo-Architecture and Landscape in China’s Geographic and Historic Context: Volume 1 Geo-Architecture Wandering in the Landscape. Springer. pp. 43–. ISBN 978-981-10-0483-4.
^ 祸从天降:汉江边4人被武汉坠毁飞机扫入江中 (in Chinese). Sina. 2000-06-22. Retrieved 2009-01-14.
^ Geoghegan, Tom (2005-04-28). "How planes survive lightning". BBC News Magazine. BBC News. Retrieved 2009-01-14.
^ "Fatal Events Since 1970 for Airlines of the People's Republic of China". AirSafe.com. 2007-12-10. Retrieved 2009-01-14.
^ Accident Report
^ "National flag of France with Hakenkreuz added by Chinese protesters" (in French). Reuters. April 19, 2008. Archived from the original on May 25, 2011. Retrieved April 19, 2008.
^ "Anti-French rallies across China", BBC, April 19, 2008
^ "National flag of France with Hakenkreuz added by Chinese protesters" (in French). Reuters. April 19, 2008. Archived from the original on May 25, 2011. Retrieved April 19, 2008.
^ "'Father' of China's Great Firewall Shouted Off Own Microblog – China Real Time Report – WSJ". Wall Street Journal. 20 December 2010. Retrieved 25 December 2010.
^ "Archived copy" "防火墙之父"北邮校长方滨兴微博遭网民"围攻" (in Chinese). Yunnan Information Times. December 23, 2010. Archived from the original on July 21, 2011. Retrieved May 20, 2011.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ "China's Great Firewall designer 'hit by shoe". BBC. 19 May 2011. Retrieved 19 May 2011.
^ GFW之父武汉大学演讲遭遇学生扔鞋抗议 (in Chinese). RTI. 19 May 2011. Retrieved 19 May 2011.
^ "Designer of Chinese web controls hit by shoe". Associated Press. 19 May 2011. Archived from the original on 24 May 2011. Retrieved 19 May 2011.
^ "Chinese Student Takes Aim, Literally, at Internet Regulator". NY Times. 19 May 2011. Retrieved 20 May 2011.
^ "Archived copy" 微博热点:方滨兴武汉大学遇"扔鞋"抗议?. Yunnan Information Times (in Chinese). May 19, 2011. Archived from the original on May 23, 2011. Retrieved May 20, 2011.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ "Shoe attack on China web censor sparks online buzz(AFP)". AFP. 19 May 2011. Retrieved 11 January 2012.
^ 三峡工程的防洪作用将提前两年实现-经济-人民网. People's Daily. Retrieved August 1, 2009.
^ 三峡工程防洪、通航、发电三大效益提前全面发挥. Chn-consulate-sapporo.or.jp. May 16, 2006. Archived from the original on December 25, 2007. Retrieved August 1, 2009.
^ Reuters Alertnet (2008-02-06). "CWS appeal: China winter storm response". Reuters Alertnet.
^ "Heat wave sweeps parts of China - China News". SINA English. Archived from the original on 7 July 2010. Retrieved 2010-07-28.
^ Associated Press, Guardian (28 July 2010). "China's Three Gorges dam close to limit as heavy rains persist". guardian.co.uk. Retrieved 6 August 2010.
^ "Heavy rainfall hits Wuhan, causing waterlogging and power interruption". Xinhua. Archived from the original on November 7, 2012. Retrieved June 10, 2011.
^ "8 dead after rain topples wall in C. China- China.org.cn". China Internet Information Center. Retrieved 8 July 2016.
^ Li, Jing; Lau, Mimi (7 July 2016). "Super typhoon Nepartak threatens further flood misery in mainland China". South China Morning Post. Retrieved 8 July 2016.
^ Huang, Zheping. "China's devastating floods can be traced back to corruption and overbuilding".
^ ab http://www.dzwww.com/xinwen/guoneixinwen/201802/t20180201_16992854.htm
^ 武汉东湖风景区. Baidu Baike.
^ 在武汉——武汉最高峰云雾山. Baidu Baijiahao. Retrieved 2018-11-30.云雾山地处黄陂区西北部,{...},主峰海拔709米,属武汉市最高峰。
^ http://wh.bendibao.com/tour/2013423/36646_3.shtm
^ Wunderground Archives (January 9, 2008). "Temperatures in Wuhan". Wunderground. Retrieved January 9, 2008.
^ 为什么重庆、武汉、南京有“三大火炉”之称? (in Chinese). Guangzhou Popular Science News Net (广州科普资讯网). 2007-09-12. Archived from the original on 2014-11-12. Retrieved 2014-11-12.
^ 中国夏季“火炉”城市重新洗牌 武汉南京退出前四-新华网. www.xinhuanet.com (in Chinese). Retrieved 2018-05-20.
^ 武汉退出全国三大“火炉”行列 “新四大火炉”出炉. hb.sina.com.cn (in Chinese). Retrieved 2018-05-20.
^ abcde
中国气象局 国家气象信息中心(1981-2010年) (in Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Archived from the original on July 10, 2014. Retrieved December 28, 2017.
^ 武汉城市介绍以及气候背景分析. Weather China (in Chinese). Retrieved 2018-05-20.
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on July 10, 2014. Retrieved November 20, 2010.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ "Extreme Temperatures Around the World". Retrieved May 22, 2013.
^ 中国气象数据网 - WeatherBk Data. China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 2018-11-09.
^ 2016年统计用区划代码和城乡划分代码:武汉市 (in Chinese). National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. 2016. Retrieved 30 March 2018.统计用区划代码 名称 420101000000 市辖区 420102000000 江岸区 420103000000 江汉区 420104000000 硚口区 420105000000 汉阳区 420106000000 武昌区 420107000000 青山区 420111000000 洪山区 420112000000 东西湖区 420113000000 汉南区 420114000000 蔡甸区 420115000000 江夏区 420116000000 黄陂区 420117000000 新洲区
^ ab 武汉市2010年第六次全国人口普查主要数据公报. Wuhan Statistics Bureau. May 10, 2011. Archived from the original on October 25, 2011. Retrieved July 31, 2011.
^ includes 208,106 in Wuhan Economic Development Zone (武汉经济技术开发区)
^ includes 396,597 in Donghu New Technology Development Zone (东湖新技术开发区), 67,641 in Donghu Scenic Travel Zone (东湖生态旅游风景区), and 36,245 in Wuhan Chemical Industry Zone (武汉化学工业区)
^ French Foreign Ministry (August 2, 2012). "Consulat General de France a Wuhan".
^ US Department of State (November 23, 2008). "Consulate General of the United States Wuhan, China". Archived from the original on June 29, 2009.
^ Embassy of the Republic of Korea in China (December 23, 2010). "Welcome to the Embassy of the Republic of Korea in China". Archived from the original on November 13, 2011. Retrieved December 23, 2010.
^ UK Government (January 6, 2015). "Consulate General of the United Kingdom Wuhan, China".
^ "U.S. Opens Consulate in China Industry Center Wuhan". Associated Press. November 20, 2008.
^ US Department of State (November 20, 2008). "The United States Consulate General in Wuhan, China Opens on November 20, 2008". Archived from the original on April 19, 2009.
^ 日本计划在汉设领事办事处. Retrieved February 23, 2014.
^ "Putin assures that Russia and China are getting closer". Retrieved September 9, 2015.
^ "How to boost your French start-up in China?". February 26, 2016.
^ ab "China Regional Spotlight: Wuhan, Hubei Province", China Briefing, Shanghai, 27 August 2013.
^ People's Daily Online (October 25, 2005). "Wuhan absorbs most French investment in China". People's Daily. Retrieved October 23, 2006.
^ CABLE, YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE AND. "YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE AND CABLE JOINT STOCK LIMITED COMPANY". Archived from the original on June 28, 2015. Retrieved March 8, 2016.
^ 烽火通信科技股份有限公司.
^ "Archived copy" 网站正在建设中. Archived from the original on May 2, 2018. Retrieved January 28, 2019.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ "Invest in Wuhan-Wuhan East Lake Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone - China Industrial Space". Retrieved May 25, 2015.
^ "Wuhan Economic & Technological Development Zone". Archived from the original on May 26, 2015. Retrieved May 25, 2015.
^ "Wuhan Export Processing Zone". Archived from the original on May 26, 2015. Retrieved May 25, 2015.
^ "Wuhan Optical Valley Software Park". Retrieved May 25, 2015.
^ "Gwinnett Chamber Economic Development signed an MOU with the Wuhan (China) National Bio-industry Base (Biolake)". Archived from the original on November 5, 2013. Retrieved May 23, 2013.
^ "Profile of Biolake". Archived from the original on April 26, 2014. Retrieved May 23, 2013.
^ "Medicilon and Wuhan Biolake successfully organized a bio-pharmaceutical salon". Archived from the original on April 10, 2013. Retrieved May 23, 2013.
^ "CLSC Partners with Wuhan Biolake for China Office". Archived from the original on November 5, 2013. Retrieved May 23, 2013.
^ "Biolake and the Booming Bio-industry in Central China". Archived from the original on July 3, 2013. Retrieved May 23, 2013.
^ Shiger, A.G. The Administrative-Territorial Divisions of Foreign Countries, 2d ed, pp. 142–144. (Moscow), 1957 (Using 1953 census). Op cit. in Shabad, Theodore. ""The Population of China's Cities".". Geographical Review, Vol. 49, No. 1, pp. 32–42. American Geographical Society, Jan. 1959. Accessed 8 October 2011.
^ Great Soviet Encyclopedia, 2d ed. (Moscow), 1958. Op cit. in Shabad, supra.
^ 中国人口统计年鉴1982. pp.43.(3rd Census)
^ 中国人口统计年鉴1990. pp.164.(4th Census)
^ "Wuhan (China) - Britannica Online Encyclopedia". Britannica.com. Retrieved 2017-01-25.
^ ab 丁燕飞. 武汉市去年净流入人口突破230万人_荆楚网. news.cnhubei.com. Retrieved 2016-03-06.
^ "China: Administrative Division of Húbĕi / 湖北省". Retrieved May 25, 2015.
^ CNBC.com, Justina Crabtree; special to (20 September 2016). "A tale of megacities: China's largest metropolises". CNBC.slide 6
^ ab Han, Junqiang; Meng, Yingying; Xu, Chengcheng; Qin, Siqi (2017). "Urban Residents' Religious Beliefs and Influencing Factors on Christianity in Wuhan, China". Religions. 8 (244). doi:10.3390/rel8110244. p. 4.
^ 铁道部规划建设北京上海广州武汉四大铁路枢纽. Sina News. 2005-03-18.
^ "Two high-speed rail links start April 1". www2.chinadaily.com.cn.
^ [Source: Beijing (AFP, Sat December 26, 7:54 am ET]
^ ab "> Asia > China > Wuhan Metro". UrbanRail.Net. Archived from the original on April 9, 2010. Retrieved April 21, 2010.
^ 武汉建设网-国内最长轻轨今晨贯通 力争7月28日通车. Zdgc.whjs.gov.cn. Archived from the original on July 7, 2011. Retrieved April 21, 2010.
^ https://www.travelchinaguide.com/cityguides/hubei/wuhan/subway-map.htm
^ 华中首条有轨电车武汉车都T1线本周五试运营_新华网. hb.xinhuanet.com. Retrieved 2017-09-04.
^ Wuhan opens Optics Valley light rail network, 2018-01-19
^ 火车轮渡守候47年的人文景观. Archived from the original on 2013-04-25. Retrieved 2013-01-17.
^ "Wuhan Ferry Company Information".
^ 1995年4月15日武汉天河机场投入营运. 荆楚网. 2008-04-17. Retrieved 2011-06-30.
^ 中國空軍漢口機場歷經10年竣工. 大公網. 2007-06-08. Retrieved 2008-02-11.
[permanent dead link]
^ 武汉地铁机场线开通 乘地铁赶飞机还需留意这两点.
^ 武汉首个通用航空机场建成启用. www.wuhan.gov.cn. Retrieved 2017-11-04.
^ 武汉开建第二座通用机场 预计2018年底竣工. finance.sina.com.cn. Retrieved 2017-12-02.
^ Susan Shaheen & Stacey Guzman (Fall 2011). "Worldwide Bikesharing". Access Magazine No. 39. University of California Transportation Center. Archived from the original on 19 July 2012. Retrieved 1 July 2012.
^ 中国掀起共享单车热潮 - FT中文网 [China’s bike-sharing boom in charts]. www.ftchinese.com. Retrieved 2017-07-05.
^ Zhang, Lihong. (2015). Sustainable bike - sharing systems: Characteristics and commonalities across cases in urban China. Journal of Cleaner Production., 97, 124 - 133.
^ "Wuhan Museum". Archived from the original on December 5, 2011. Retrieved January 28, 2019.
^ Marden, Duane. "Happy Valley (Wuhan, Hubei, China)". Roller Coaster DataBase. Retrieved 17 November 2012.
^ 武汉三大名胜之古琴台 [One of the Three Famous Ancient Sites the Lute Platform]. Retrieved March 24, 2014.
^ Hugh Thompson, Kathryn Lane, eds. (2005). Eyewitness Travel Guides China. London: Dorling Kindersley Limited. p. 266. ISBN 0-7566-0919-4.CS1 maint: Uses editors parameter (link)
^ Carissa Bluestone, et al., eds. (2002). Fodor's China. Random House. p. 393. ISBN 0-676-90126-3.CS1 maint: Uses editors parameter (link)
^ http://wuhanzoo.com.cn/
^ 大汉网络 (September 3, 2004). "The Thoroughfare to Nine Provinces-Wuhan City". Cnhubei.com. Retrieved February 4, 2010.
^ 武汉市统计局; 国家统计局武汉调查队. 2013年武汉市国民经济和社会发展统计公报 [2013 Statistic Report of National Economy and Social Development in Wuhan]. 武汉组工网. Archived from the original on July 27, 2014. Retrieved August 25, 2014.
^ "教育部 财政部 国家发展改革委 关于公布世界一流大学和一流学科建设高校及建设 学科名单的通知 (Notice from the Ministry of Education and other national governmental departments announcing the list of double first class universities and disciplines)".
^ "Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology". Study Abroad in China. Archived from the original on August 26, 2014. Retrieved August 26, 2014.
^ "History". HUST. Archived from the original on March 14, 2015. Retrieved August 26, 2014.
^ "华中科技大学两院院士".
^ "2019 US News and World Report Best Global Universities, Huazhong University of Science and Technology".
^ "Why HUST".
^ "Wuhan University". Chinadaily. Retrieved August 26, 2014.
^ "Introduction". CAS Wuhan Branch. Retrieved August 25, 2014.
^ "FiberHome Technologies Group". China Daily. Retrieved August 25, 2014.
^ 武汉市志(1840-1985)·新闻志·概述 [Wuhan City Annals 1840-1985·News Media Annals·Introduction]. 武汉市地情文献. Retrieved August 27, 2014.
^ https://xw.qq.com/hb/20180419008684/HBC2018041900868400
^ Hankou Zhuzhici (an ancient book recording stories about Wuhan) produced during the Daoguang Period of the Qing dynasty
^ http://bbs.tianya.cn/post-free-197497-1.shtml
^ http://www.wuhanews.com/read/67.html Archived March 30, 2018, at the Wayback Machine 汉剧中的二黄唱调,是现代京剧唱腔的主要组成部分,所以汉剧又有“京剧唱腔之祖山”的美誉。 {...}1962年武汉市成立了武汉汉剧院
^ 湖北省博物馆.楚腔汉调 : 汉剧文物图说:湖北人民,2013
^ "Meet the Super Six! The CAFL's Teams, Names and Official Logos". China Arena Football League. Archived from the original on May 5, 2016. Retrieved May 27, 2016.
^ Tianxingzhou highway-railway Bridge in Wuhan opens to traffic Archived March 30, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. english.cnhubei.com 2009-12-28
^ "AAAAA Scenic Areas". China National Tourism Administration. November 16, 2008. Archived from the original on April 4, 2014. Retrieved April 9, 2011.
^ "Wuhan Center Tower". The Skyscraper Center. Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat. Retrieved 26 April 2016.Height: To Tip 438 m / 1,437 ft Height: Architectural 438 m / 1,437 ft
^ "Minsheng Bank Building".
^ "Minsheng Bank Building".
^ "WUHAN greenland center". greenlandsc.com. Greenland Group. Retrieved 2016-01-17.
^ Zhang, Sarah (June 17, 2014). "The Insane Plan to Build the World's Tallest Towers in a Lake in China". Gizmodo. Retrieved June 17, 2014.The monstrosity, recently unveiled by the British studio Chetwoods, will rise one kilometer out of a lake in Wuhan, China—taller than the Burj Khalifa and as tall as the yet-t0-be-finished Kingdom Tower in Jeddah.
^ "#2 Wu Yi Vice Premier, minister of health". Forbes. November 2005.
^ 图文:女子拳击世锦赛落幕 汤洁丽夺80KG级冠军. Retrieved May 25, 2015.
^ "Chi Li, a Special Figure among Chinese Writers".
^ 武汉国际友好城市一览表(List of sister cities of Wuhan). www.whfao.gov.cn(Foreign Affairs Office of Wuhan Municipal Government). Archived from the original on 2018-04-13. Retrieved September 7, 2018.
^ http://www.visitoruk.com/Manchester/20th-century-T1235.html 1986 Manchester was twinned with Wuhan in China.
^ "Bordeaux, ouverte sur l'Europe et sur le monde". Archived from the original on March 16, 2015. Retrieved 1 September 2015.
^ "Wuhan, China : Christchurch City Council". Christchurch City Council. Retrieved 1 September 2015.A Friendship City Agreement was signed between the Mayors of Wuhan and Christchurch on Tuesday 4 April 2006.
^ http://en.hubei.gov.cn/opening/sister_provinces_cities/201204/t20120421_346446.shtml
^ http://en.hubei.gov.cn/opening/sister_provinces_cities/201604/t20160422_823950.shtml
^ "Tijuana, Mexico becomes Wuhan's 20th sister city". Archived from the original on April 2, 2015. Retrieved March 1, 2015.
^ http://en.hubei.gov.cn/opening/sister_provinces_cities/201305/t20130521_449893.shtml
^ "Wuhan - Saratov, Russia".
^ http://en.hubei.gov.cn/opening/sister_provinces_cities/201604/t20160425_824857.shtml
^ 图文:武汉与英国斯旺西结为友好城市.
^ 刚刚!武汉和曼谷正式缔结为友好城市!.
^ 武汉市国际友好交流城市结好时间表 [List of Dates of Establishment for Overseas Cities With Friendly Exchange Relationship]. www.whfao.gov.cn(Foreign Affairs Office of Wuhan Municipal Government). Retrieved November 15, 2018.
^ Samuel Turvy (2008). "The Goddess of the Yangtze". Witness to Extinction: How we Failed to Save the Yangtze River Dolphin. pp. 3–4. ISBN 978-0-19-954947-4. ASIN 0199549486.
^ Man Chong's biography in the Sanguozhi mentioned that these events took place in the 3rd year of the Taihe era (227–233) of Cao Rui's reign, i.e., the year 229. This is a mistake. It was actually in the 2nd year of the Taihe era, i.e., the year 228, according to the Zizhi Tongjian.[30]
Further reading
.mw-parser-output .refbegin{font-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul{list-style-type:none;margin-left:0}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>dd{margin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100{font-size:100%}
Chi, Li (2000). Lao Wuhan (Old Wuhan): Yong Yuan De Lang Man... (part of the "Lao Cheng Shi" series). Nanjing: Jiangsu Meishu Chubanshe.
Coe, John L. (1962). Huachung University (Huazhong Daxue). New York: United Board for Christian Higher Education.
Danielson, Eric N. (2005). "The Three Wuhan Cities," pp.1–96 in The Three Gorges and the Upper Yangzi. Singapore: Marshall Cavendish/Times Editions.
Latimer, James V. (1934). Wuhan Trips: A Book on Short Trips in and Around Hankow. Hankow: Navy YMCA.
MacKinnon, Stephen R. (2000). "Wuhan's Search for Identity in the Republican Period," in Remaking the Chinese City, 1900–1950, ed. by Joseph W. Esherick. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press.
Rowe, William T. (1984). Hankou: Commerce and Society, 1796–1889. Stanford: Stanford University Press.
Rowe, William T. (1988). Hankou: Conflict and Community in a Chinese City, 1796–1895. Stanford: Stanford University Press.
Song, Xiaodan & Zhu, Li (1999). Wuhan Jiu Ying (Old Photos of Wuhan). Beijing: Renmin Meishu Chubanshe (People's Fine Arts Publishing House).
- Walravens, Hartmut. "German Influence on the Press in China." - In: Newspapers in International Librarianship: Papers Presented by the Newspaper Section at IFLA General Conferences. Walter de Gruyter, January 1, 2003.
ISBN 3110962799, 9783110962796. Also available at (Archive) the website of the Queens Library - This version does not include the footnotes visible in the Walter de Gruyter version. Also available in Walravens, Hartmut and Edmund King. Newspapers in international librarianship: papers presented by the newspapers section at IFLA General Conferences. K.G. Saur, 2003.
ISBN 3598218370, 9783598218378.
External links
- Wuhan Government website
- Wuhan Time
- Google Maps Wuhan
 Wuhan travel guide from Wikivoyage
Wuhan travel guide from Wikivoyage
| Preceded by Guangzhou | Capital of China 1927 | Succeeded by Nanjing |
| Preceded by Nanjing | (wartime) Capital of China 1937 | Succeeded by Chongqing (wartime) |
Largest cities or municipalities in China Sixth National Population Census of the People's Republic of China (2010) Urban area population | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Rank | Name | Province | Pop. | Rank | Name | Province | Pop. | ||
 Shanghai  Beijing | 1 | Shanghai | SH | 20,217,748 | 11 | Chongqing | CQ | 6,263,790 |  Shenzhen  Guangzhou |
| 2 | Beijing | BJ | 16,446,857 | 12 | Nanjing | JS | 5,827,888 | ||
| 3 | Shenzhen | GD | 10,358,381 | 13 | Shenyang | LN | 5,718,232 | ||
| 4 | Guangzhou | GD | 9,702,144 | 14 | Xi'an | SN | 5,206,253 | ||
| 5 | Tianjin | TJ | 9,562,255 | 15 | Hangzhou | ZJ | 5,162,093 | ||
| 6 | Wuhan | HB | 7,541,527 | 16 | Harbin | HL | 4,933,054 | ||
| 7 | Dongguan | GD | 7,271,322 | 17 | Dalian | LN | 3,902,467 | ||
| 8 | Hong Kong | HK | 7,071,576 | 18 | Zhengzhou | HA | 3,677,032 | ||
| 9 | Foshan | GD | 6,771,895 | 19 | Shantou | GD | 3,644,017 | ||
| 10 | Chengdu | SC | 6,316,922 | 20 | Jinan | SD | 3,527,566 | ||




